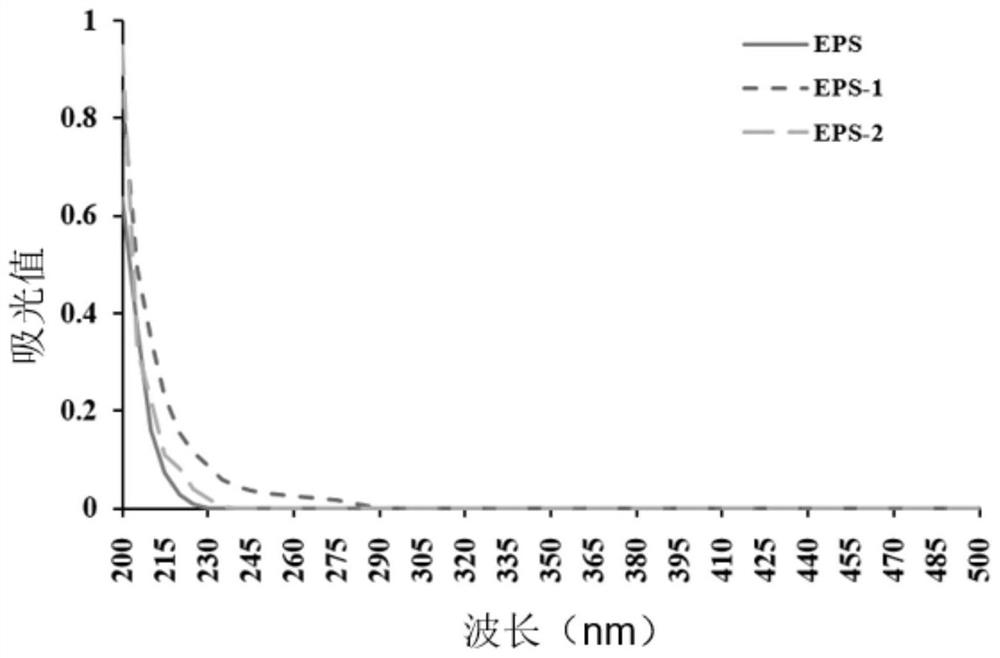
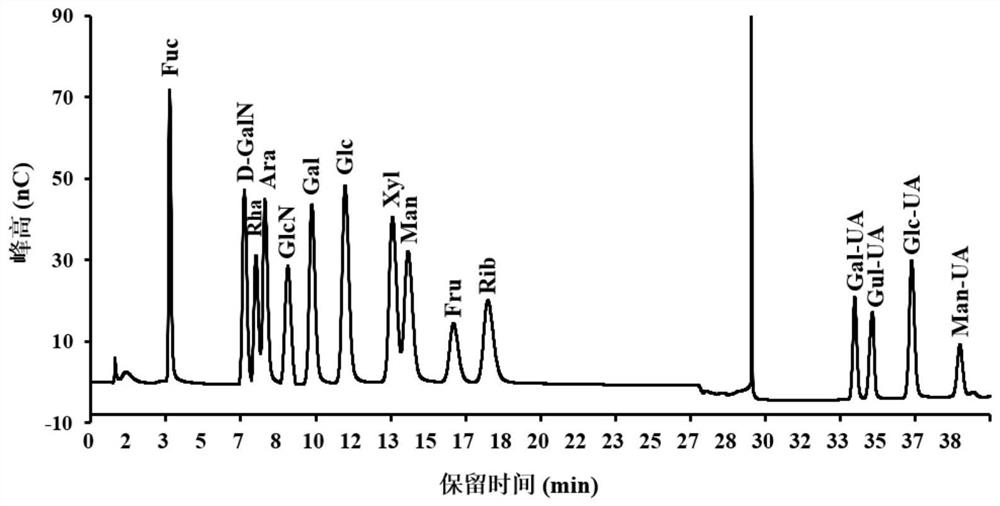
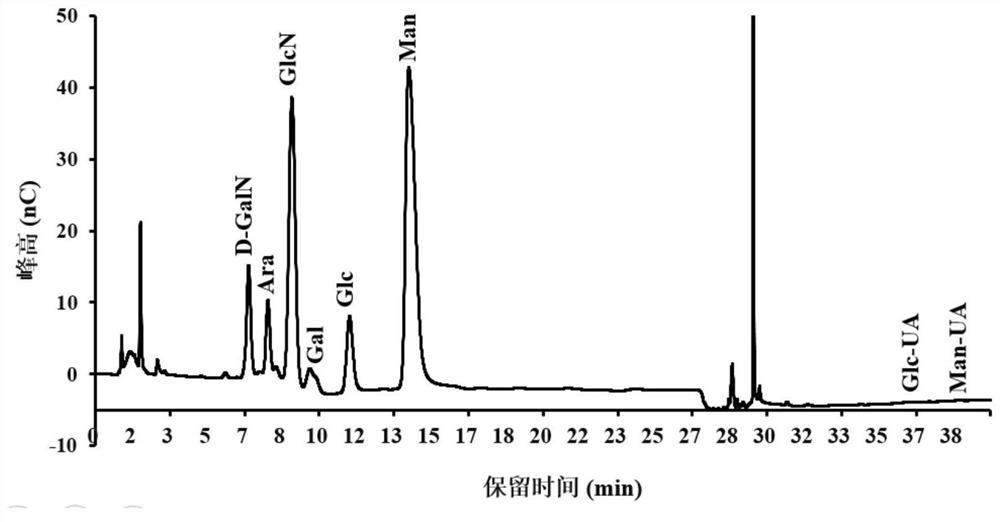
Extracellular polysaccharide-containing extract, exopolysaccharide and composition
A technology of exopolysaccharides and extracts, applied in the field of extracts containing exopolysaccharides, can solve the problems of low yield and limited market application, and achieve excellent synergistic effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0097] 1.1 Extraction of crude exopolysaccharide (i.e. exopolysaccharide extract)
[0098] (1) Inoculate 10 μL of glycerol bacteria of Bacillus thuringiensis 4D19 into 5 mL of liquid LB medium, and activate at 30°C and 220 r / min for 10 hours to obtain activated bacterial liquid;
[0099] (2) Transfer the activated bacterial solution to 100mL liquid LB culture medium and the liquid sugar-producing medium whose substrate is glucose with a 1% inoculation amount, and cultivate it in a 500mL Erlenmeyer flask for 30 hours;
[0100] (3) Collect the bacterial solutions cultured in the three mediums respectively, adjust the pH of the bacterial solutions to 8.5 with 1mol / L NaOH, centrifuge at 4°C, 7000r / min for 30min, and collect the first supernatant;
[0101] (4) Add 1 / 10 volume of 5wt% trichloroacetic acid aqueous solution to the first supernatant, and denature the protein for 2 hours at 25°C;
[0102] (5) 4°C, 7000r / min, centrifuge for 30min, collect the second supernatant, adjust ...
Embodiment 2
[0112] Crude exopolysaccharide extraction is the same as the first section 1.1 in Example 1, the difference is:
[0113] In step (2), the activated bacterial liquid was transferred to 100 mL liquid LB medium and sucrose-based liquid sugar-producing medium with an inoculation amount of 1%, and cultivated in a 500 mL Erlenmeyer flask for 30 h;
