Multifunctional medium-high density fiber base material
A high-density fiber, multi-functional technology, used in wood processing appliances, building components, wood veneer bonding and other directions, can solve the problems of limited application of flame retardant materials and poor flame retardant effect.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
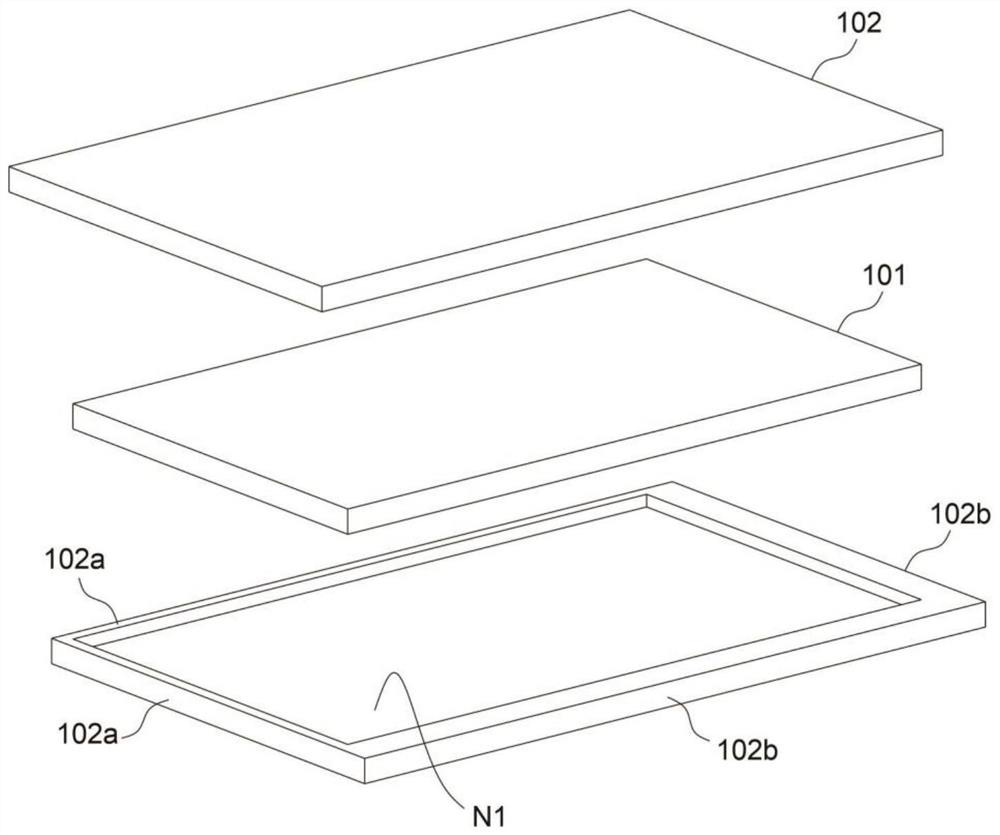
[0037] refer to Figure 1 to Figure 3 , is the first embodiment of the present invention, this embodiment provides a kind of multi-functional high-density fiber base material, it is characterized in that: comprise core material 101 and coating layer 102, core material 101 is wood layer, coating layer 102 In order to make a uniform flame retardant layer, it has the advantages of fire prevention, moisture resistance and corrosion resistance; the core material 101 is clamped by the cladding layers 102 on both sides, and the core material 104 and the cladding layer 105 are bonded by an adhesive, and passed through Secondary hot pressing realizes the advantages of high strength, high impact resistance and high bending resistance.
[0038] Wherein, the coating layer 102 forms a certain length margin 102a around the core material 101, and the length margin 102a of the coating layer 102 on both sides is attached to each other; that is, the core material 101 is surrounded by a length m...
Embodiment 2
[0047] refer to Figure 4 to Figure 9 This embodiment is different from the first embodiment in that: one side of the accommodating cavity N2 is provided with a buckle groove N3, and the core material 101 is provided with a block 101a matching with the buckle groove N3; When installed in the cavity N1, the core material 101 can be fixed by establishing a connection with the buckle groove N3 through the clamping block 101a.
[0048] Specifically, the buckle slots N3 of the cladding layers 102 on both sides are located on different sides of the accommodating cavity N2, and the clamping blocks 101a on the core material 101 are arranged correspondingly, so that the cladding layers 102 on both sides can align the core material 101 from different directions. Fixing, improving the fixing stability of the core material 101. Further, the buckling grooves N3 of the cladding layers 102 on both sides are located at opposite sides of the accommodating cavity N2 , and the locking blocks 10...
