High-frequency ground wave radar clutter classification method based on U-Net network
A high-frequency ground wave radar and classification method technology, applied in neural learning methods, biological neural network models, image analysis, etc., can solve the problem of low accuracy, reduce the probability of false alarms, and improve detection performance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
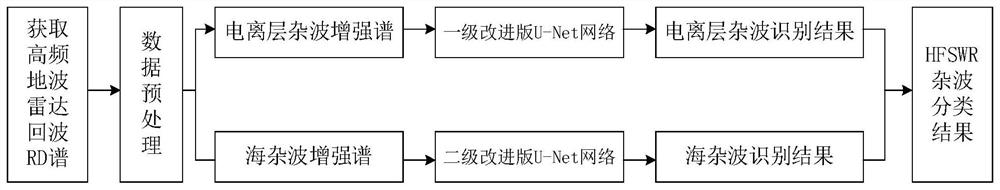
[0021] Specific implementation mode one: combine Figure 1-7 Specifically illustrate the present embodiment, a kind of high-frequency ground wave radar clutter classification method based on U-Net network in the present embodiment, comprises the following steps:
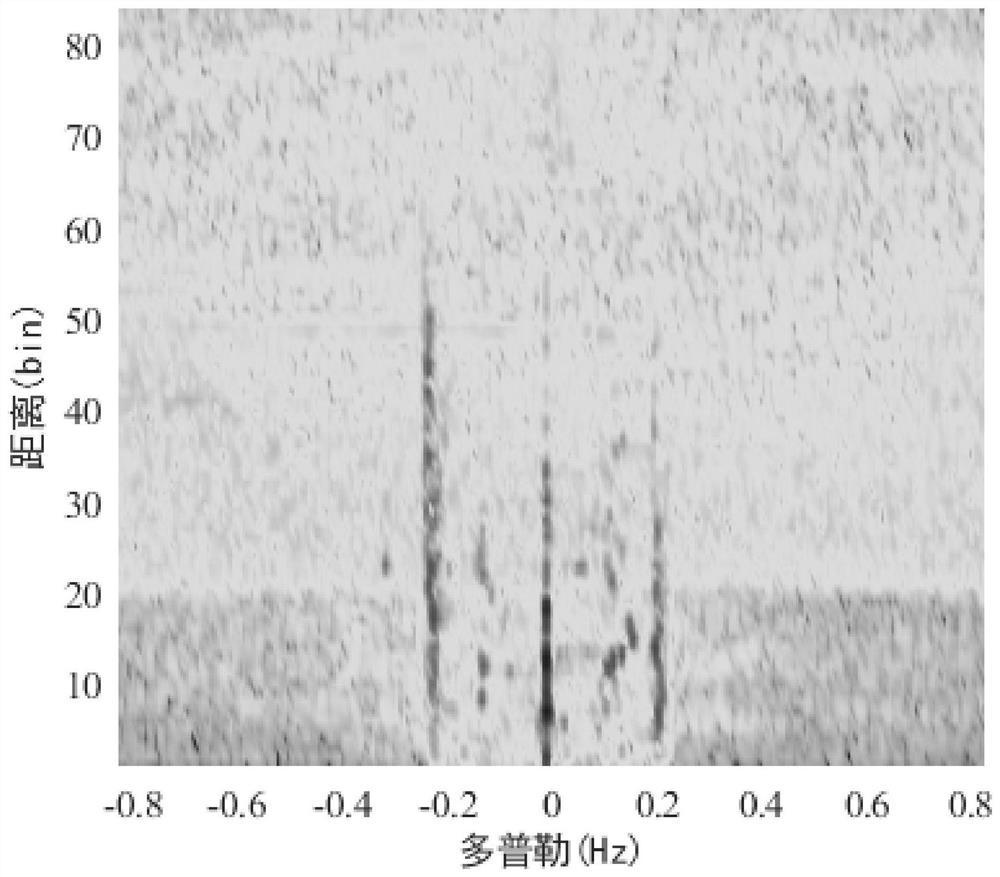
[0022] Step 1. Obtain the range Doppler spectrum of the high-frequency ground wave radar echo (such as figure 2 shown), the range Doppler spectrum is preprocessed to obtain the ionospheric clutter enhanced spectrum and the first-order sea clutter enhanced spectrum; the ionospheric clutter enhanced spectrum is used as training set 1, and the first-order sea clutter enhanced spectrum The spectrum is used as the training set 2;
[0023] Step 2. Use the training set 1 to train the ionospheric clutter recognition network to obtain the trained ionospheric clutter recognition network, such as Figure 5 As shown, due to the uneven number of samples of clutter and noise, the present invention changes the loss function in t...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0029] Embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that in the step 1, data preprocessing is performed on the range Doppler spectrum to obtain the ionospheric clutter enhanced spectrum and the first-order sea clutter enhanced spectrum; The specific process includes:
[0030] Step 11, performing logarithmic processing on the data in the range Doppler spectrum to obtain the logarithmically processed range Doppler spectrum I;
[0031] Step 12: Use a bilateral filter to filter I to suppress background noise and target interference, thereby obtaining the ionospheric clutter enhanced spectrum I 1 , by using the bilateral filter to filter the range Doppler spectrum, it can not only reduce the interference of the target on clutter identification, but also separate the sea clutter and ionospheric clutter to avoid the mutual influence between the two in the identification process;
[0032] Step 13, calculate the difference between the range Doppler spectrum...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0037] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is that in the step one or two, the bilateral filter is used to filter I to obtain the ionospheric clutter enhanced spectrum I 1 , the specific process includes:
[0038]
[0039] Among them, i represents the distance dimension coordinate; j represents the Doppler dimension coordinate; k represents the distance dimension coordinate of the adjacent unit; l represents the Doppler dimension coordinate of the adjacent unit; (k,l) represents the adjacent unit of (i,j) Position coordinates; I(k,l) represents the magnitude of the distance Doppler I at the position (k,l) after coordinate logarithm processing; the weight coefficient w(i,j,k,l) is defined by the domain The product of the kernel d(i,j,k,l) and the range kernel r(i,j,k,l) is determined, namely:
[0040] w(i,j,k,l)=d(i,j,k,l)×r(i,j,k,l).
[0041] Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodime...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com