Method for producing low-carbon low-silicon ultralow-sulfur steel by adopting LF single-link process
A low-carbon, low-silicon, ultra-low-sulfur technology, applied in the field of steelmaking, can solve the problems of high rate of revision, surface quality defects, and low control difficulty.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
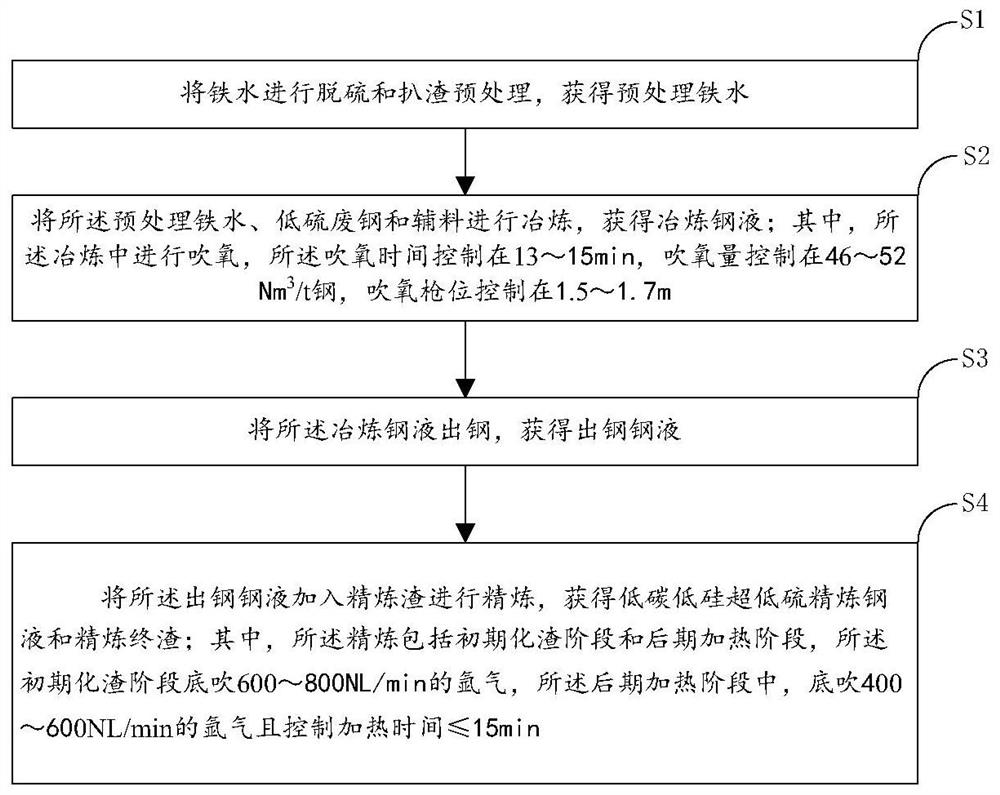
[0053] Steel type SPHC, the target finished product carbon content is 0.030%-0.050%, silicon content ≤0.050%, sulfur content ≤0.0020%, the smelting process route adopted is: KR desulfurization pretreatment—converter smelting—LF furnace refining—continuous casting and rolling .
