Industrial cultivation method for basswood of edible mushrooms
A cultivation method and edible fungus technology, applied in cultivation, plant cultivation, mushroom cultivation and other directions, can solve the problems of lack of sterilization, long cultivation period, extensive management, etc. Increase the effect of walking paths
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] A method for industrial cultivation of edible fungus Basswood, comprising the following steps:
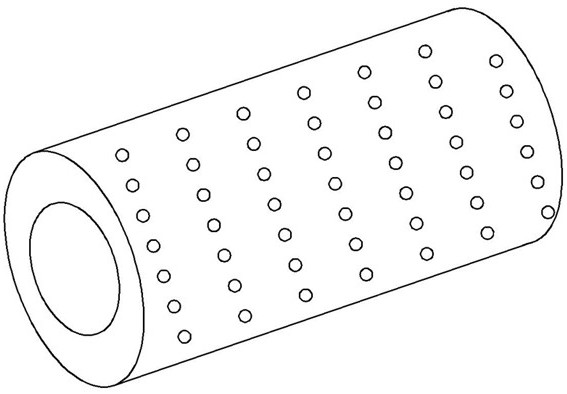
[0023] 1) Basswood preparation: select basswood with uniform thickness, tall and straight without bending, divide the basswood into several basswood segments, dig out the center part of the divided basswood segments to form the center hole of the basswood, the center hole The radius is 1 / 2 of the radius of the basswood section. When drilling, leave a margin of 2cm at the end of the basswood as the "cover" of the center hole, and then use the punching equipment to punch some small holes with a diameter of 1mm on the surface of the basswood section. Hole, finished basswood structure see figure 1 ;
[0024] 2) Preparation of strain blocks: use manual inoculation or mechanical inoculation to plant the strains into the edible fungus culture medium, and wait for the strains to grow into strain blocks for later use. The edible fungus culture medium includes the following raw mater...
Embodiment 2
[0030] A method for industrial cultivation of edible fungus Basswood, comprising the following steps:
[0031] 1) Basswood preparation: select basswood with uniform thickness, tall and straight without bending, divide the basswood into several basswood segments, dig out the center part of the divided basswood segments to form the center hole of the basswood, the center hole The radius is 1 / 3 of the radius of the basswood section. When drilling, leave a margin of 3cm at the end of the basswood as the "cover" of the center hole, and then use the punching equipment to punch some small holes with a diameter of 2mm on the surface of the basswood section. Hole, finished basswood structure see figure 1 ;
[0032] 2) Preparation of strain blocks: use manual inoculation or mechanical inoculation to plant the strains into the edible fungus culture medium, and wait for the strains to grow into strain blocks for later use. The edible fungus culture medium includes the following raw mater...
Embodiment 3
[0038] A method for industrial cultivation of edible fungus Basswood, comprising the following steps:
[0039] 1) Basswood preparation: select basswood with uniform thickness, tall and straight without bending, divide the basswood into several basswood segments, dig out the center part of the divided basswood segments to form the center hole of the basswood, the center hole The radius is 1 / 3 of the radius of the basswood section. When drilling, leave a margin of 2.5cm at the end of the basswood as the "cover" of the center hole, and then use the punching equipment to punch some holes with a diameter of 1.5mm on the surface of the basswood section. Small through holes, finished basswood structure see figure 1 ;
[0040] 2) Preparation of strain blocks: use manual inoculation or mechanical inoculation to plant the strains into the edible fungus culture medium, and wait for the strains to grow into strain blocks for later use. The edible fungus culture medium includes the follow...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com