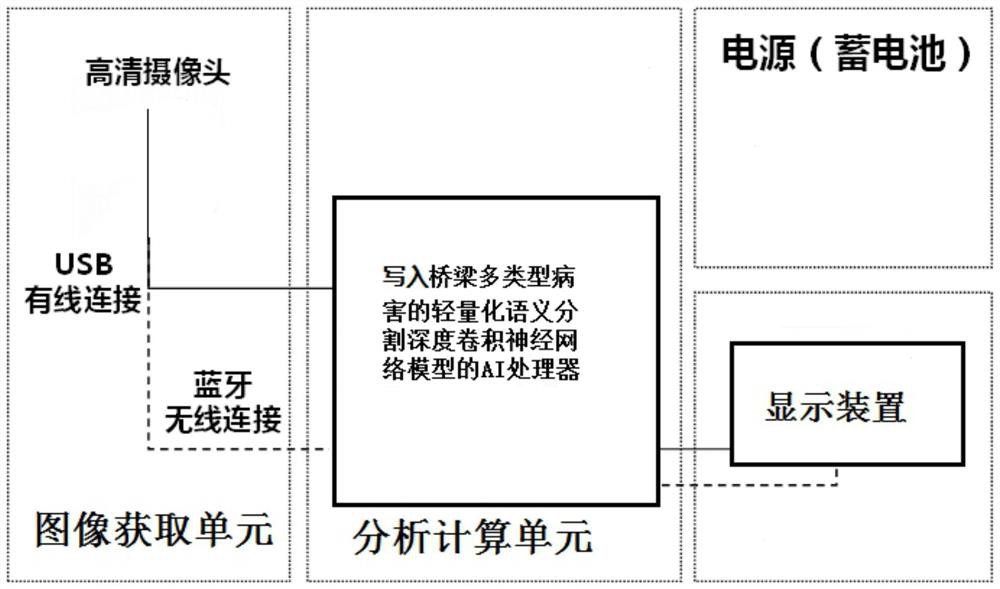
Computer vision method and intelligent camera system for bridge health diagnosis
A computer vision and bridge technology, applied in computing, neural learning methods, image analysis, etc., can solve the problems of low image recognition accuracy, poor real-time performance, and low efficiency, and achieve good real-time performance, high accuracy, and slow solution speed Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
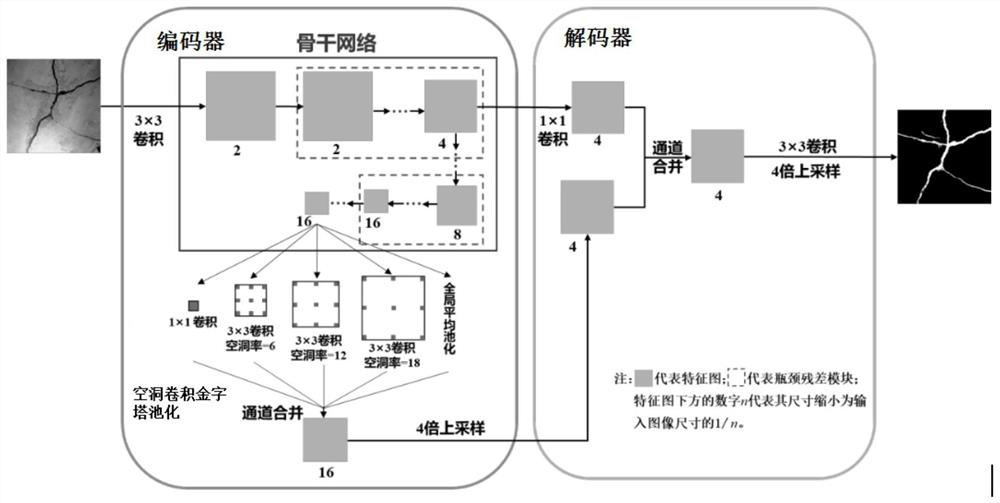
[0078] Embodiment 1, see figure 1 This embodiment will be described. This embodiment provides a computer vision method for bridge health diagnosis, and the method includes:
[0079] Step 1. Establish a lightweight semantic segmentation deep convolutional neural network model for multiple types of bridge defects, which includes an encoder and a decoder;
[0080] The encoder includes a backbone network and dilated convolutional pyramid pooling;
[0081] The backbone network includes a convolution module and several bottleneck residual modules, the first layer is the convolution module, and the convolution module is used to extract low-level features from the input image, and output low-level feature maps to the first a bottleneck residual module;
[0082] The several bottleneck residual modules are connected in sequence, and each bottleneck residual module sequentially reduces the size of the feature map output by the previous layer according to the preset value and performs ...
Embodiment approach 2
[0099] Embodiment 2. This embodiment is a further limitation of the computer vision method for bridge health diagnosis described in Embodiment 1. In this embodiment, the preset values and preset reduction conditions related to reducing the size of the input image in the backbone network Further restrictions are made, specifically:
[0100] The size of the low-level feature map is 1 / 2 the size of the input image;
[0101] The preset values are 1 / 4, 1 / 8 and 1 / 16 of the input image;
[0102] The preset reduction condition is specifically to reduce the size of the feature map output by the previous layer to 1 / 16 of the input image.
[0103] Such as figure 1 As shown, the numbers 2, 4, 8, and 16 below the feature map mean that the size of the feature map at this level is reduced to 1 / 2, 1 / 4, 1 / 8, and 1 / 16 of the input image size, that is, the higher the level The size of the feature map is gradually reduced, and the number of layers increases with the direction of the arrow,...
Embodiment approach 3
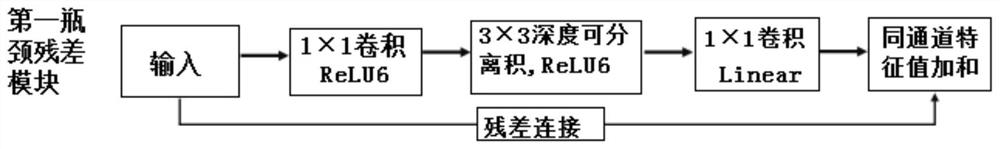
[0107] Embodiment 3. This embodiment is a further limitation of the computer vision method for bridge health diagnosis described in Embodiment 2. In this embodiment, the bottleneck residual module is further limited, specifically:
[0108] The bottleneck residual module includes a first bottleneck residual module and a second bottleneck residual module;
[0109] The step size of the second bottleneck residual module is twice the step size of the first bottleneck residual module.
[0110] It should be noted that choosing a relationship of 2 times can prevent over-sampling, and the high information loss rate will affect the accuracy rate; this design can realize the acquisition of multi-scale feature maps, and different step lengths can be used to obtain feature maps of different scales. Increase the ability to extract features from input images.
[0111] In this embodiment, the step size of the first bottleneck residual module can be set to 1, and the step size of the second b...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com