Embodiment 3
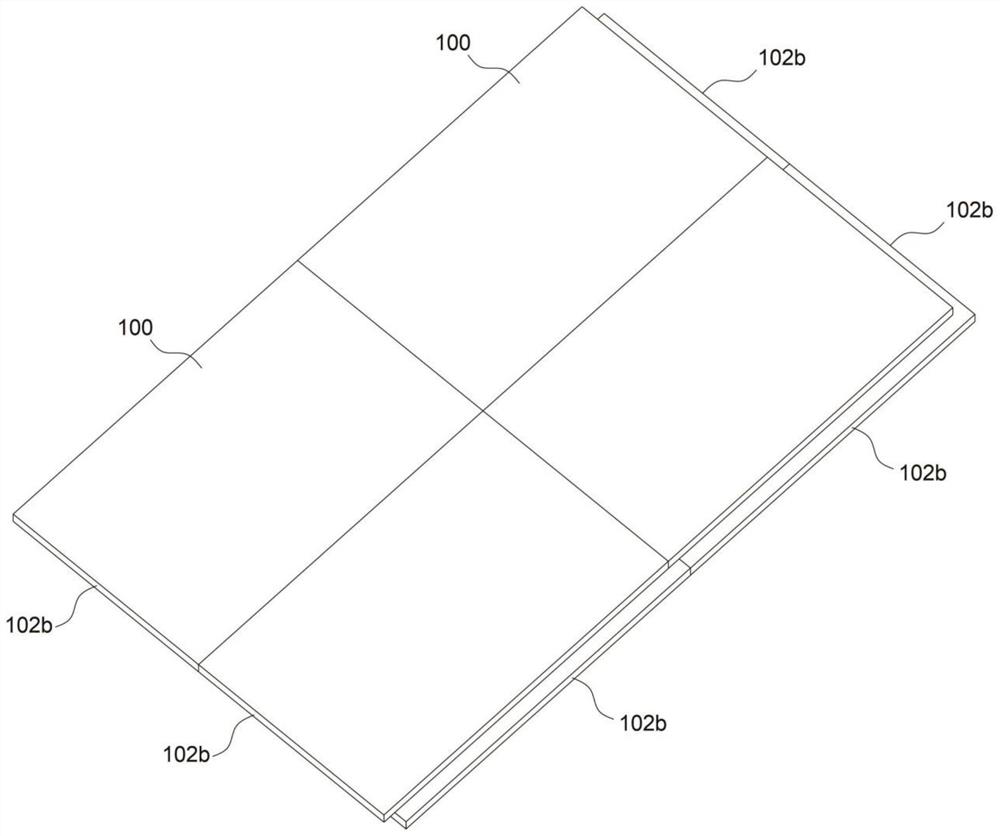
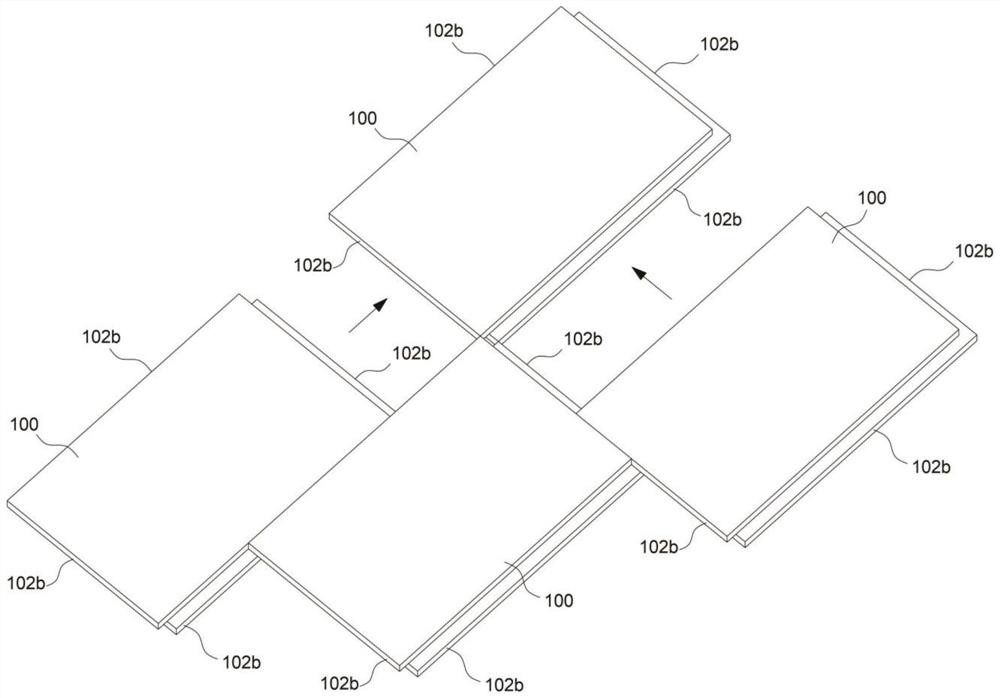
[0052] refer to Figure 10 , this embodiment is different from the first embodiment in that: the length allowance 102a of the opposite end of the cladding layer 102 on both sides extends outward in the opposite direction; the length allowance 102a extending outward forms a splicing portion 102b; wherein, two The fiber substrates 100 can be spliced with each other through the splicing portion 102 b , that is, the splicing portion 102 b of one fibrous substrate 100 is placed on the splicing portion 102 b of the other fibrous substrate 100 .
[0053] When this embodiment is installed, especially at the corners of the wall, due to the existence of the length margin of the outer extension of the cladding layer 102, there may be no coverage of the core material 101 at the corners of the wall, resulting in an empty package. and other defects exist, therefore, during installation, the length margin of the outer extension of the cladding layer 102 can be cut off, such as sawing; at t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com