Application of bufanolide alkene compound in preparation of medicine or health care product for treating EGFR and/or STAT3 driven diseases
A technology of bufastenes and compounds, which is applied in the field of new applications of bufastenes, can solve the problems of unclear efficacy of tumors and limiting the value of anti-tumor medicines, so as to promote cytotoxicity, prevent cell cycle, and inhibit cell proliferation Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
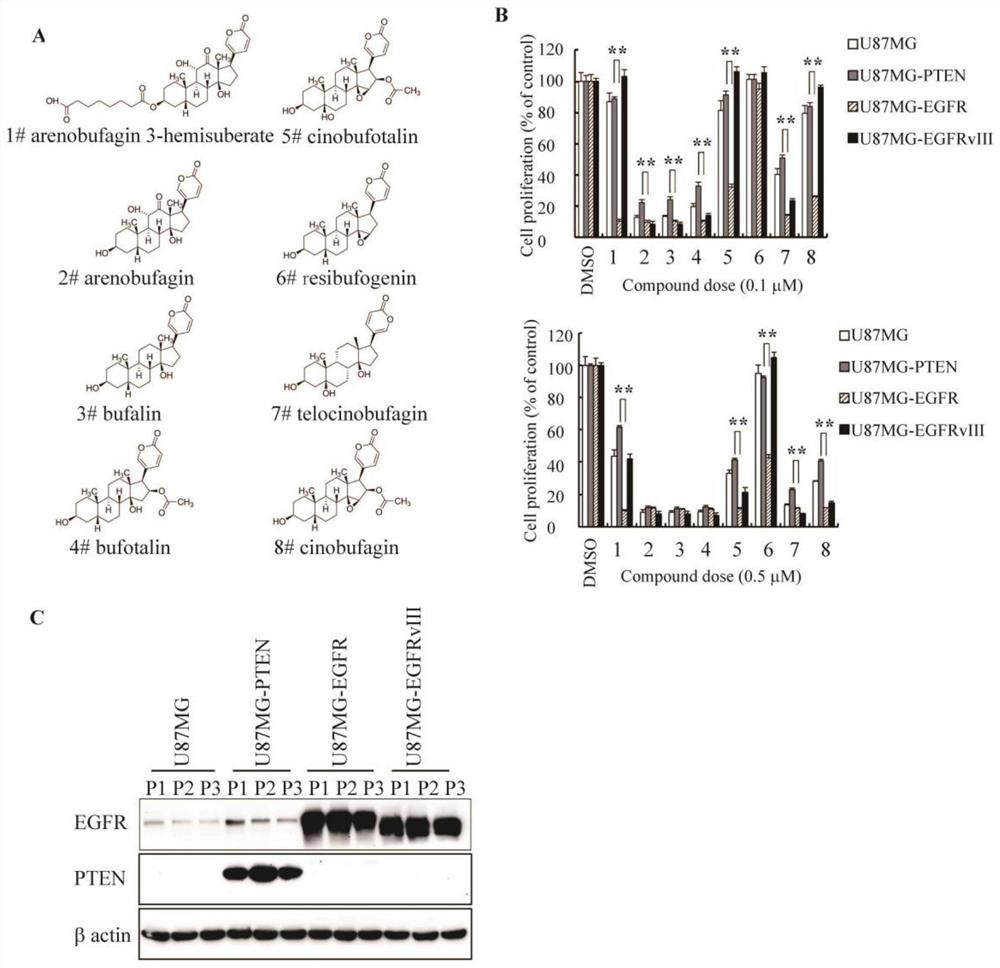
[0066] Bufadene compounds inhibit the proliferation of EGFR-overexpressing PTEN-deficient glioma cells.
[0067] figure 1 It reflects the inhibitory effect of eight bufadenoids on the proliferation of EGFR overexpressing glioma cells (U87MG-EGFR and U87MG-EGFRvIII) and control cells (U87MG and U87MG-PTEN). The modification of different sites on the nucleus affects the selectivity and activity of this type of compound. Comprehensive analysis shows that cinobufagin and cinobufotalin are more effective in inhibiting the proliferation of U87MG-EGFR and U87MG-EGFRvIII cells, while Less impact on other cells, better selectivity. The control DMSO had no inhibitory effect on the cells. **P<0.01.
