Vibration damping system for offshore wind turbine generator and assembling method of vibration damping system
A vibration reduction system and offshore wind power technology, applied in the control of wind turbines, wind power generation, wind turbines, etc., can solve the problems of single energy consumption mechanism, heavy mass, and large displacement amplitude of mass blocks, so as to prolong the service life. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
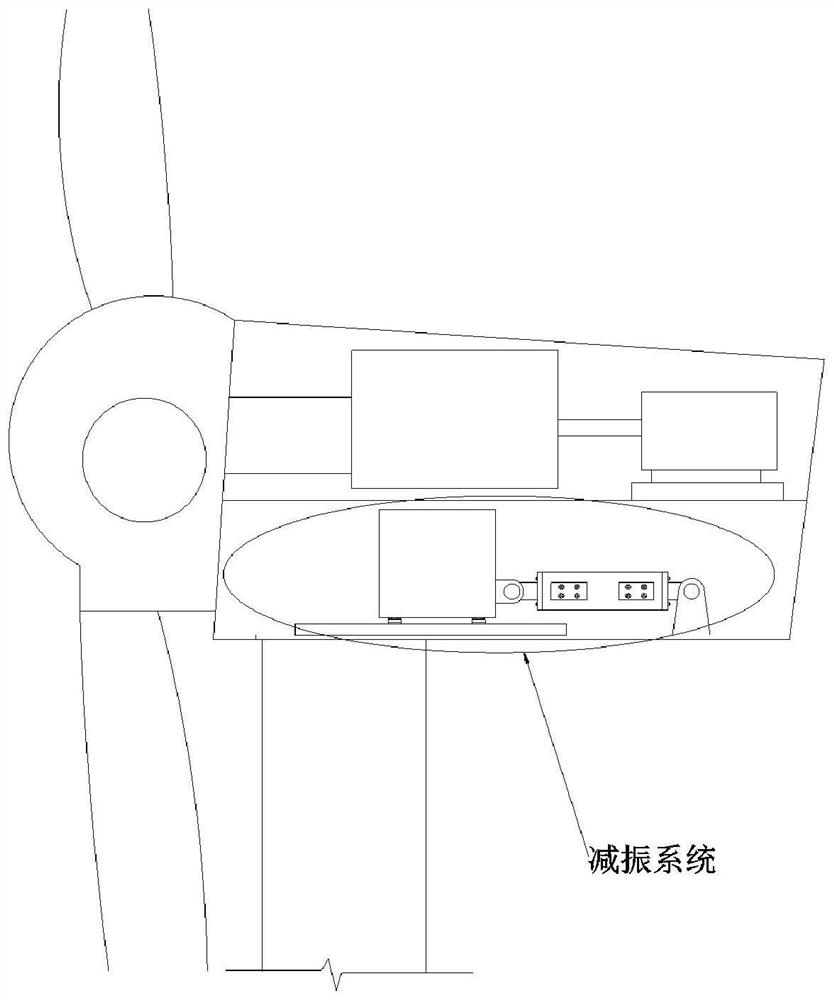
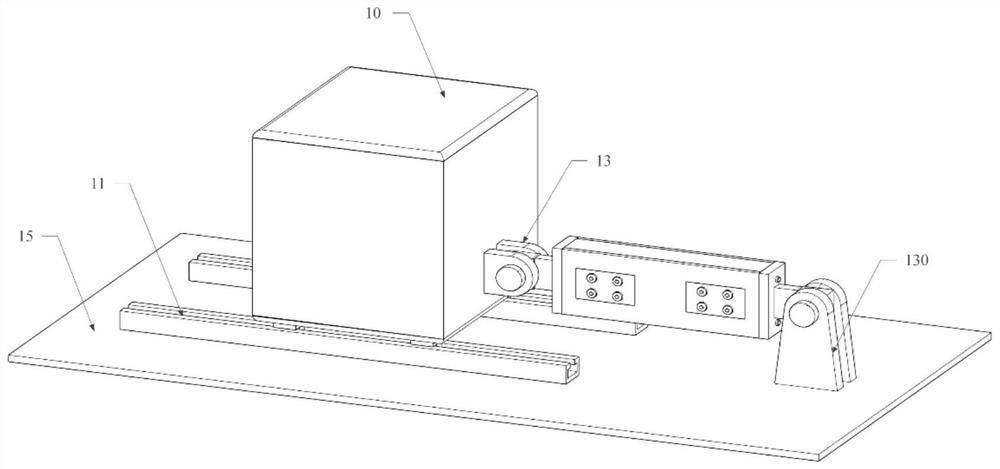
[0047] see figure 1 and figure 2 , this embodiment provides a vibration reduction system for offshore wind turbines, including a damper, a mass water tank 10, a slide rail 11, a connecting plate I13 and a connecting plate II130. The slide rail 11 and the connecting plate II 130 are arranged on the nacelle floor 15 of the wind power generating set.
