Tomato fermented product and preparation method thereof
A fermented product, tomato technology, applied in the field of tomato fermented products and its preparation, can solve problems such as single taste, high loss of lycopene, incomplete utilization of raw materials, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] A preparation method of tomato fermented products, comprising the following steps:
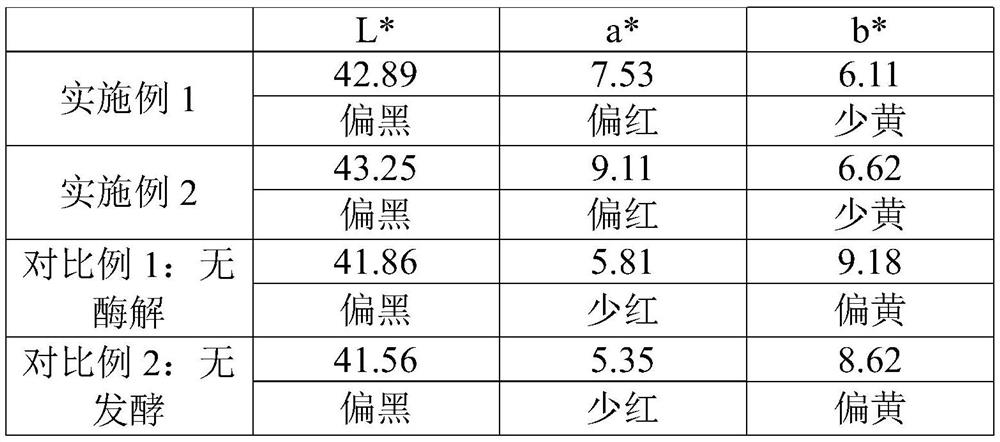
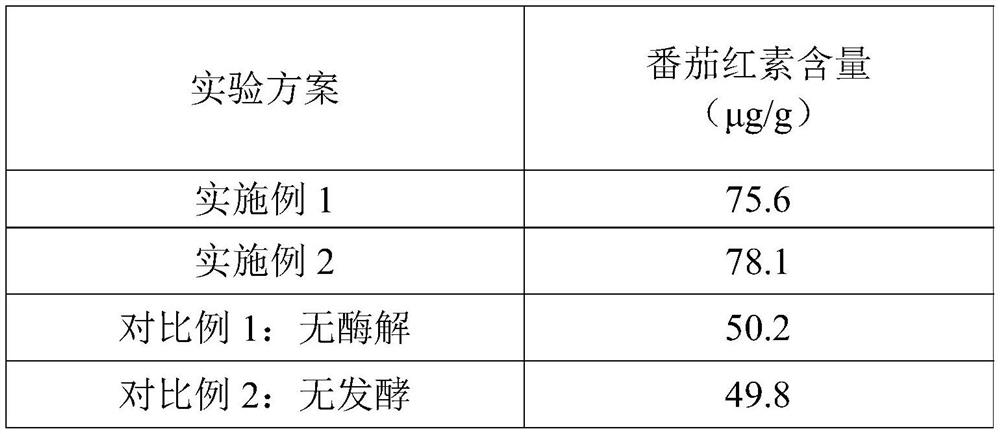
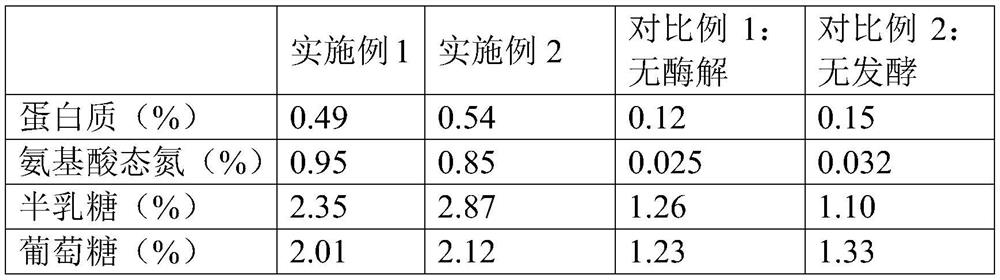
[0038] (1) Tomato screening: use a color sorter to screen the raw materials, and select bright red tomatoes: the content of tomatine is less than or equal to 50 μg / g (by dry weight), and the content of lycopene is greater than or equal to 2500 μg / g (by dry weight) count).
[0039] (2) Cleaning and preparation of raw materials: Remove rot, mildew, mud feet, impurities and other parts that cannot be used for production from the screened fresh red tomatoes, and use a high-pressure rotary cleaning machine to clean and then cut into pieces. After the raw materials are processed, weigh the following components in proportion, 6 parts of yeast powder, 12 parts of edible salt, 3 parts of white sugar, 9 parts of monosodium glutamate, 6 parts of chicken fat, 2.5 parts of garlic powder, 2.5 parts of ginger powder, 5'- 1.2 parts of taste nucleotide disodium, 0.1 part of sodium D-erythorbate, 79 par...
Embodiment 2
[0046] A preparation method of tomato fermented products, comprising the following steps:
[0047] (1) Tomato screening: use a color sorter to screen the raw materials, and select bright red tomatoes: the content of tomatine is less than or equal to 50 μg / g (by dry weight), and the content of lycopene is greater than or equal to 2500 μg / g (by dry weight) count).
[0048] (2) Cleaning and preparation of raw materials: Remove rot, mildew, mud feet, impurities and other parts that cannot be used for production from the screened fresh red tomatoes, and use a high-pressure rotary cleaning machine to clean and then cut into pieces. After the raw materials are processed, weigh the following components in proportion, 7 parts of yeast powder, 15 parts of edible salt, 4 parts of white sugar, 11 parts of monosodium glutamate, 8 parts of chicken fat, 3 parts of garlic powder, 3 parts of ginger powder, 5'- Flavor nucleotide disodium 1.5 parts, D-isoascorbate sodium 0.2 parts, fresh tomato...
Embodiment 3
[0055] A preparation method of tomato fermented products, comprising the following steps:
[0056] (1) Tomato screening: use a color sorter to screen the raw materials, and select bright red tomatoes: the content of tomatine is less than or equal to 50 μg / g (by dry weight), and the content of lycopene is greater than or equal to 2500 μg / g (by dry weight) count).
[0057] (2) Cleaning and preparation of raw materials: Remove rot, mildew, mud feet, impurities and other parts that cannot be used for production from the screened fresh red tomatoes, and use a high-pressure rotary cleaning machine to clean and then cut into pieces. After the raw materials are processed, weigh the following components in proportion, 8 parts of yeast powder, 15 parts of edible salt, 4 parts of white sugar, 12 parts of monosodium glutamate, 9 parts of chicken fat, 3 parts of garlic powder, 3 parts of ginger powder, 5'- 2 parts of taste nucleotide disodium, 0.2 part of sodium D-isoascorbate, 82 parts o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com