[0114] In step (3), collect the bacterial liquid cultured in the three mediums respectively, adjust the pH of the bacterial liquid to 8 with 1mol / L NaOH, centrifuge at 3°C, 6000r / min for 40min, and collect the first supernatant ;
[0115] In step (4), add 1 / 10 volume of 4wt% trichloroacetic acid aqueous solution to the first supernatant, and denature the protein at 35°C for 3 hours;
[0116] In step (5), centrifuge at 3°C, 8000r / min for 30min, collect the second supernatant, and adjust the pH to 6;
[0117] In step (6), add 3 times the volume of absolute ethanol and precipitate in a refrigerator at 2°C for 16 hours;
[0118] In step (...
Embodiment 3
[0121] Crude exopolysaccharide extraction is the same as the first section 1.1 in Example 1, the difference is:
[0122] In step (3), collect the bacterial liquids cultured in the three mediums respectively, adjust the pH of the bacterial liquids to 9 with 1mol / L NaOH, centrifuge at 8000r / min at 10°C for 30min, and collect the first supernatant ;
[0123] In step (4), add 1 / 10 volume of 5wt% trichloroacetic acid aqueous solution to the first supernatant, and denature the protein at 25°C for 1.5 hours;
[0124] In step (5), centrifuge at 3°C, 6000r / min for 40min, collect the second supernatant, and adjust the pH to 7;
[0125] In step (6), add 3 times the volume of absolute ethanol to precipitate in a refrigerator at 8°C for 20 hours;
[0126] In step (7), centrifuge at 10° C. and 8000 r / min for 30 minutes to discard the supernatant, and freeze-dry the precipitate to obtain crude exopolysaccharide powder.
[0127] After quantification, the amount of exopolysaccharide in the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com