Application of RNA helicase DHX33 inhibitor in preparation of medicine for treatment of leukemia
A technology of DHX33 and leukemia, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of poor targeting of therapeutic drugs, no obvious improvement in the treatment of acute leukemia, and inability to fully achieve the expected therapeutic effect, and achieve the inhibition of programmed cell apoptosis. Important medicine development value, efficacy in the treatment of leukemia
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1D
[0124] Example 1 DHX33 protein inhibitors play an important role in lymphocytic leukemia, and the inhibition of DHX33 protein significantly inhibits the growth of lymphocytic leukemia cells
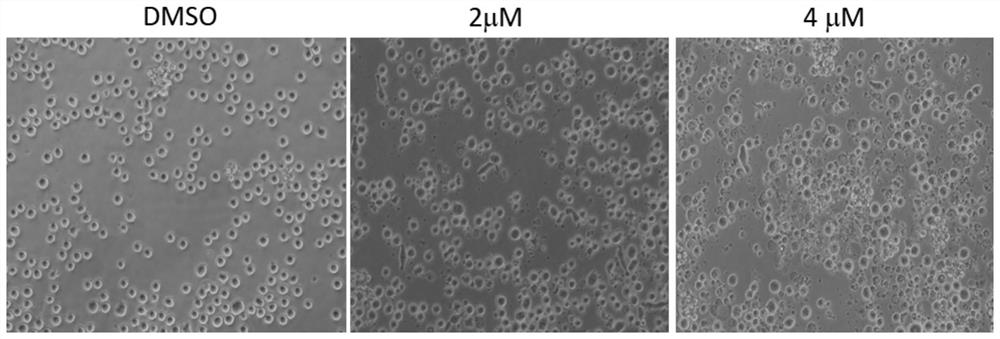
[0125] A variety of human leukemia model cell lines were cultured in vitro, including Jurkat T cell line, Raji cell line, Daudi cell line, K562 cell line and Nalm6 cell line, and cell activity experiments were performed in vitro. Jurkat cells, a suspension cell, are a model cell used to study human acute T-cell leukemia. Raji is a human B-lymphoma cell model, which is of B-cell origin. The Daudi cell line is a human Burkkit lymphoma cell, which carries Epstein-Barr virus, and is a typical B lymphoblastoid cell line, which is used for the study of the pathogenesis of leukemia. The K562 cell line is a human chronic myeloid leukemia cell line. The Nalm6 cell line is a human acute lymphoblastic leukemia cell line.
[0126] experiment as figure 1 As shown, compared with the DMSO control gr...
Embodiment 2D
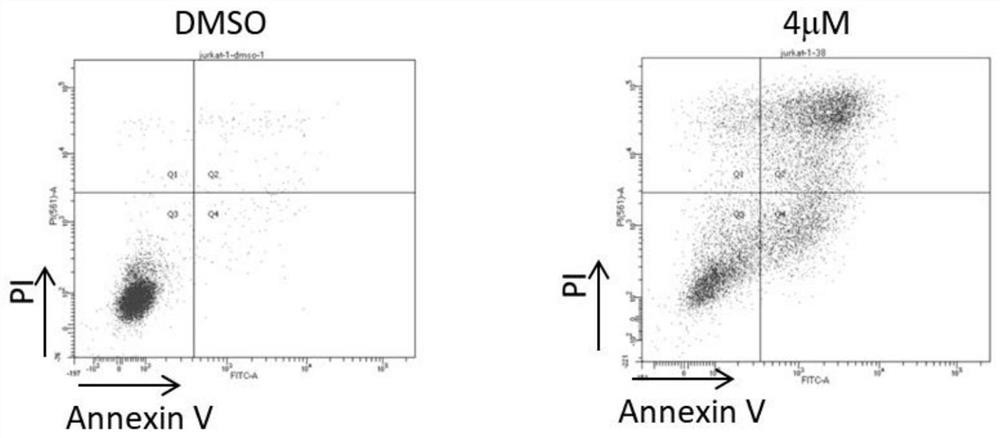
[0131] Example 2 The programmed apoptosis induced by DHX33 inhibitor is the main cause of leukemia cell death
[0132] The B-cell lymphoma-2 gene is referred to as Bcl-2 (B-cell lymphoma-2), which is the B-cell lymphoma / leukemia-2 gene. The role of apoptosis, it is often highly expressed in leukemia cells. BCL2 gene was down-regulated in Jurkat T cells treated with DHX33 protein inhibitor A.
[0133] BMF (bcl-2-modifying factor) is a member of the Bcl-2 family with pro-apoptotic effects. Under normal physiological conditions, endogenous BMF is continuously anchored to the cytoskeleton in the cytoplasm, and it always senses the intracellular Once the injury stimulus acts on the cells, BMF transfers from the cytoplasm to the mitochondria, triggers the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway, and induces apoptosis. The Jurkat T cells treated with the DHX33 inhibitor compound A up-regulated the BMF gene, which promoted the apoptosis of leukemia cells.
[0134] As a member of Bcl-2 fami...
Embodiment 3
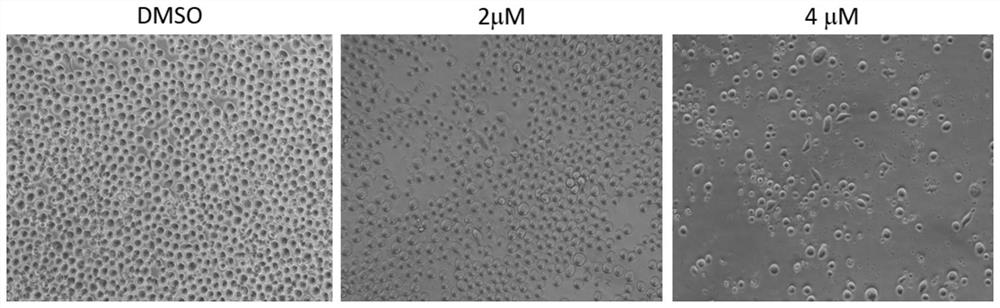
[0136] The highly active compound C obtained after optimization in Example 3 is more effective in inducing programmed apoptosis of cancer cells
[0137] Because compound A has a higher half-inhibitory concentration of cells, that is, the activity is relatively low, compound B was selected after molecular optimization of compound A (IC 50 =10-20nM) and compound C (IC 50 =0.15 μM) (see CN112661754A) to further analyze the apoptosis-inducing effect of DHX33 inhibitors on leukemia cells. Figure 9 Shows the half-inhibitory concentration analysis of Jurkat T cells treated with compounds B, C and D, and the results show that the inhibitor concentrations of these compounds in Jurkat T cells, i.e. IC 50 , between 0.025 and 0.18 μM, the activity of compound A is significantly improved.
[0138] First, on the basis of increasing the dose of compound C, the apoptosis index was analyzed. Cancer cells were treated with 0, 0.1, 0.25, 0.5, and 1 μM for 24 hours. After the cells were harve...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com