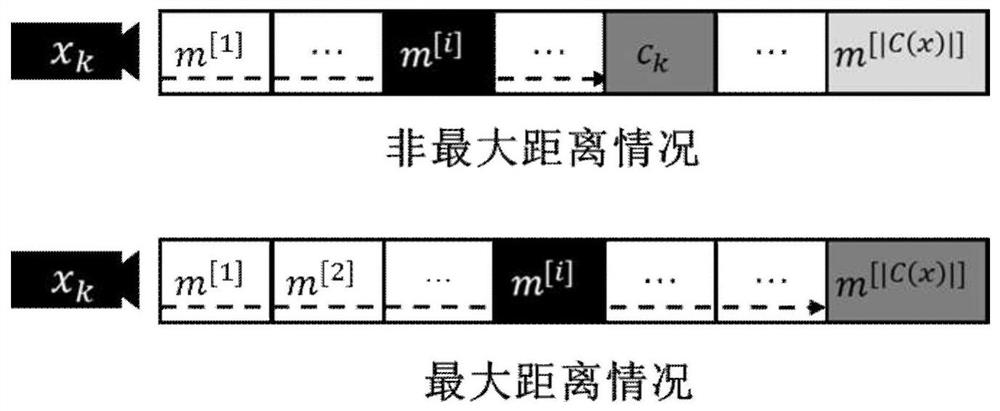
Robot mapping method based on continuous confidence distribution
A confidence level and robot technology, applied in the field of robot perception, can solve the problems of unbalanced accuracy and efficiency, without considering the dependence of map grid units, etc., and achieve the effect of improving the accuracy of mutual information
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
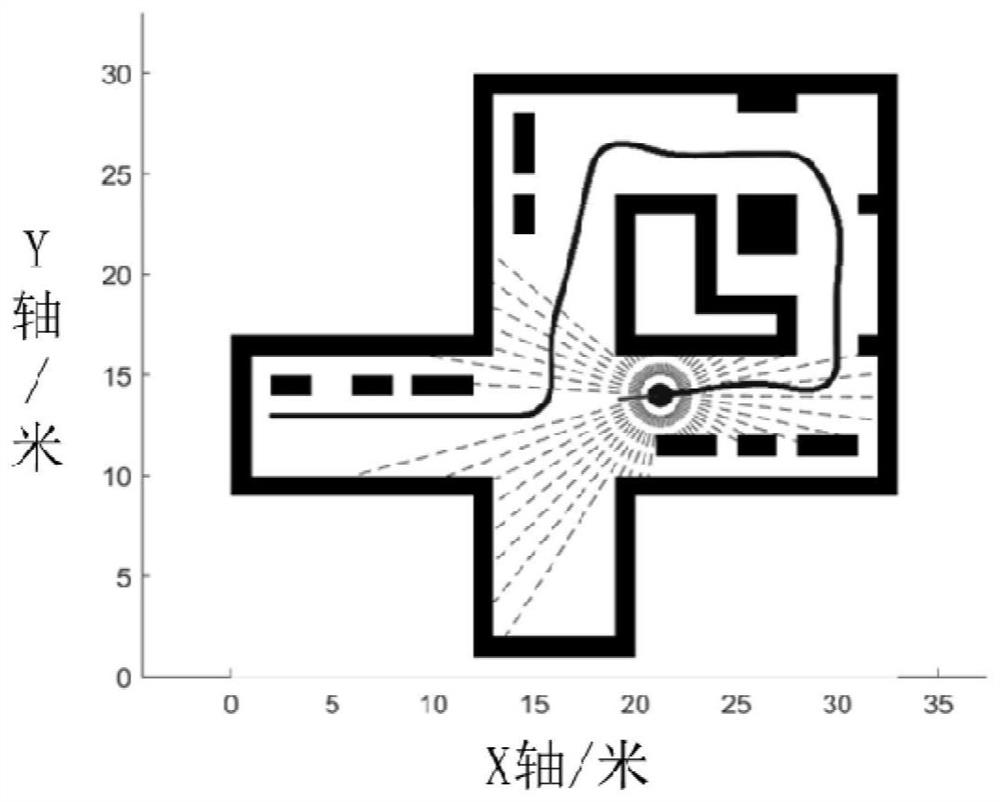
[0098] Example 1: Small-scale narrow, messy simulation environment
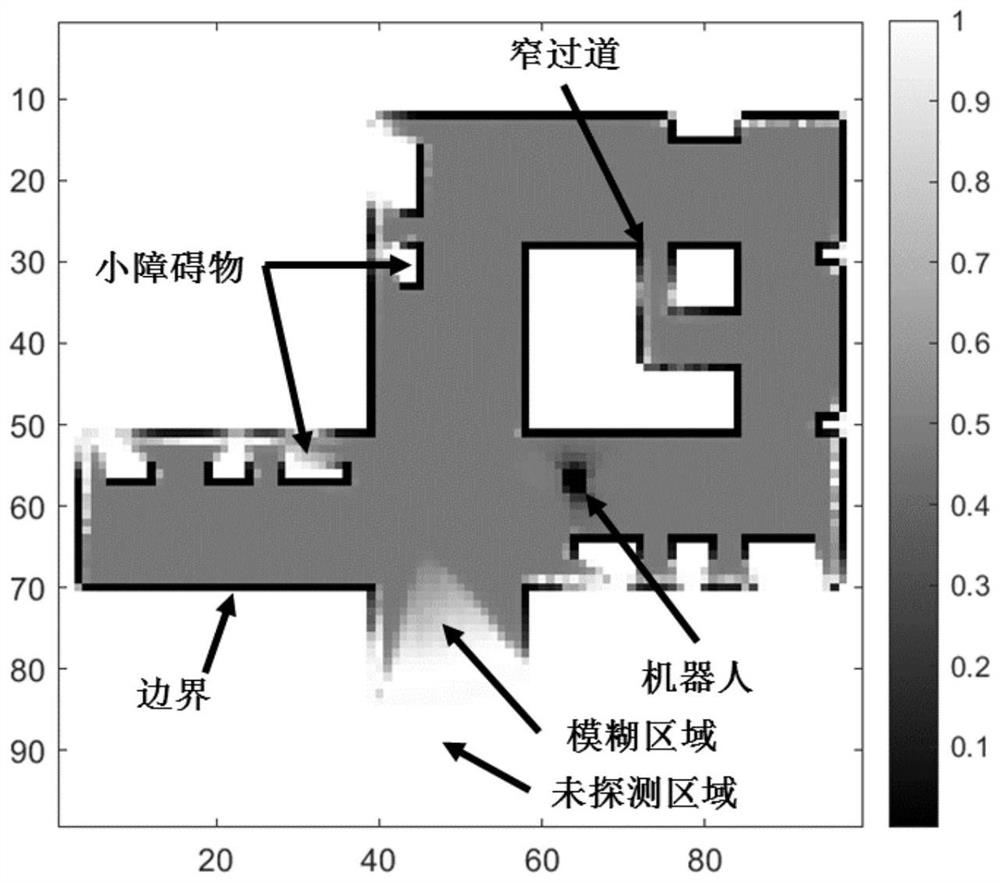
[0099] In this embodiment, the simulation robot is equipped with a two-dimensional omnidirectional laser radar, which can evenly emit 60 beams, and the maximum measurement distance z MAX =8m, a total of 1144 frames of scan data were collected on the preset trajectory. Such as figure 2 As shown, the size of the simulation environment is 33m×33m, and the map resolution is λ M = 0.33m. The results of the confidence-enhanced mutual information CRMI in this embodiment are as follows: image 3 As shown, the values of MI are all in the range of [0,1]. It can be seen that the CRMI distinction of boundary, free area, fuzzy area and undetected area is very obvious, and the order is increasing. The CRMI around the boundary and the robot itself is the smallest (dark black), which is mainly due to the cumulative calculation of the vacancy value (ie, 1 minus the occupancy value) during the SCM calculation and the b...
Embodiment 2
[0103] Example 2: Office environment experiment