Embodiment 2
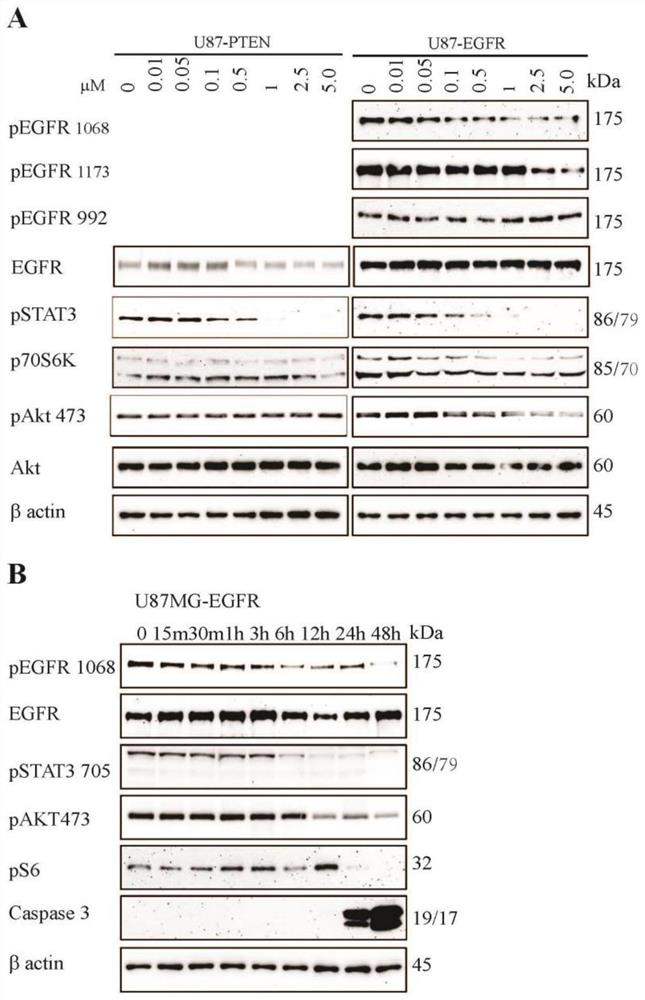
[0069] Bufadene compounds induce apoptosis, cytotoxicity, arrest cell cycle and inhibit cell proliferation by inhibiting EGFR / STAT3 signaling pathway.
[0070] figure 2 It embodies the molecular mechanism of the bufasteine compound cinobufagin to specifically inhibit the EGFR / STAT3 signaling pathway: the inhibitory effect of cinobufagin on the EGFR / STAT3 signaling pathway is dose-dependent and time-dependent, and DMSO without drugs The control has no effect on the EGFR / STAT3 signaling pathway;
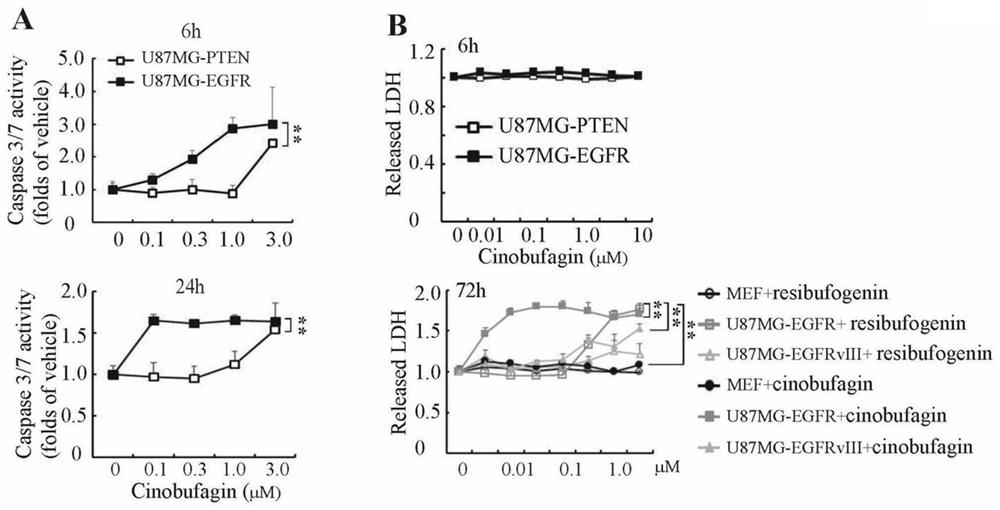
[0071] image 3 It reflects the effects of bufasteine compounds cinobufagin and esterbufagenin on specifically inducing the apoptosis and cytotoxicity of EGFR overexpressing glioma cells: cinobufagin induces apoptosis of U87MG-EGFR cells (caspase3 / 7 activity) and cytotoxicity (LDH release) were significantly stronger than those of the control cells U87MG-PTEN and MEF, and the cytotoxicity induced by cinobufagin in U87MG-EGFR was stronger than that of bufagenin;
[0072] Figur...
Embodiment 3
[0074] The bufasteine compound cinobufagin inhibits the proliferation of EGFR-positive tumor cells by inhibiting the EGFR / STAT3 signaling pathway
[0075] Figure 5 It reflects the effect and mechanism of the bufasteine compound cinobufagin on specifically inhibiting the proliferation of EGFR-positive and mutant lung cancer cells by inhibiting the EGFR / STAT3 signaling pathway. sex;
[0076] Image 6 It reflects the effect and mechanism of the bufasteine compound cinobufacien to specifically inhibit the proliferation of EGFR-positive colorectal cancer cells by inhibiting the EGFR / STAT3 signaling pathway: the inhibitory effect of cinobufacien on the EGFR-positive cell HCT116 is significantly higher than that of the control cell SW620 ;
[0077] Figure 7 It reflects the effect and mechanism of the bufasteine compound cinobufaginin specifically inhibiting the proliferation of EGFR-positive liver cancer cells by inhibiting the EGFR / STAT3 signaling pathway.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com