Cooling fan control method and system of traction motor and freight train
A technology for cooling fans and traction motors, used in pump control, electric vehicles, machines/engines, etc., can solve the problems of low control efficiency and slow response of cooling fans, and achieve the effects of fast response, high efficiency, and comprehensive data and information
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
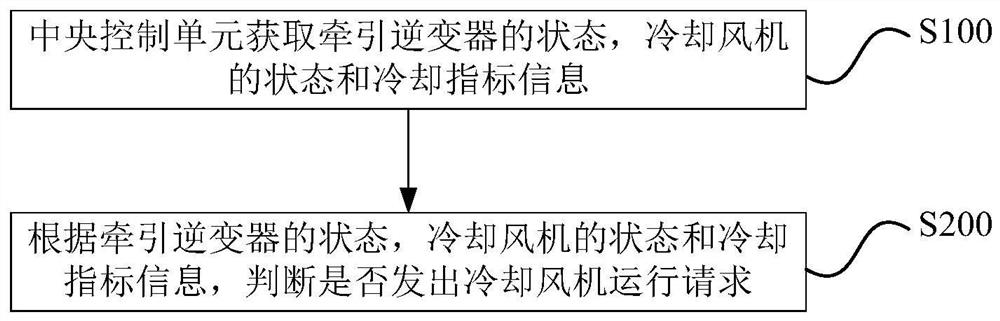
[0053]Such as figure 1 As shown, the cooling fan control method of the rail train traction motor of the embodiment of the present application includes the following steps:
[0054] Step S100: the central control unit obtains the state of the traction inverter, the state of the cooling fan and cooling index information;
[0055] Step S200: According to the state of the traction inverter, the state of the cooling fan and the cooling index information, determine whether to issue a cooling fan operation request;
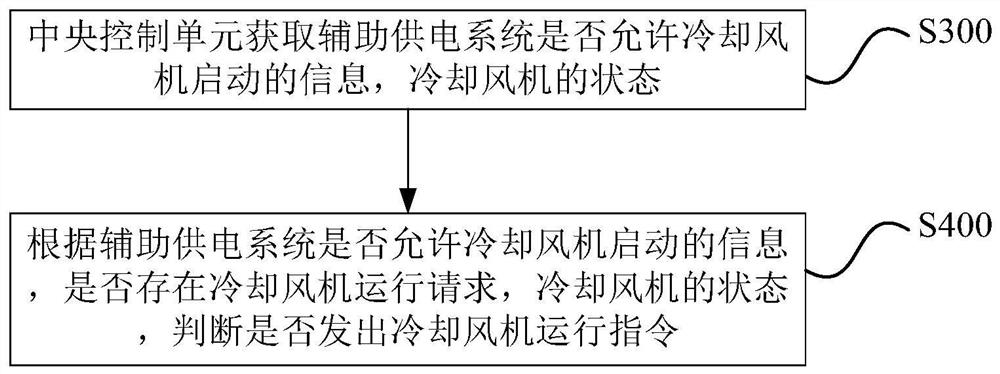
[0056] Among them, the central control unit obtains the state of the traction inverter from the traction control unit, obtains the state of the cooling fan from the electric switch of the power supply line of the cooling fan, and obtains the cooling index information from the system where the cooling index information collection device is located.
[0057] In the method for controlling the cooling fan of the rail train traction motor in the embodiment of the present app...
Embodiment 2
[0095] On the basis of the first embodiment, the method for controlling the cooling fan of the rail train traction motor according to the embodiment of the present application has the following characteristics.
