Method for co-treating electroplating waste residues and chromium-containing heavy metal ion waste liquid
A technology for heavy metal ions and electroplating waste residues, applied in chemical instruments and methods, filtration treatment, water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of slow reaction speed, high pH of waste liquid, high hardness of effluent water, etc., and achieve mild reaction conditions and low cost , the effect of easy operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0014] Treatment of Cr in chrome tanning waste liquor with Zn electroplating waste residue 3+ Ions: collect chrome tanning waste liquid, filter to remove solid skin residue, in which Cr 3+ The ion concentration is 1300mg / L, and the pH value of the waste solution is 5; add 1g of Zn electroplating waste residue to 40mL of the waste solution, and react at 25°C for 12h.
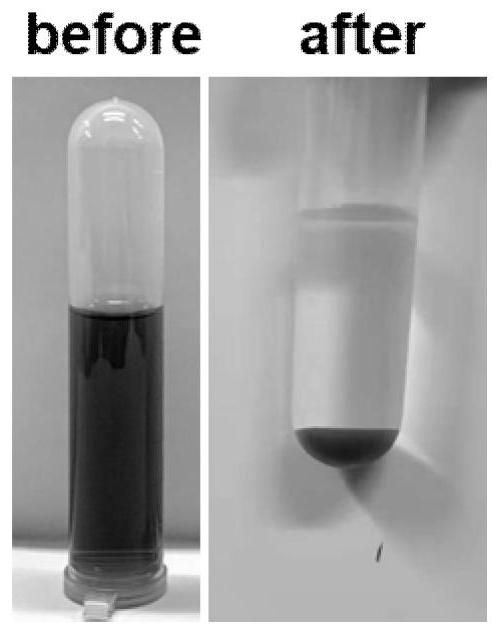
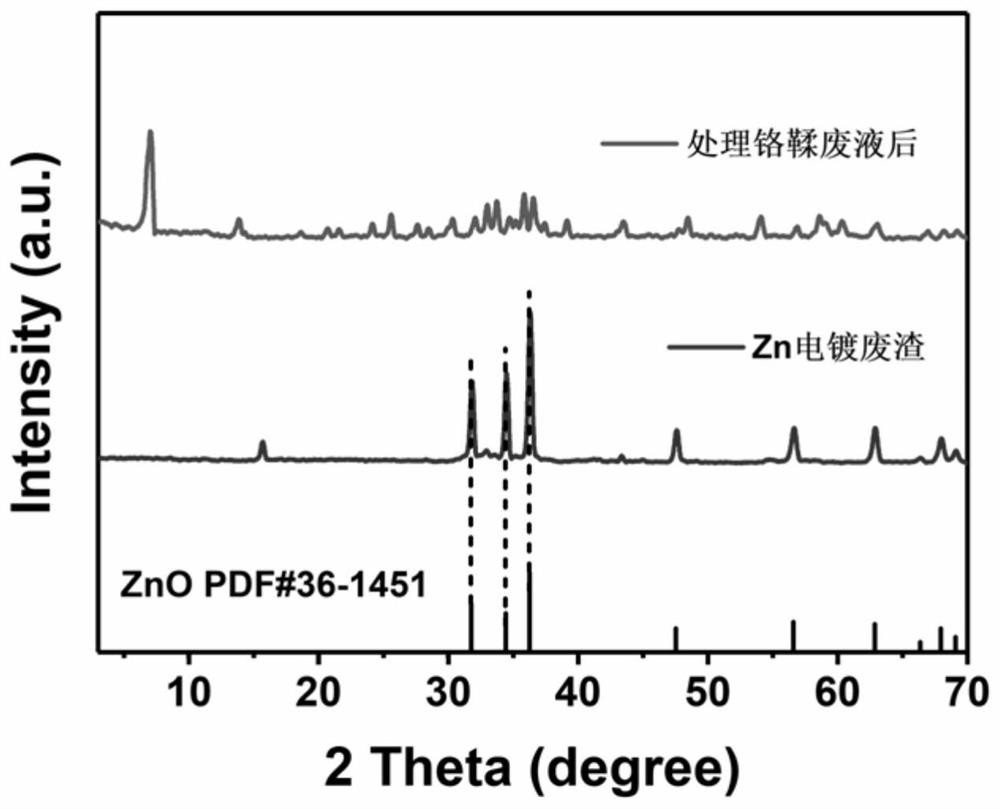
[0015] After the reaction was completed, it was filtered, and the supernatant obtained became clear, from dark green to colorless (such as figure 2 shown), the pH value is neutral, after testing, the supernatant heavy metal Cr after treatment 3+ The concentration is less than 1mg / L, and the removal efficiency reaches 99.92%, which can continue to be used for tanning production water. The resulting solid precipitate was filtered from figure 1 In the XRD of Zn electroplating residues, the mineralization products obtained after treating chrome tanning waste liquor can be seen, and the characteristic peaks such a...
Embodiment 2
[0017] Treatment of Cr in chrome tanning waste liquor with Cu electroplating waste residue 3+ Ion: Using Cu electroplating waste residue to treat Cr in chrome tanning waste liquor 3+ Ions: collect chrome tanning waste liquid, filter to remove solid skin residue, in which Cr 3+ The ion concentration was 1300 mg / L, and the pH value of the waste liquid was 5; 1 g of Cu electroplating waste was added to 40 mL of waste liquid; the reaction was carried out at 35°C for 12 hours. After the reaction is completed, it is filtered, and the obtained supernatant is continuously used for tanning production water; the obtained solid precipitate is used for adsorption and removal of organic dyes.
Embodiment 3
[0019] Treatment of Cr in chrome tanning waste liquor with Ni electroplating waste residue 3+ Ion: Treatment of Cr in chrome tanning waste liquor with Zn electroplating waste residue 3+ Ions: collect chrome tanning waste liquid, filter to remove solid skin residue, in which Cr 3+ The ion concentration was 1300 mg / L, and the pH value of the waste liquid was 5; 1 g of Ni electroplating waste was added to 40 mL of waste liquid; the reaction was carried out at 35°C for 12 hours. After the reaction is completed, it is filtered, and the obtained supernatant is continuously used for tanning production water; the obtained solid precipitate is used for adsorption and removal of organic dyes.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com