Patents
Literature
901 results about "Assise" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
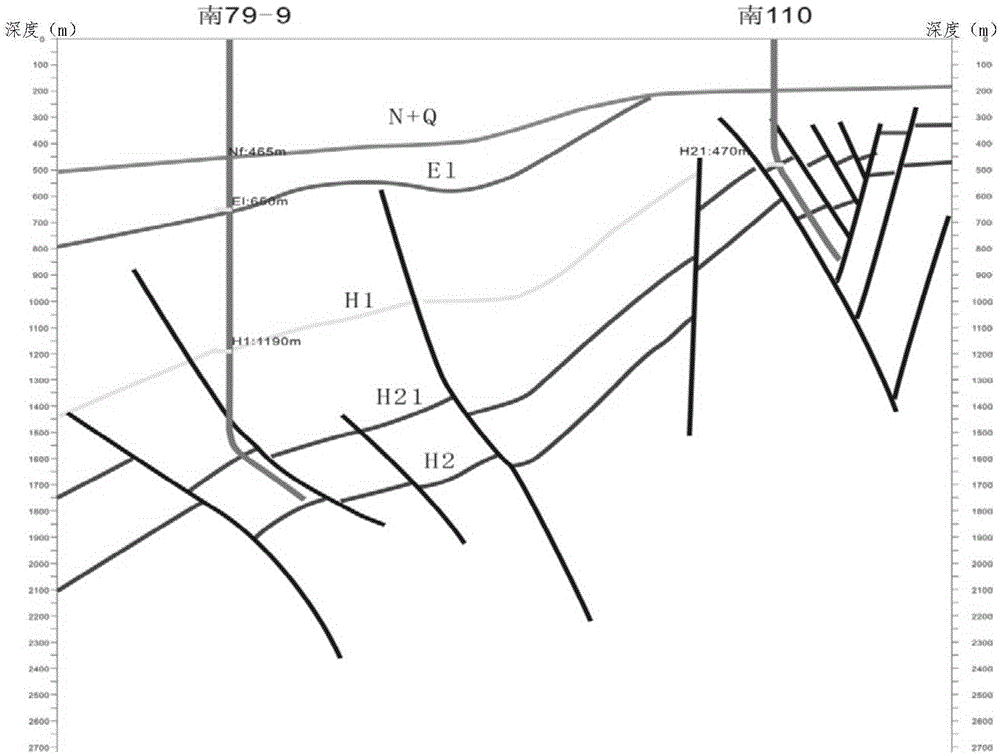
An assise (from the Fr., derived from Latin assidere, "to sit beside"), is a geological term for two or more beds or strata of rock