Ground stress direction determination method and device, storage medium and computer equipment
A technology for determining the method and stress direction, applied in geophysical measurement, instrumentation, climate sustainability, etc., can solve the problems of difficult to draw clear regional geological conditions, lack of continuity, small amount of data, etc., to achieve optimized well trajectory , Strong practicability and high precision
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
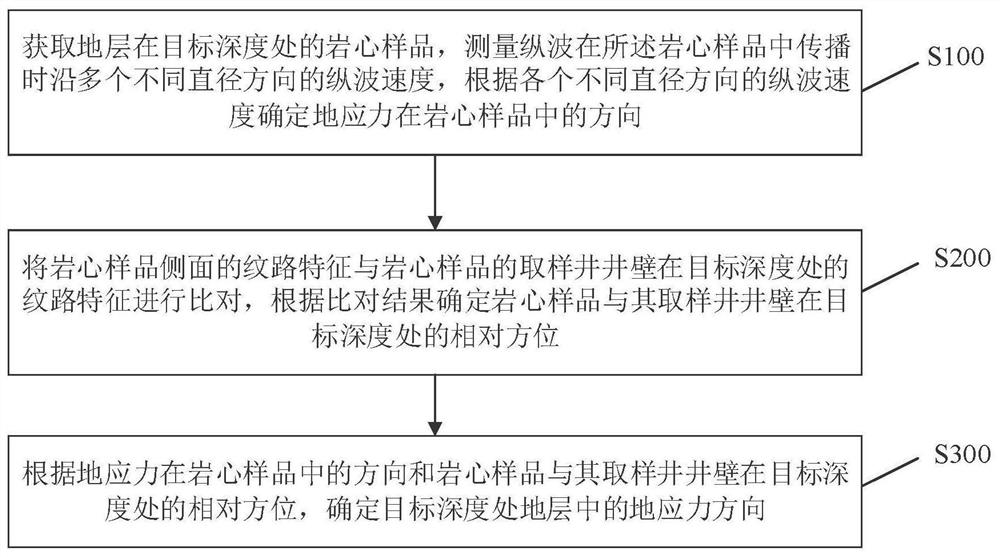
[0028] figure 1 It is a flowchart of a method for determining the direction of ground stress according to an exemplary embodiment of the present application. Such as figure 1 As shown, the present embodiment provides a method for determining the direction of in-situ stress, comprising the following steps:
[0029] S100: Obtain a core sample of the formation at the target depth, measure the longitudinal wave velocity along multiple different diameter directions when the longitudinal wave propagates in the core sample, and determine the direction of the in-situ stress in the core sample according to the longitudinal wave velocity in each different diameter direction;
[0030] S200: comparing the texture features on the side of the core sample with the texture features of the core sample's sampling well wall at the target depth, and determining the relative orientation of the core sample and the sampling well wall at the target depth according to the comparison result;
[0031]...
Embodiment 2
[0033] This embodiment provides a method for determining the direction of ground stress, comprising the following steps:
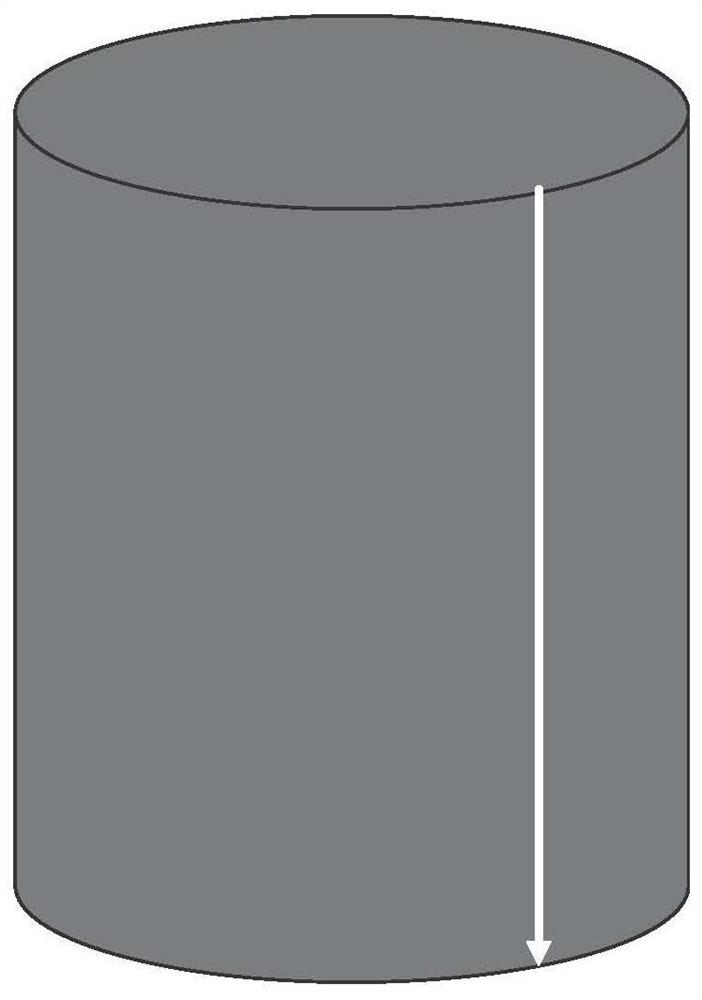
[0034] Step 1: Obtain a rock core sample of the formation at the target depth, and set a reference line parallel to the axial direction of the rock core sample on the side of the rock core sample, wherein the rock core sample is cylindrical, and the rock core sample can be a full-diameter core sample .