[0048] The inner cavity of the mass water tank 10 is filled with viscous liquid. A connecting plate I13 is arranged on the side wall of the mass water tank 10 . The bottom of the mass water tank 10 has rollers 12 . The mass water tank 10 is arranged on the slide rail 11 through rollers 12 . The mass water tank 10 can move axially along the slide rail 11 .
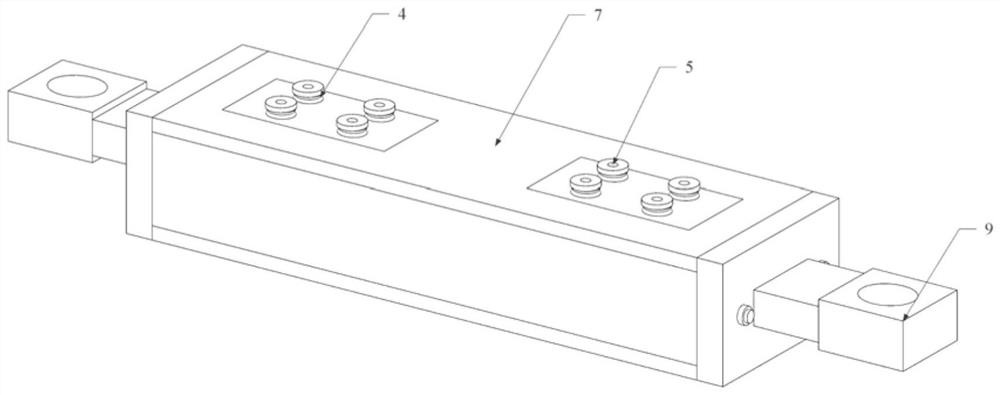
[0049] see image 3 , Figure 4 , Figure 5 and Figure 6 , the damper includes 4 groups of wedge-shaped friction pairs 1, middle sliding plate 2, piston plate I3, piston plate II30, shape memory alloy gasket 4, high strength bolt 5, horizontal shape memory alloy cable...
Embodiment 2
[0058] see Figure 7 The main structure of this embodiment is the same as that of Embodiment 1, wherein the friction surface of the outer wedge-shaped friction block 101 includes a first quadrangular truss segment, a first straight segment and a second quadrangular truss segment connected one by one. The bottom surfaces of the first quadrangular truss section and the second quadrangular truss section are right-angled trapezoids. The first quadrangular frustum segment forms a first inclined friction surface 1011 and a first planar friction surface 1012 . The first straight section forms the second plane friction surface 1013 . The second truss section forms a second inclined friction surface 1014 and a third flat friction surface 1015 .
[0059] The friction surface of the inner wedge-shaped friction block 102 includes a triangular truss section, a second straight section, a third quadrangular truncated section and a third straight section connected one by one. The bottom su...
Embodiment 3
[0063] The main structure of this embodiment is the same as that of Embodiment 1, wherein the material of the horizontal shape memory alloy cable 6 and the shape memory alloy washer 4 is nickel-titanium shape memory alloy. Nickel-titanium shape memory alloys have superelastic properties. When loading, before the alloy stress reaches the phase transformation stress, the material is in the austenite state, undergoes elastic deformation, and has high rigidity. When the stress of the alloy reaches the critical stress, the shape memory alloy undergoes a martensitic phase transformation, the stiffness rapidly decays, and enters the "yield" stage equivalent to steel. When the alloy stress reaches the end stress of the positive martensitic transformation, the alloy changes completely from austenite to martensite. After unloading, the alloy undergoes a reverse phase transformation from martensite to austenite. When the load is zero, the alloy only produces a small residual deformation...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com