united by the occurrence of the same characteristic species or genera. In the hierarchy of stratigraphic units, an assise lies between a stage (or sub-stage) and a stratum.
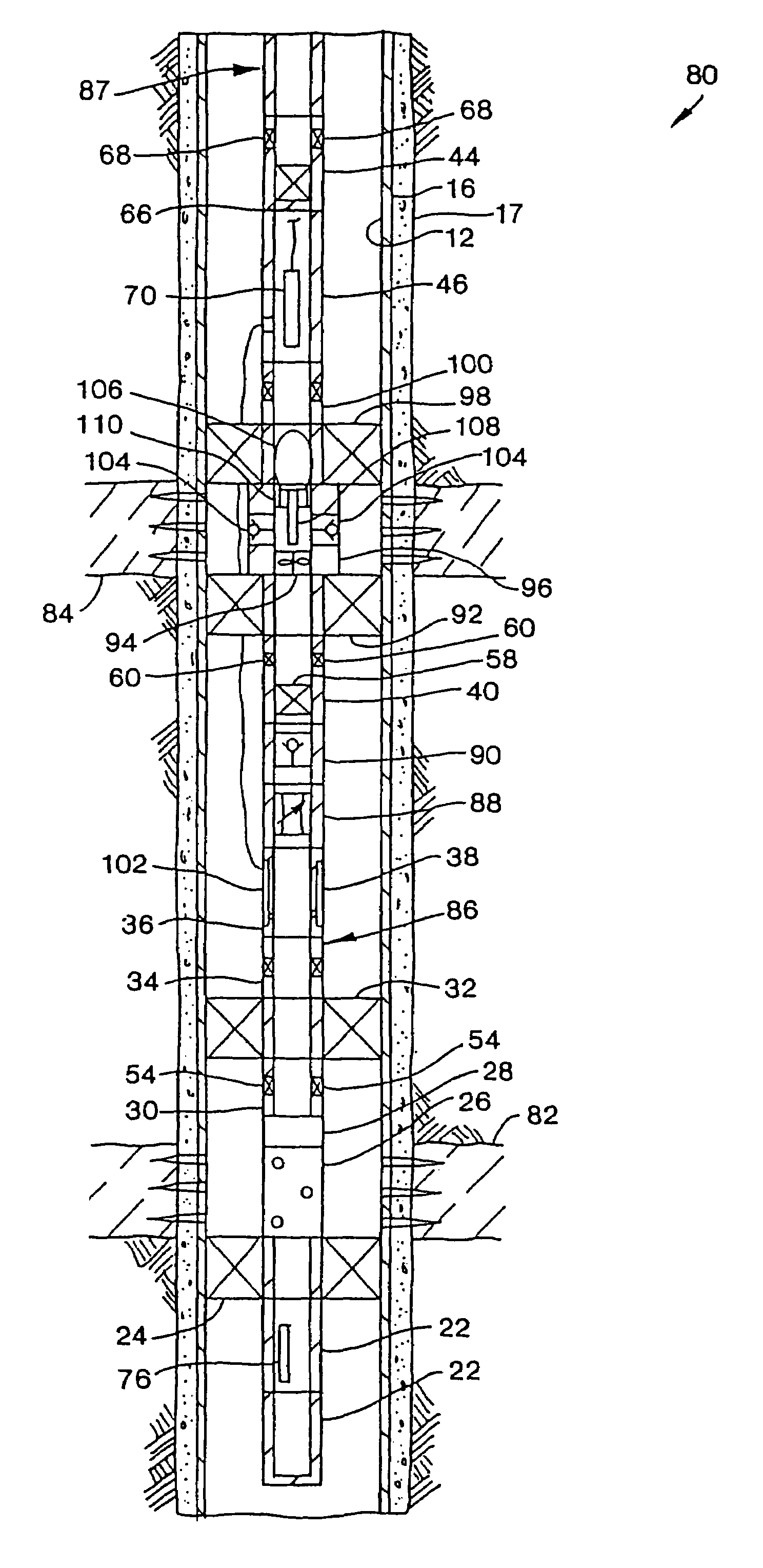
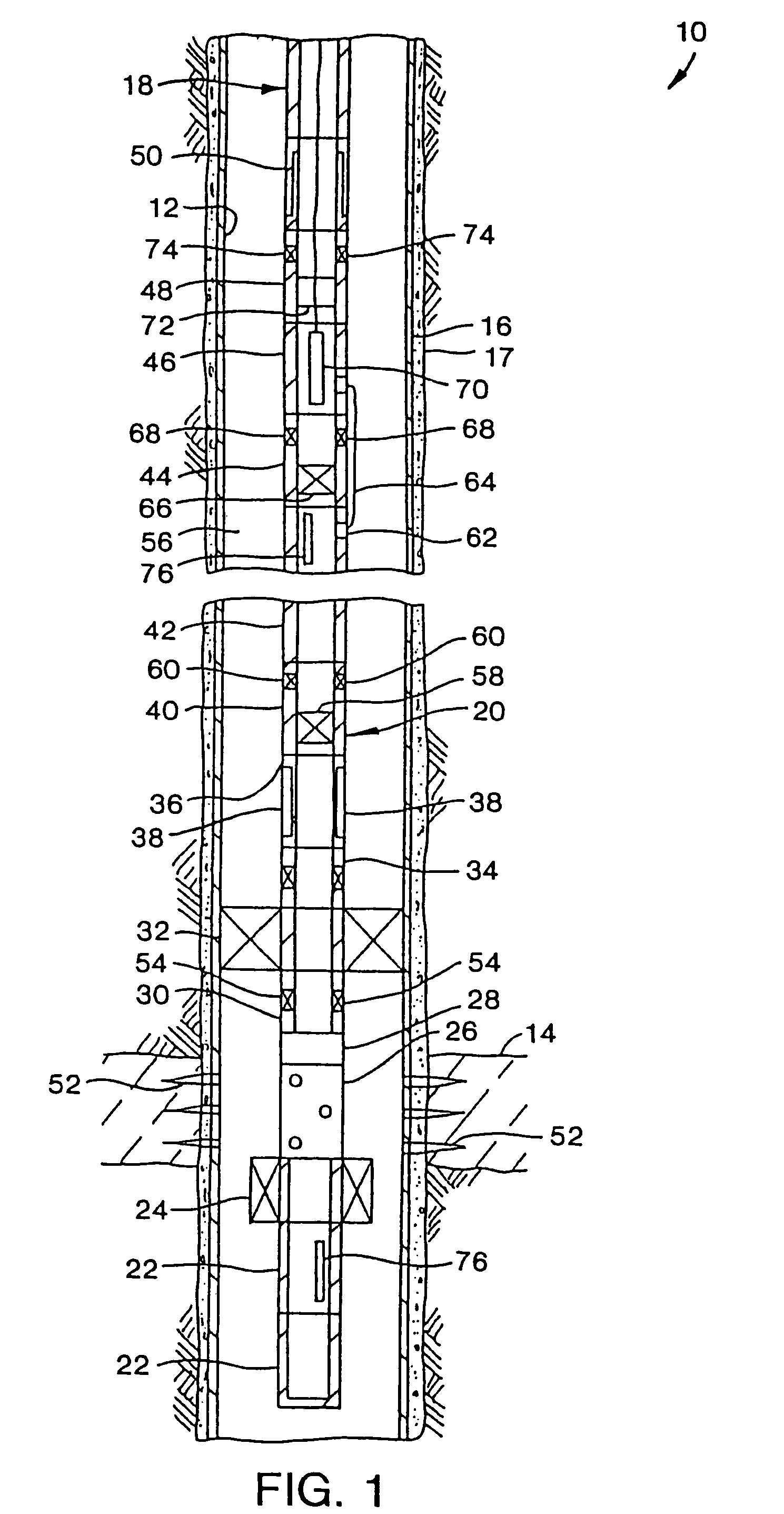
