Quantitative description method for Bi segregation degree at Sn-Bi solder interface based on addition of alloying element M
A technology for quantitative description of alloying elements, applied in the fields of electrical digital data processing, design optimization/simulation, and special data processing applications, etc., can solve the problems of unclear potential mechanism of Bi segregation, degradation of solder mechanical properties, and wide application in the field of electronic packaging and other issues to achieve the effect of reducing large quantities of repetitive work, solving bottleneck problems, and promoting R&D and production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] The present invention provides a quantitative description method based on adding elements to alleviate the degree of Bi segregation at the Sn-Bi solder interface, and the specific steps are as follows:
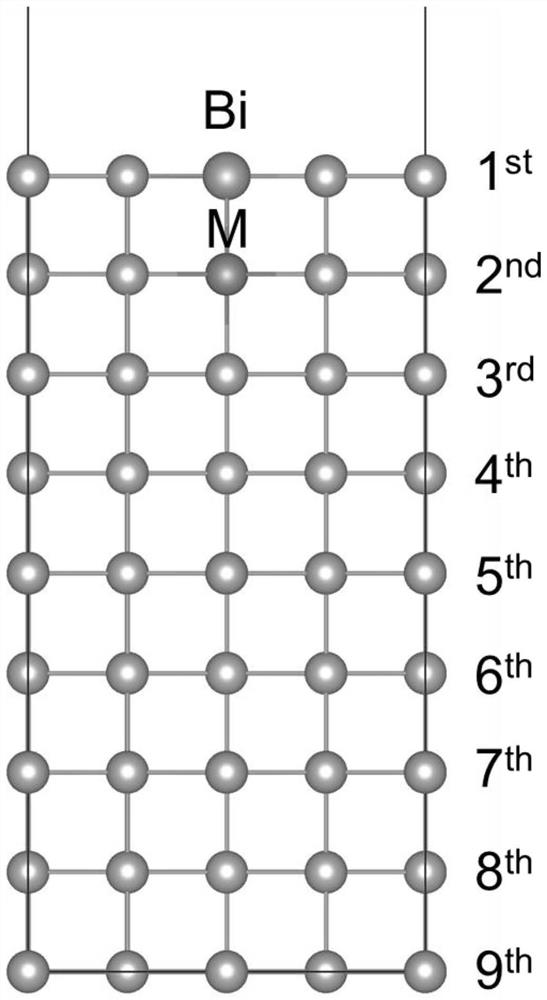
[0038] 1) Construct a stable Sn surface model: first establish the Sn matrix primitive cell, and obtain the lattice constant of Sn by the first principle calculation method of quantum mechanics as On this basis, by comparing the surface energy, it is found that the most stable surface of Sn is Sn(100). Therefore, the surface model constructed in the simulation is a (2×3) Sn(100) surface, with a total of 9 layers of atoms and a vacuum layer. for structured as figure 1 shown;
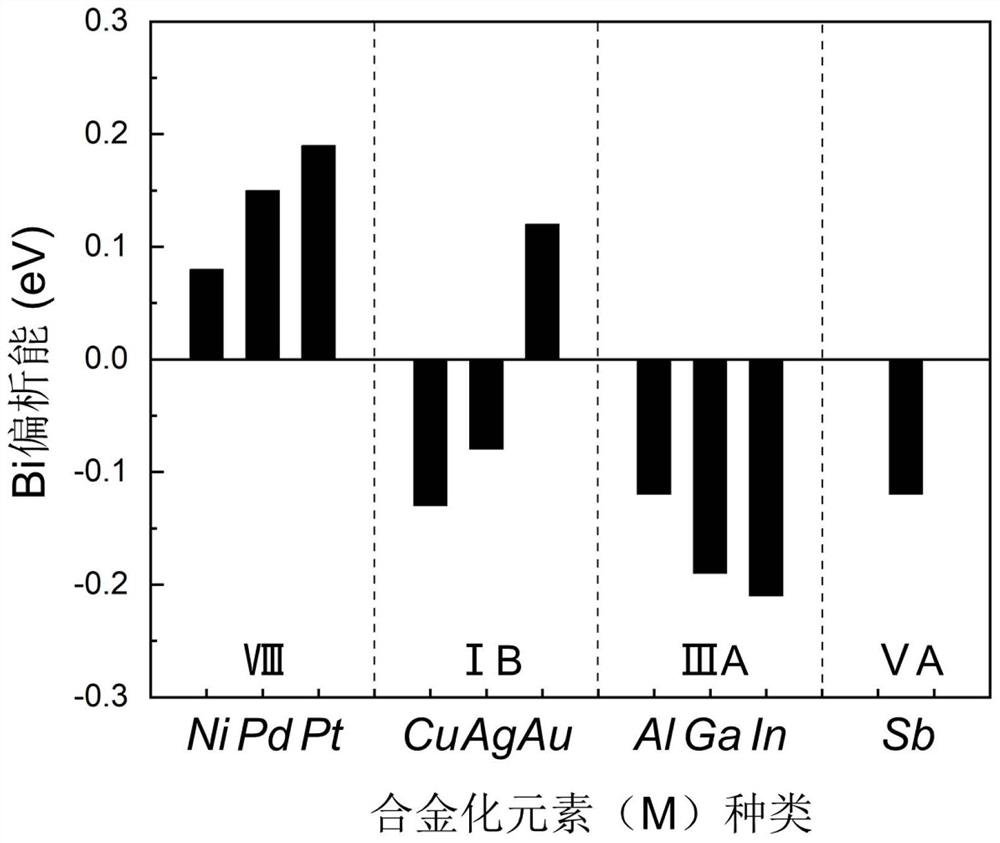
[0039] 2) Propose the main descriptor to quantify the degree of Bi segregation on the Sn surface: add a Bi to the Sn(100) surface model, replace a Sn lattice position at a thermodynamically stable position, place Bi on the Sn surface 1 st -5th , to calculate the diffusion activation energy and...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com