Cooling electronic devices in a data center
A technology for data centers and electronic equipment, applied in data centers, electrical equipment components, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve problems such as insufficient cooling, insufficient, high cost, etc., and achieve good performance results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
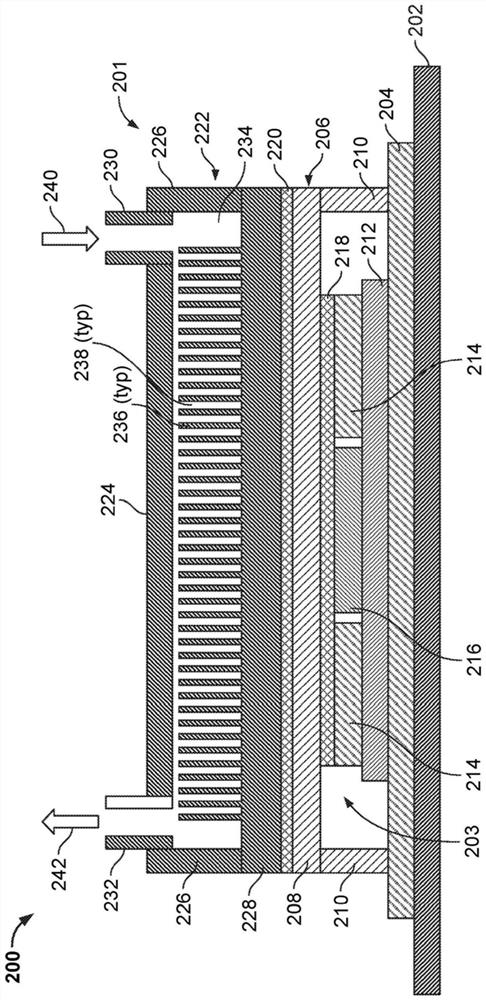
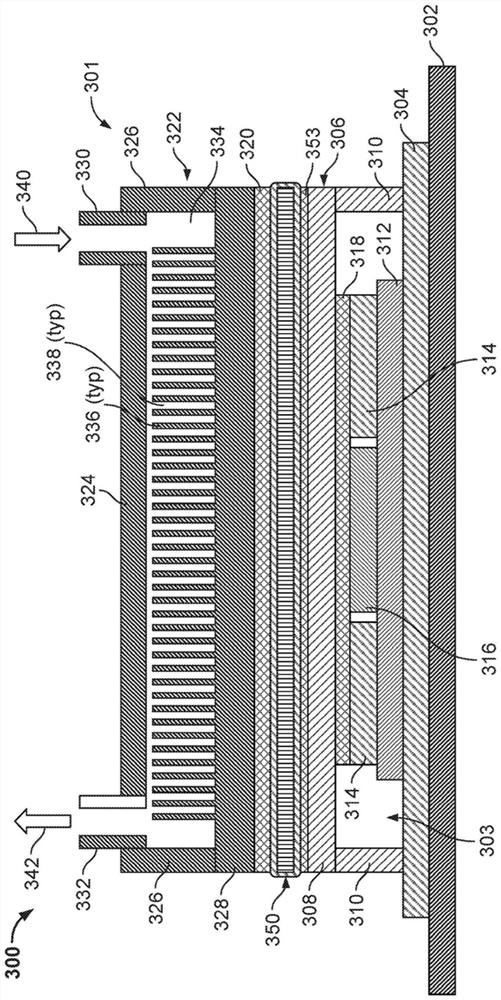
[0048] In some example embodiments, a cooling system for rack-mounted electronic equipment (eg, servers, processors, storage, networking equipment, etc.), such as in a data center, is disclosed. In various disclosed embodiments, the cooling system may be or include a liquid cooling plate assembly that is part of or integrated with the server tray enclosure. In some embodiments, a liquid cooling plate assembly includes a base and a top that in combination form a cooling fluid flow path and a thermal interface between one or more heat generating devices and the cooling fluid through which cooling fluid is circulated .
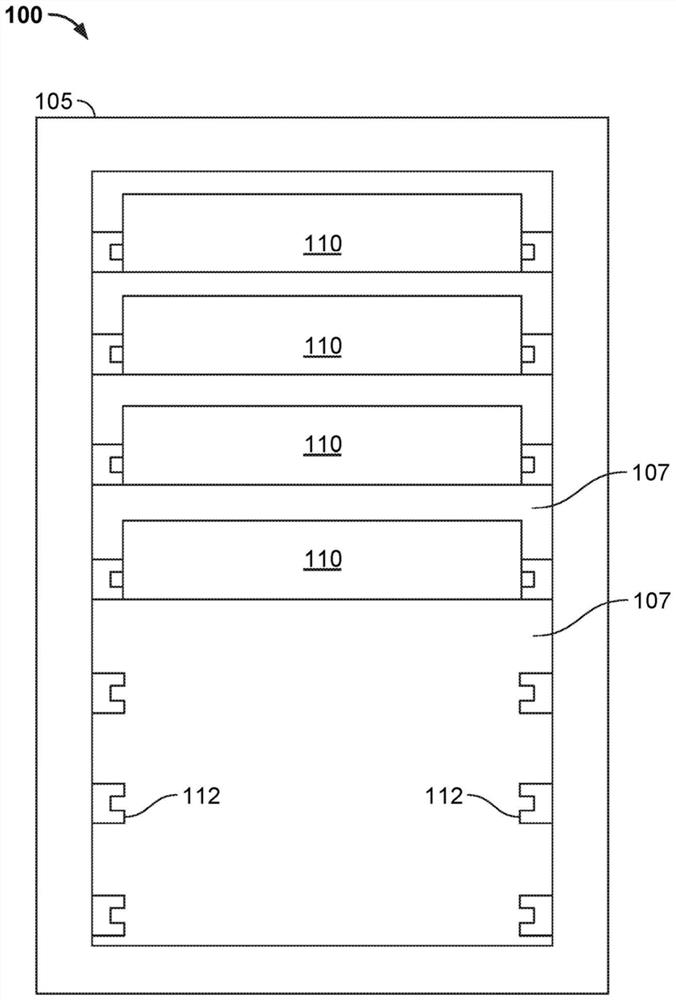
[0049] figure 1 An example system 100 is shown that includes a server rack 105 (eg, a 13-inch or 19-inch server rack) and a plurality of server rack subassemblies 110 mounted within the rack 105 . While a single server rack 105 is shown, server rack 105 may be one of several server racks within system 100, which may include a server farm or contain various rack...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com