[0104] This example uses the public dataset Intel Research Lab (Seattle), which contains 910 lidar scans, where the map size is set to 30m×30m, and the map resolution is λ M =0.2m, the maximum measurement distance is set to z MAX =8m,λ z = 0.1 m. Figure 6 For the real map of the dataset, Figure 7 and Figure 8 Schematic diagrams of CRMI and OGMI in this region, respectively. It can be seen that CRMI describes more details of the cluttered environment, such as corners, small objects and rooms, etc., while OGMI is relatively vague in these areas, and shows "overconfidence" in corridors and walls, which will also lead to Robots using information controllers have strong repulsive behavior in these areas, which may cause the robot to quickly pass over the area, making it difficult to complete the task of map construction and exploration in this small, restricted area.
Embodiment 3
[0105] Example 3: Large-scale campus scene environment experiment
[0106] In this embodiment, the public dataset Freiburg Campus containing 2008 laser radar scans is used. The scene is a large-scale unstructured outdoor environment, such as Figure 9 shown on the satellite map. In this embodiment, the map size is set to 250m×250m, and the map resolution is λ M =0.33m, the maximum measurement distance is set to z MAX = 50m. Such as Figure 10 As shown, CRMI exhibits similar performance to Embodiments 1 and 2, especially in the estimation of blurred areas, cluttered areas and undetected areas, which is more conservative, and at the same time, it shows refined estimation for small objects. The time consumption comparison in Table 2 also proves that the present invention can improve the estimation accuracy of MI without significantly increasing the computational complexity, which shows the superiority of the present invention.
[0107] Table 2 Time consumption comparison (MI...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com