PARMS marker based on SNP mutation in coding region of rice blast resistance gene Pita and application of PARMS marker
A rice blast and resistance gene technology, applied in the field of PARMS markers and applications, can solve the problems of inapplicability to large-scale genotype analysis, low degree of automation, use of toxic substances, etc., and achieve reliable preparation of detection results, easy to grasp, error-prone effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] A PARMS marker and application based on the SNP mutation of the rice blast resistance gene Pita coding region, comprising the following steps:
[0036] 1) Identification of blast resistance of rice materials: using Nipponbare as a control, 226 rice materials were artificially inoculated at the seedling stage for identification of blast resistance, and the material Y224 resistant to blast disease races ZB1 and ZB9 was screened out;
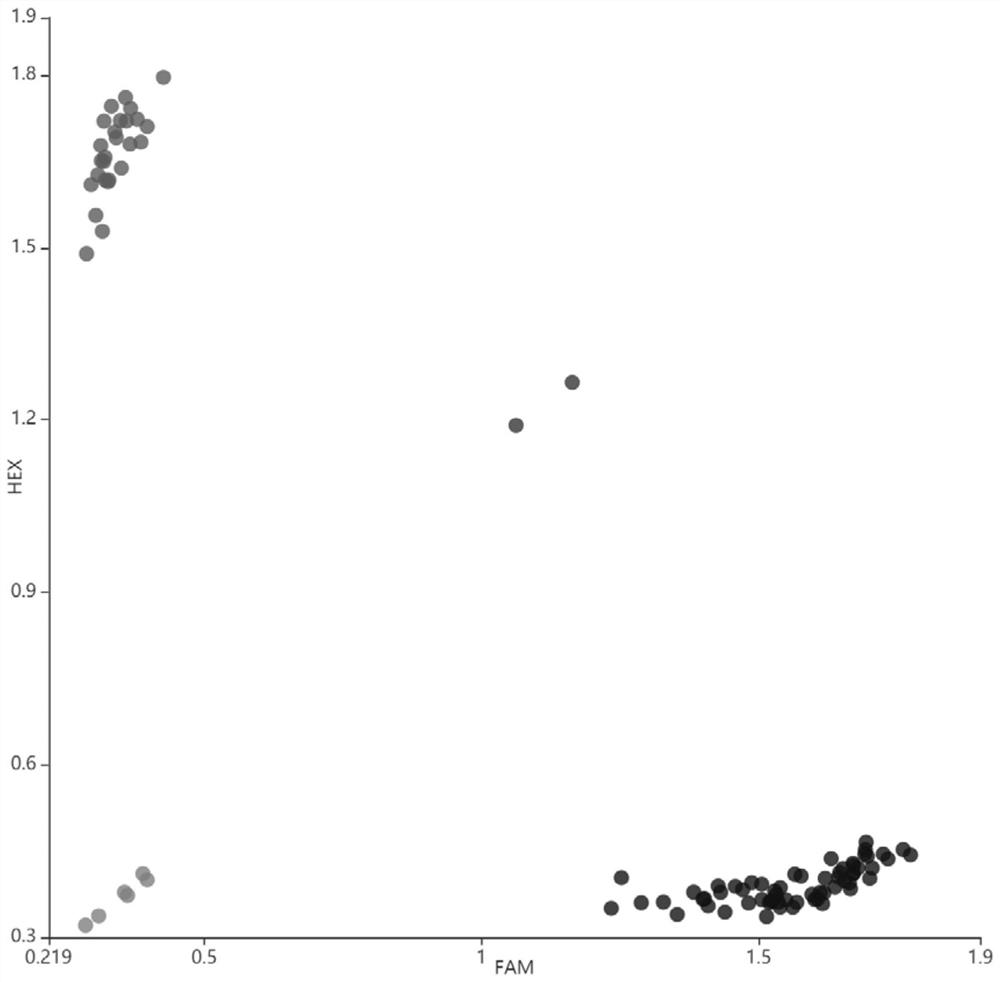
[0037] 2) Analysis of Pita gene structure: The DNA of fresh leaves of Y224 and Nipponbare was extracted by CTAB method, amplified in segments, purified and then sent to the biological company for sequencing. The software Vector NTI 11 was used to analyze the differences of Pita genes in the two rice materials, and found A G→T mutation occurred at the 17bp site in the coding region of the gene (see attached figure 1 );
[0038] 3) Design and synthesis of Pita gene functional markers: According to the G→A mutation at position 555 of the Pita...
Embodiment 2
[0059] A PARMS marker and application based on the SNP mutation of the rice blast resistance gene Pita coding region, comprising the following steps:
[0060] 1) Identification of blast resistance of rice materials: using Nipponbare as a control, 200 rice materials were artificially inoculated at the seedling stage to identify the resistance to blast disease, and the material Y224 resistant to blast disease races ZB1 and ZB9 was screened out;
[0061] 2) Analysis of Pita gene structure: The DNA of fresh leaves of Y224 and Nipponbare was extracted by CTAB method, amplified in segments, purified and then sent to the biological company for sequencing. The software Vector NTI 11 was used to analyze the differences of Pita genes in the two rice materials, and found A G→T mutation occurred at the 17bp site in the coding region of the gene (see attached figure 1 );
[0062] 3) Design and synthesis of Pita gene functional markers: According to the G→A mutation at position 555 of the...
Embodiment 3
[0075] A PARMS marker and application based on the SNP mutation of the rice blast resistance gene Pita coding region, comprising the following steps:
[0076] 1) Identification of blast resistance of rice materials: Using Nipponbare as a control, 250 rice materials were artificially inoculated at the seedling stage to identify the resistance to blast disease, and the material Y224 resistant to blast disease physiological races ZB1 and ZB9 was screened out;
[0077] 2) Analysis of Pita gene structure: The DNA of fresh leaves of Y224 and Nipponbare was extracted by CTAB method, amplified in segments, purified and then sent to the biological company for sequencing. The software Vector NTI 11 was used to analyze the differences of Pita genes in the two rice materials, and found A G→T mutation occurred at the 17bp site in the coding region of the gene (see attached figure 1 );
[0078] 3) Design and synthesis of Pita gene functional markers: According to the G→A mutation at posit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com