[0035] The second step: measure the longitudinal wave velocity along multiple different diameter directions when the longitudinal wave propagates in the rock core sample, and determine the direction of the in-situ stress in the rock core sample according to the longitudinal wave velocity in each different diameter direction. Specifically, the in-situ stress in the rock core sample can be determined. The direction in is relative to the central angle of the reference line, and the central angle is used to describe the direction of the geostress in the core s...
Embodiment 3
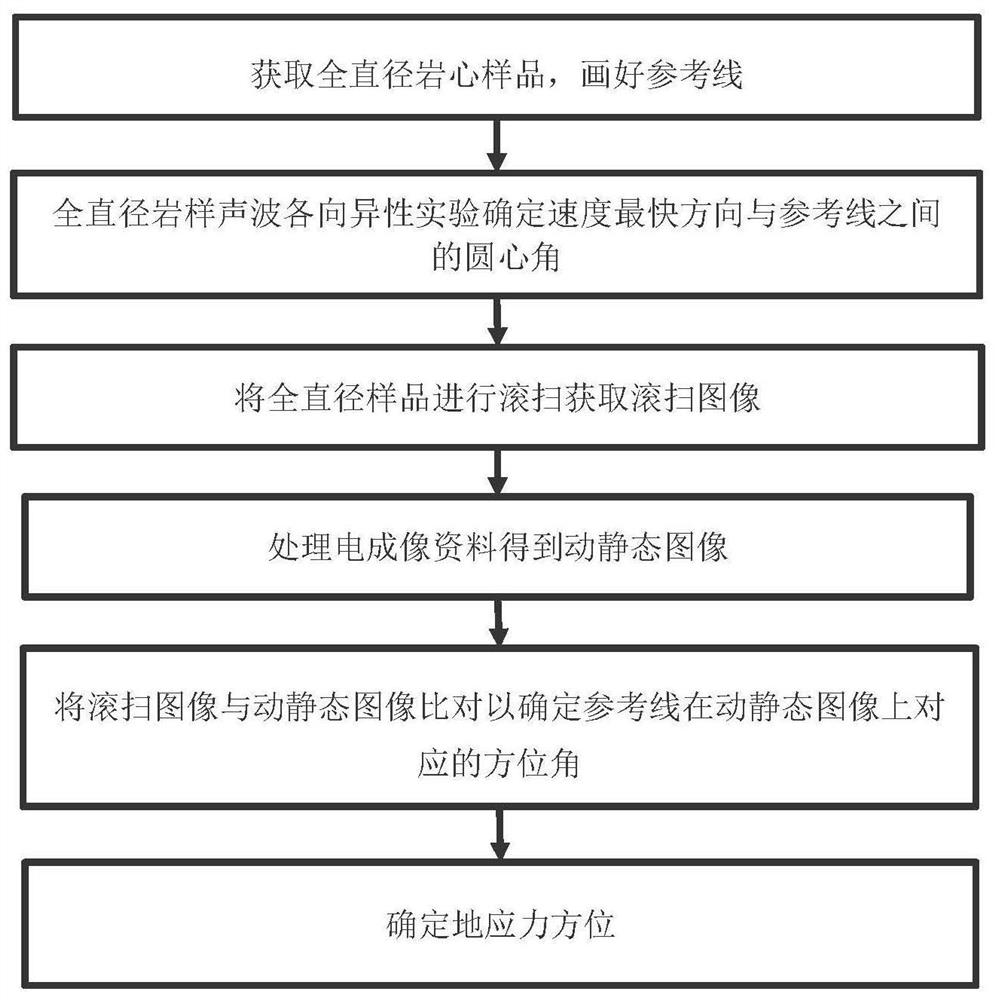
[0043] figure 2 It is a flowchart of a method for determining the direction of ground stress according to a specific embodiment of the present application. Such as figure 2 As shown, the method for determining the direction of in-situ stress includes the following steps:
[0044] S1: Obtain the full-diameter rock core sample of the formation at the target depth. The full-diameter rock core sample is cylindrical, and a reference line parallel to the axial direction of the full-diameter rock core sample is set on the side of the full-diameter rock core sample (such as Figure 3A with Figure 3B shown). in, Figure 3B The number mark in is the mark made by the mud logger after the core sample is taken out from the ground. The number in front of the fractional line indicates the number of cylinders, the denominator indicates how many core samples there are in total in the cylinder, and the numerator indicates the number of core samples in the current cylinder. Piece. Figu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com