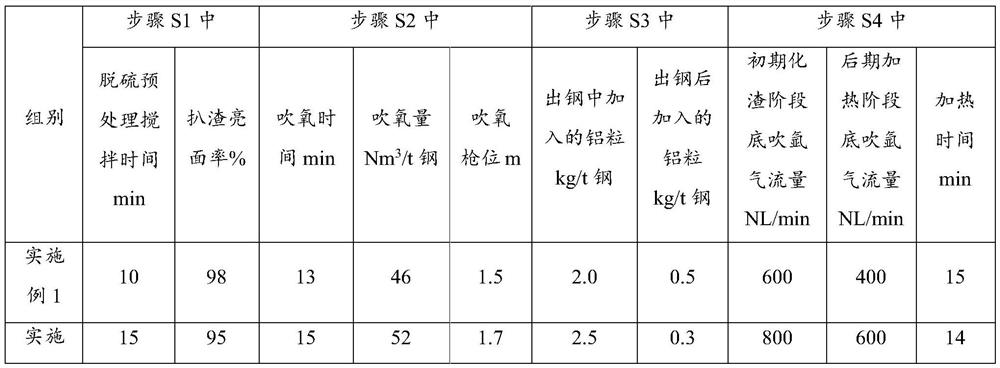
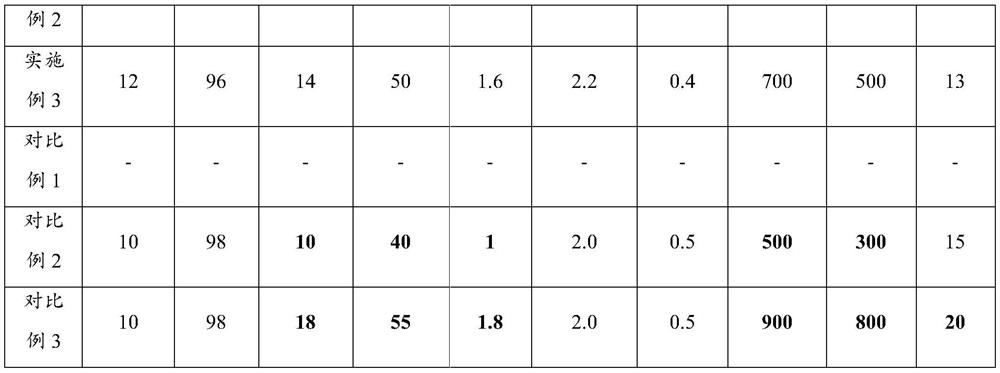
[0054] Step S1, controlling the stirring time during the desulfurization pretreatment to 10 minutes; finally removing the top slag, the slag brightening rate is 98%, and obtaining pretreated molten iron with an S content of 0.0015%;
[0055] Step S2, using low-sulfur steel scrap and auxiliary materials for converter smelting, and controlling the total sulfur content of the scrap steel and auxiliary materials to ≤0.0050%; smelting the pretreated molten iron, low-sulfur steel scrap and auxiliary materials to obtain molten steel; wherein, in the smelting Carry out oxygen blowing, the time of said oxygen blowing is controlled at 13~15min, and the amount of oxygen blowing is controlled at 46~52Nm 3 / t stee...
Embodiment 2
[0061] Steel type SPHC, the target finished product carbon content is 0.030%-0.050%, silicon content ≤0.050%, sulfur content ≤0.0020%, the smelting process route adopted is: KR desulfurization pretreatment—converter smelting—LF furnace refining—continuous casting and rolling .
[0062] Step S1, controlling the stirring time during the desulfurization pretreatment to 15 minutes; finally removing the top slag, the slag brightening rate is 95%, and obtaining pretreated molten iron with an S content of 0.0015%;
[0063] Step S2, using low-sulfur steel scrap and auxiliary materials for converter smelting, and controlling the total sulfur content of the scrap steel and auxiliary materials to ≤0.0050%; smelting the pretreated molten iron, low-sulfur steel scrap and auxiliary materials to obtain molten steel; wherein, in the smelting Carry out oxygen blowing, the oxygen blowing time is controlled at 15min, and the oxygen blowing amount is controlled at 52Nm 3 / t steel, the position o...
Embodiment 3
[0069] For steel grade SPA, the target carbon content of the finished product is 0.025%-0.045%, the silicon content is ≤0.040%, and the sulfur content is ≤0.0020%. The smelting process route adopted is: KR desulfurization pretreatment—converter smelting—LF furnace refining—continuous casting and rolling .
[0070] Step S1, controlling the stirring time during the desulfurization pretreatment to be 12 minutes; finally removing the top slag, the slag brightening rate is 96%, and the pretreated molten iron with an S content of 0.0015% is obtained;
[0071] Step S2, using low-sulfur steel scrap and auxiliary materials for converter smelting, and controlling the total sulfur content of the scrap steel and auxiliary materials to ≤0.0050%; smelting the pretreated molten iron, low-sulfur steel scrap and auxiliary materials to obtain molten steel; wherein, in the smelting Carry out oxygen blowing, the oxygen blowing time is controlled at 14min, and the oxygen blowing amount is controll...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com