Method for judging alarm threshold value for water disaster micro-earthquake
A water damage and microseismic technology, which is applied to earth drilling, mining equipment, mining equipment, etc., can solve problems such as inability to dynamically adjust
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
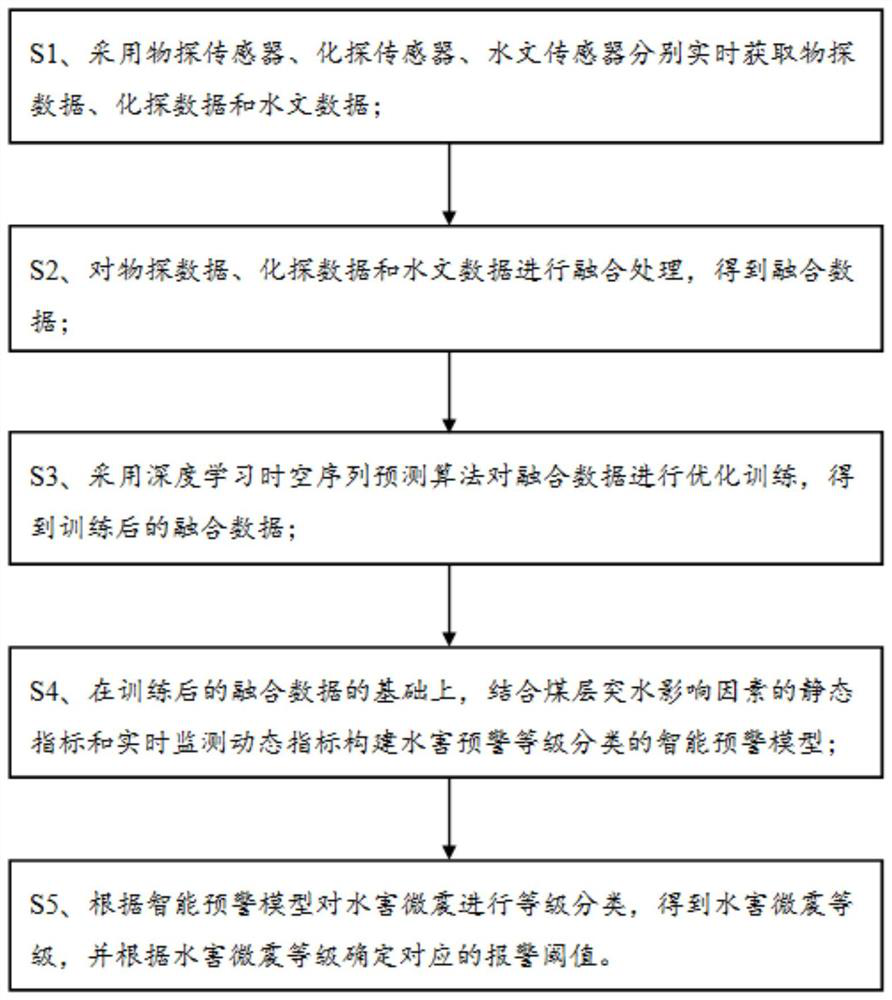
[0046] The embodiment is basically as attached figure 1 shown, including:
[0047] S1. Using geophysical sensors, geochemical sensors, and hydrological sensors to acquire geophysical data, geochemical data, and hydrological data in real time, respectively;
[0048] S2. Perform fusion processing on geophysical data, geochemical data and hydrological data to obtain fusion data;
[0049] S3. Using the deep learning space-time sequence prediction algorithm to optimize the training of the fusion data, and obtain the fusion data after training;
[0050] S4. On the basis of the fused data after training, combine the static indicators of coal seam water inrush influencing factors and real-time monitoring dynamic indicators to construct an intelligent early warning model for classification of water hazard early warning levels;
[0051] S5. According to the intelligent early warning model, classify the water damage microseisms to obtain the level of water damage microseisms, and deter...
Embodiment 2
[0061] The only difference from Embodiment 1 is that in S41, the preset ratio is generated in a random manner, so that the data content of the training set and the test set can be continuously updated while being random, and the calibration effect can be improved.
Embodiment 3
[0063] The only difference from Embodiment 2 is that after the corresponding alarm threshold is determined according to the water damage microseismic level, the alarm threshold is also corrected. In this embodiment, the water damage microseism is caused by the pressure and impact of groundwater on the mine floor: on the one hand, because the groundwater is in a state of continuous flow, the groundwater will have an impact on the mine floor; on the other hand, the pressure of the groundwater will also Under the influence of these two aspects, the groundwater forms a water damage micro-seismic on the mine floor.
[0064] Relevant geological exploration research results show that the groundwater in the mine floor is usually flowing, and the fine particles of the rock layer or coal seam under the mine floor will gradually melt into the groundwater. Due to the great difference in the composition of different rock layers or coal seams, the composition of the groundwater is different ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com