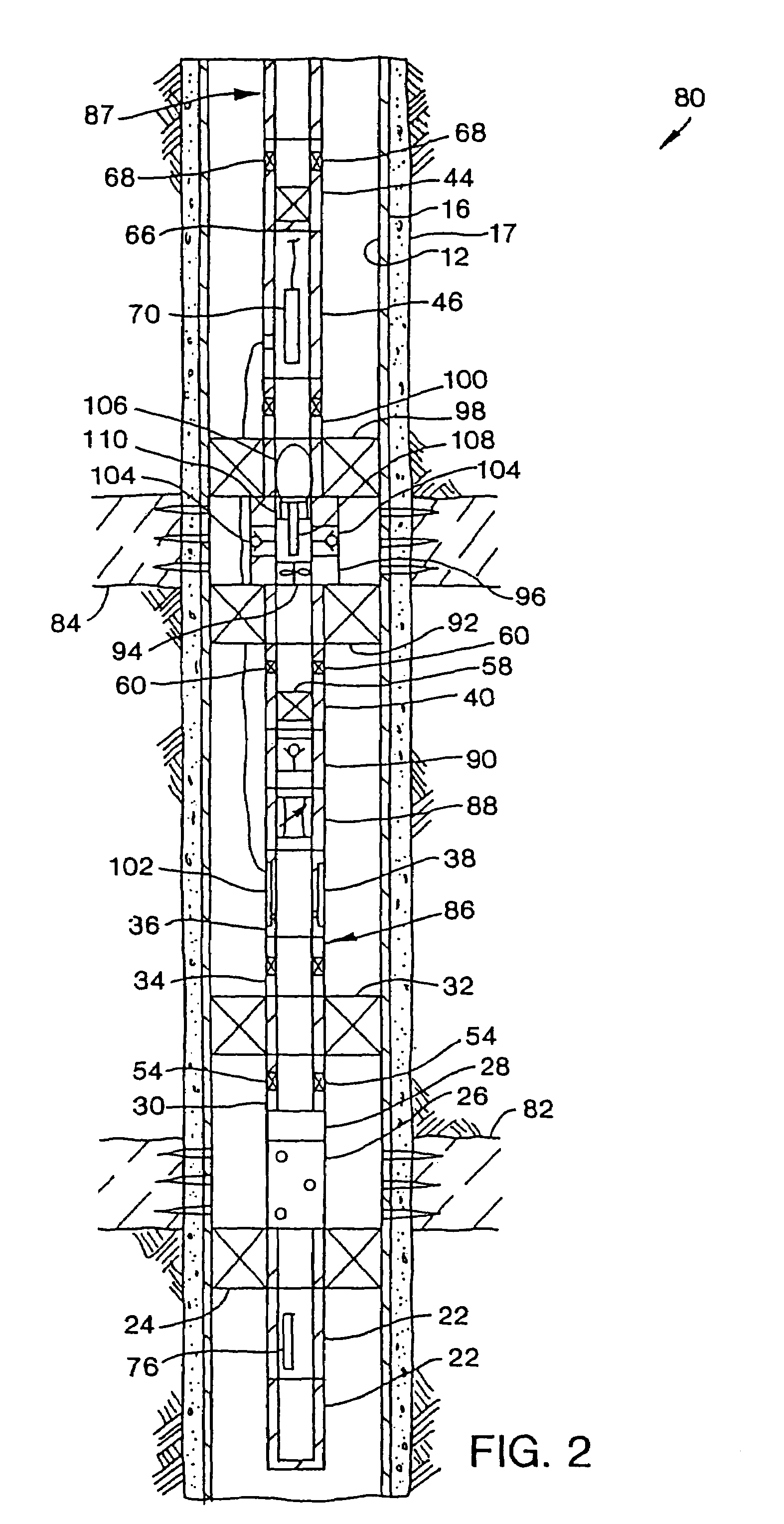
Time release multisource marker and method of deployment
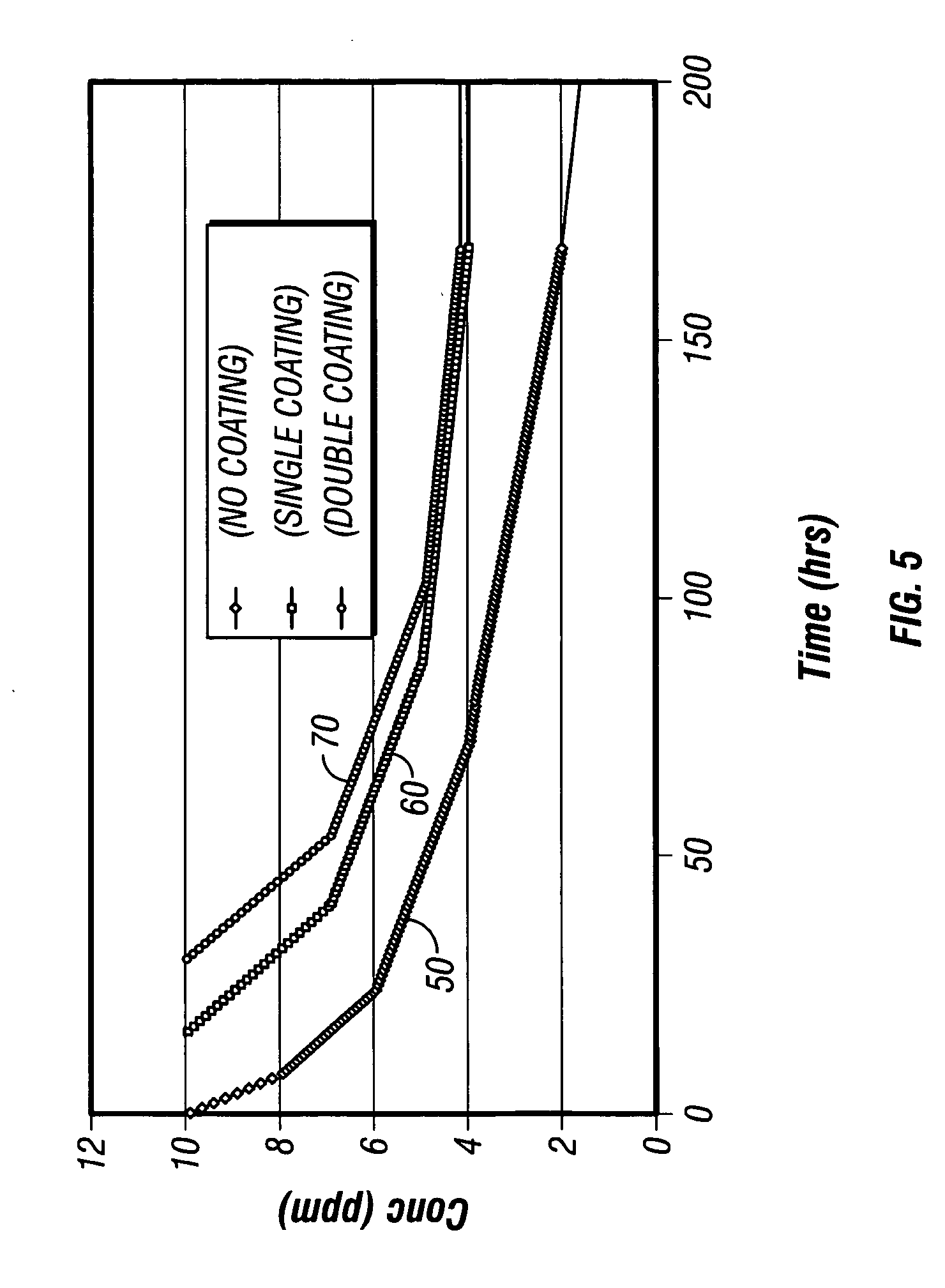
InactiveUS20060052251A1Delay releaseImprove practicalityConstructionsDrilling compositionSoil scienceMarking out
