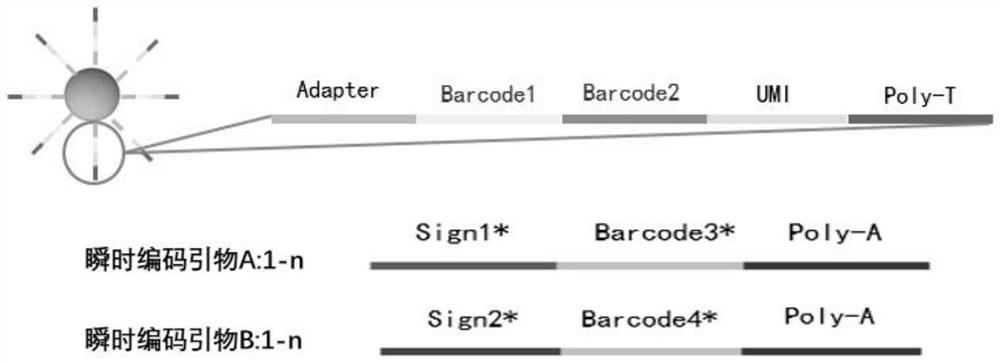
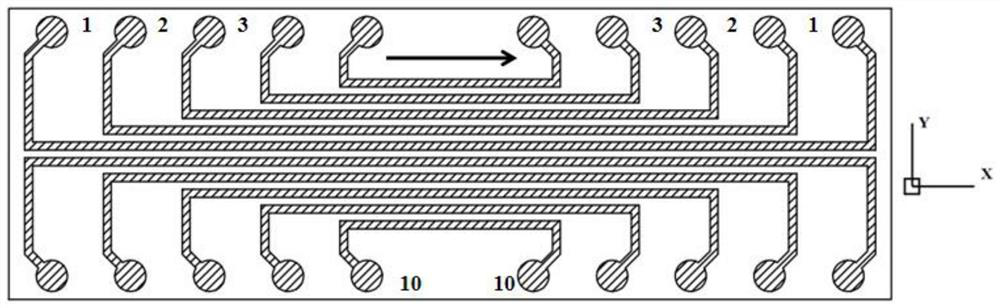
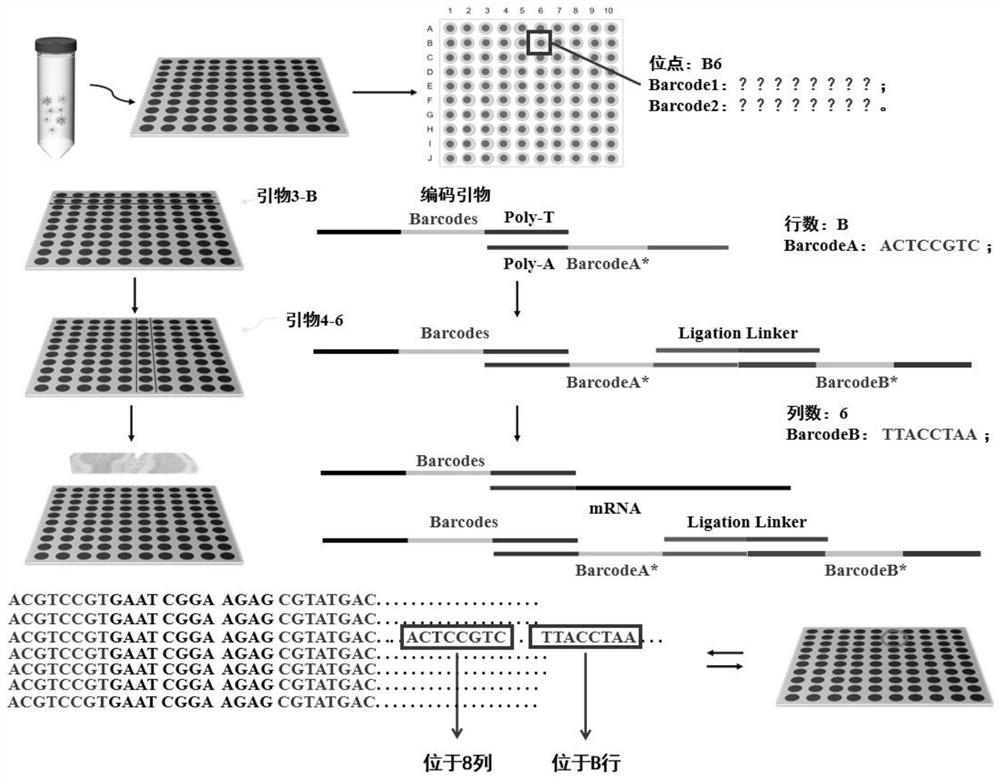
Spatial transcriptome sequencing and decoding method based on transient coding
A technology of spatial transcription and decoding method, which is applied in the field of spatial transcriptome sequencing, can solve the problems of high price, inability to link positions, cover up intercellular heterogeneity of new cell types, etc., and achieve the effect of low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0033] The spatial information encoding microspheres with a particle size of 10 μm were washed three times with 1 ml TE buffer (10 mM Tris-HCL, 1 mM EDTA), and finally dispersed in 1 ml TE buffer to obtain a final concentration of 10 6 pcs / ml microsphere suspension, take 100 μL of microsphere solution and add it dropwise to a microwell plate with a hole diameter of 12 μm and a hole depth of 12 μm, and then place the microwell plate on a magnet for 1 min to increase the Mark the X and Y directions on the microwell plate. Then cover the microfluidic channel on the microporous plate, add the transient coding primer solution with known sequence to the sample hole in a certain order, connect the negative pressure pump at the sample outlet, and provide power to make the transient coding primer solution pass through each Microfluidic channels flow through the microplate, forming n 2 ([x 1 ,y 1 ], [x 1 ,y 2 ]...[x n ,y n ]) a two-dimensional space site, the spatial information ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com