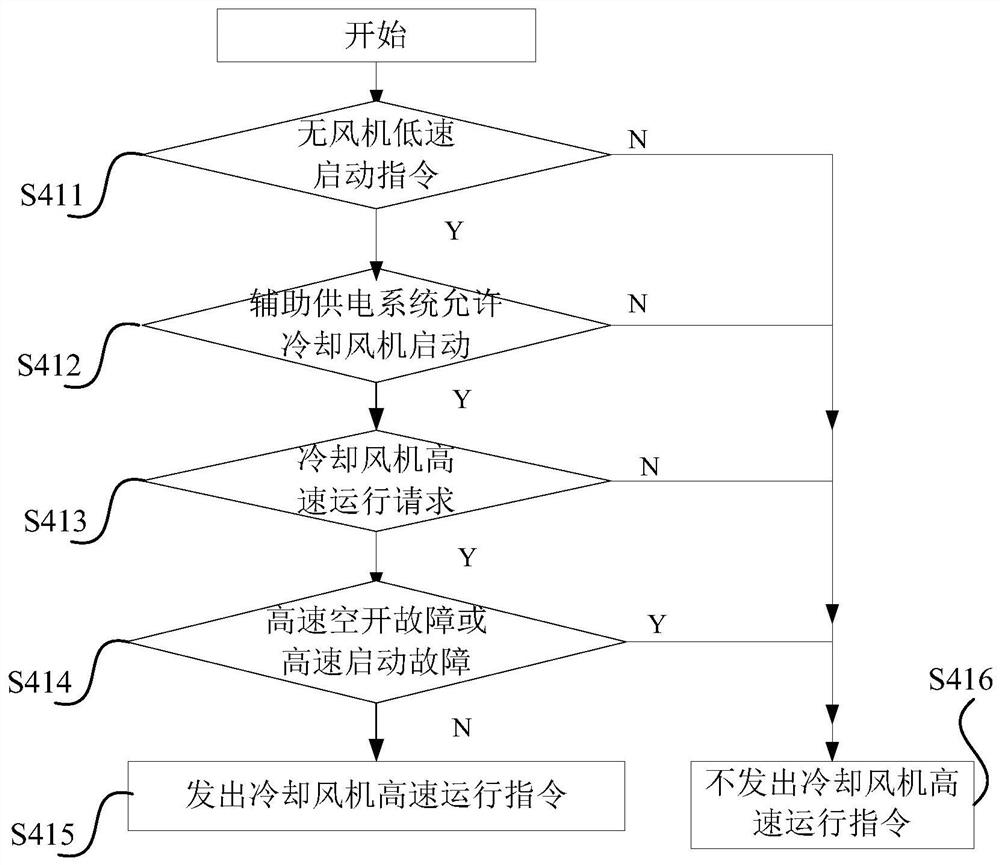
[0096]During implementation, in the operation control of high-speed air cooling, the step of judging whether to issue a request for high-speed operation of the cooling fan includes the following steps:
[0097] A plurality of sub-steps for judging whether to issue a cooling fan high-speed operation request;
[0098] In any sub-step of judging whether to issue a request for high-speed operation of the cooling fan, if the judgment result is that a request for high-speed operation of the cooling fan is issued, a request for high-speed operation of the cooling fan is issued.
[0099] Specifically, a plurality of sub-steps of judging whether to issue a cooling fan high-speed operation request specifically include:
[0100] When the state of the traction inverter is in the...
Embodiment 3
[0160] On the basis of the second embodiment, the method for controlling the cooling fan of the rail train traction motor in the embodiment of the present application has the following characteristics.
[0161] During implementation, in the operation control of low-speed air cooling, the step of judging whether to issue a request for low-speed operation of the cooling fan includes the following steps:
[0162] A plurality of sub-steps for judging whether to send a cooling fan low-speed operation request;
[0163] In any sub-step of judging whether to issue a cooling fan low-speed operation request, if the judgment result is a cooling fan low-speed operation request, then issue a cooling fan low-speed operation request.
[0164] Specifically, a plurality of sub-steps of judging whether to issue a cooling fan low-speed operation request specifically include:
[0165] When the state of the traction inverter is working, and the cooling fan is low-speed air-cooled without failure;...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com