The present invention provides time released markers for use with single reservoir and commingled wells. The invention accomplishes the time release of markers by coating or encapsulating marker particles or by coating a proppant which has been saturated with a marker. After coating or encapsulation, the marker is injected into a well as is known in the art. The marker remains in the well. The marker is released after an elapsed of time. The elapsed time can be in a wide range. After the elapsed time, production is taken from the well and tested for the presence of the marker. Various types of known analyses can be performed to test for the presence and concentration of the marker in the production fluid. The concentration of the marker in the production fluid allows the apportioning of production from the reservoir. In addition, different markers may be added to each zone within a reservoir where each marker has a different elapsed time increment. The zones can be any different layer or area in the reservoir such as different strata or layer of rock, limestone or sand. Differing marker combinations allow contribution from different zones to be monitored over an extended time.
Owner:CORE LAB LP
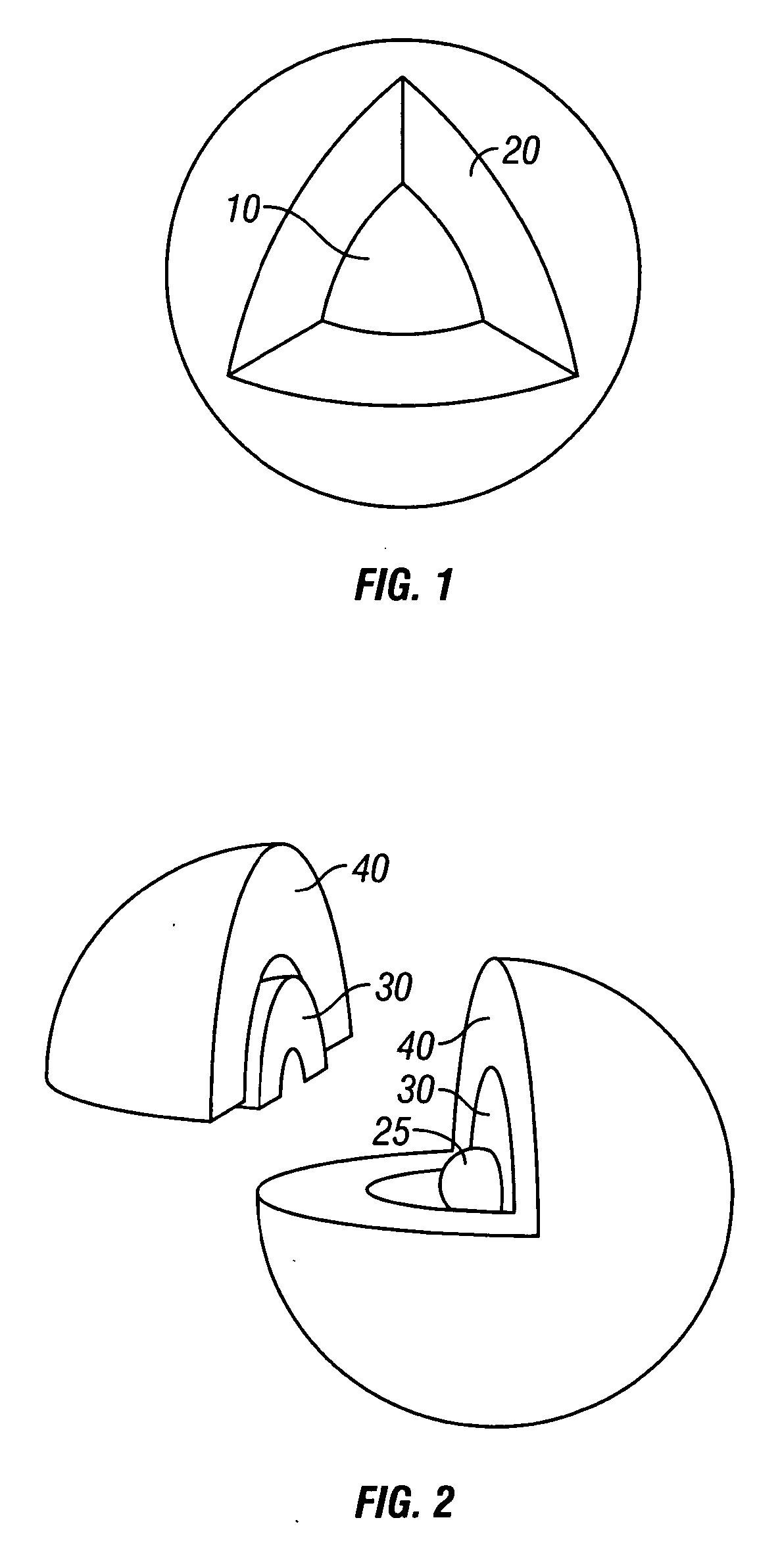
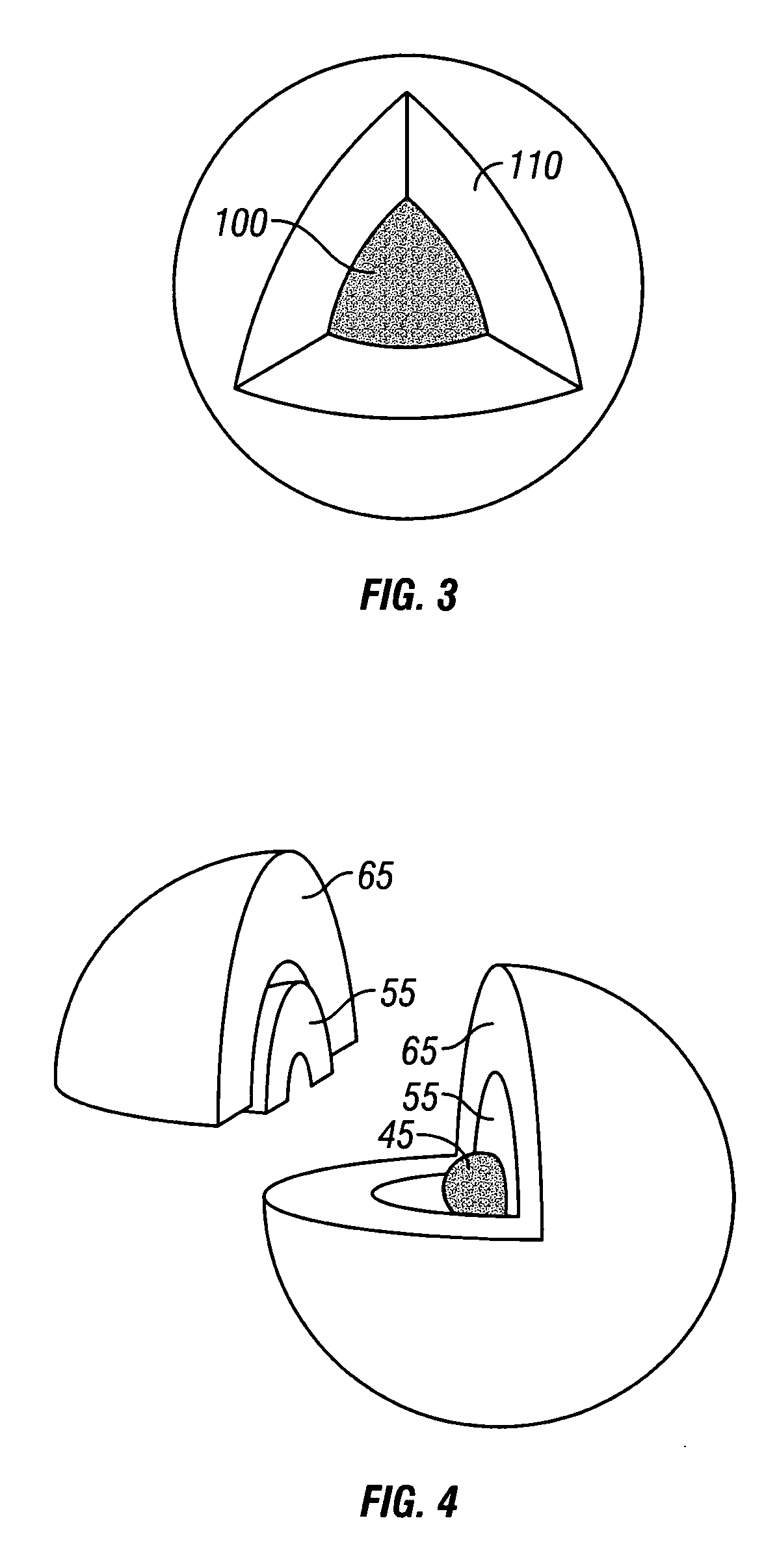
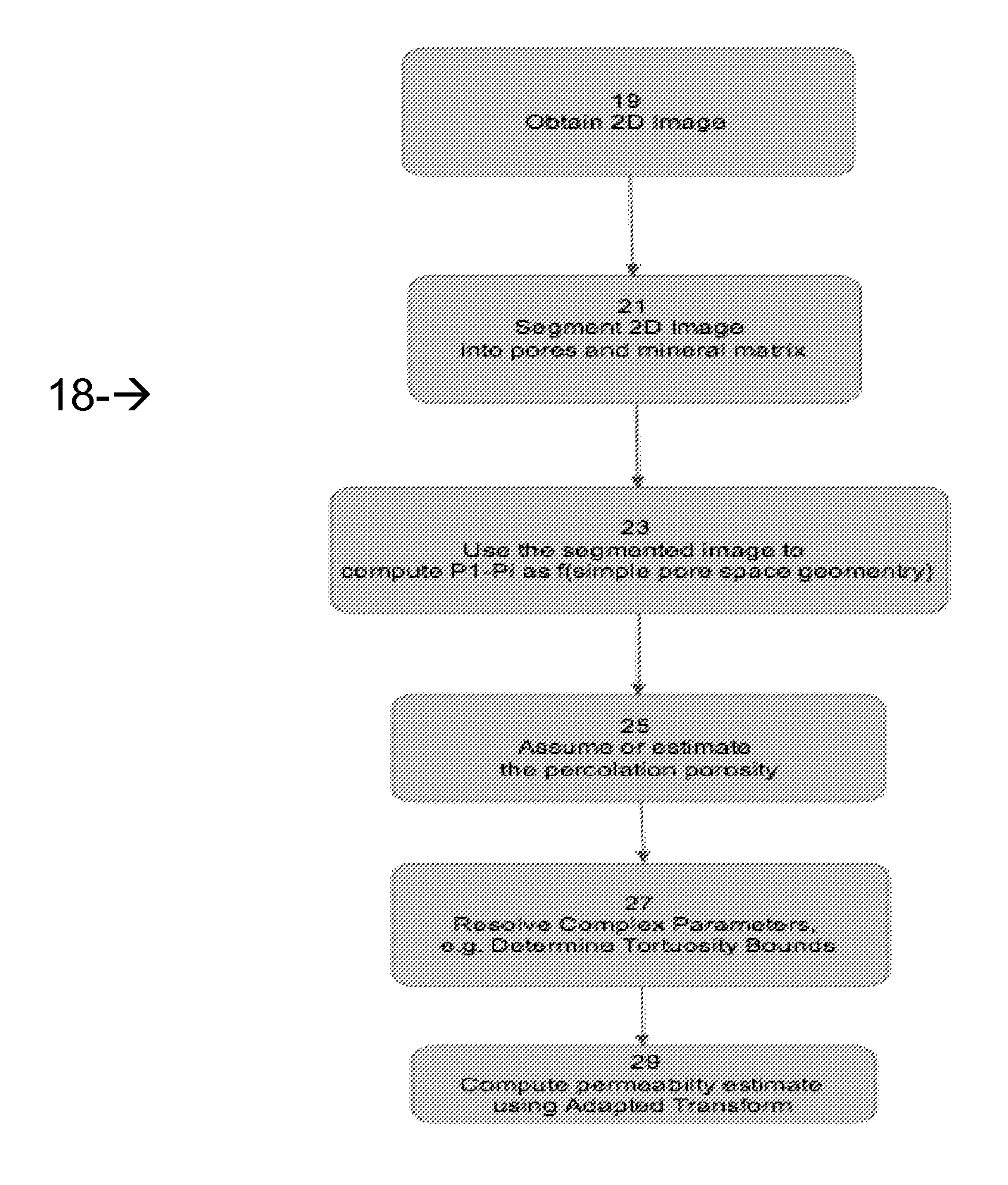
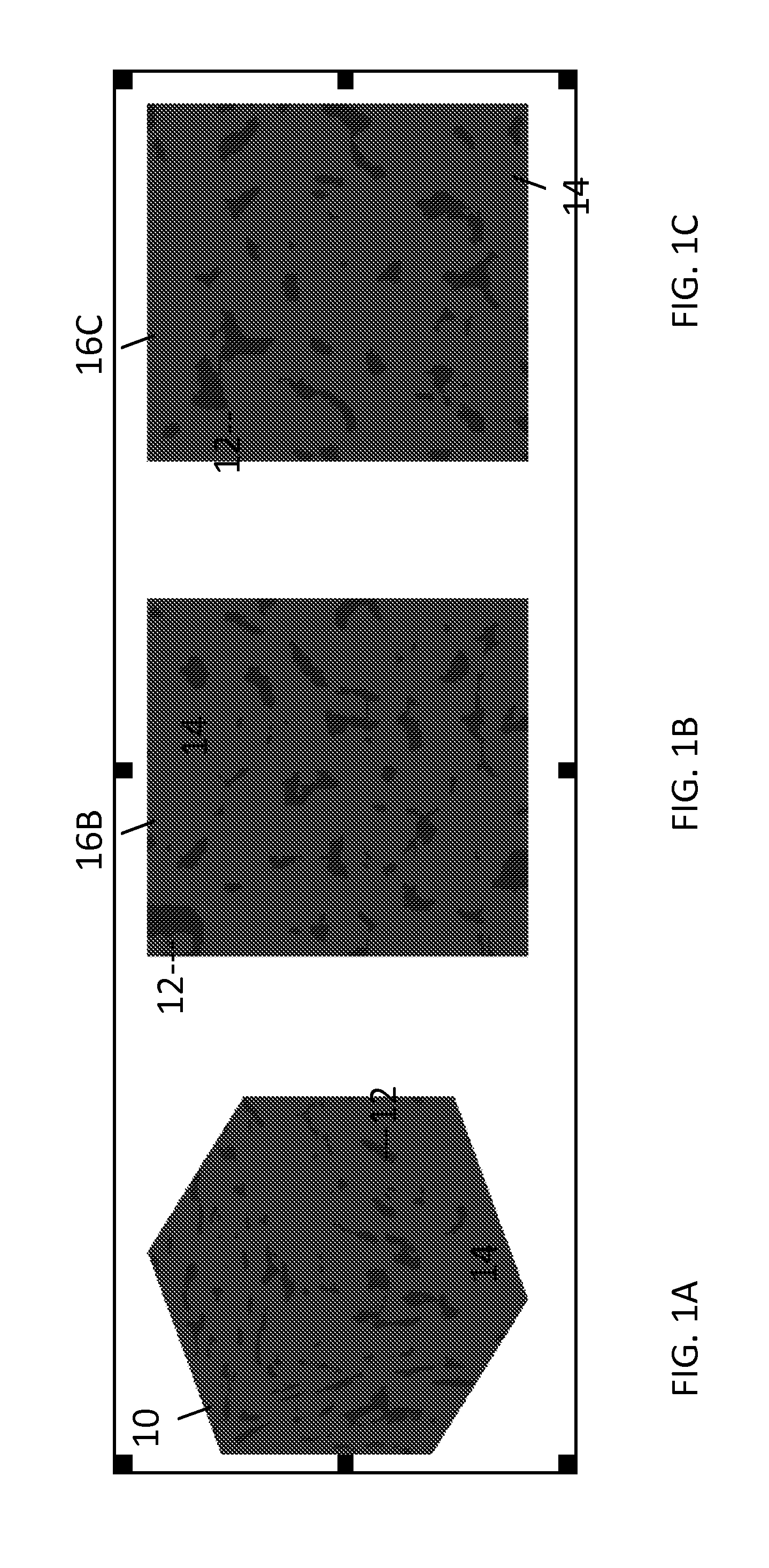
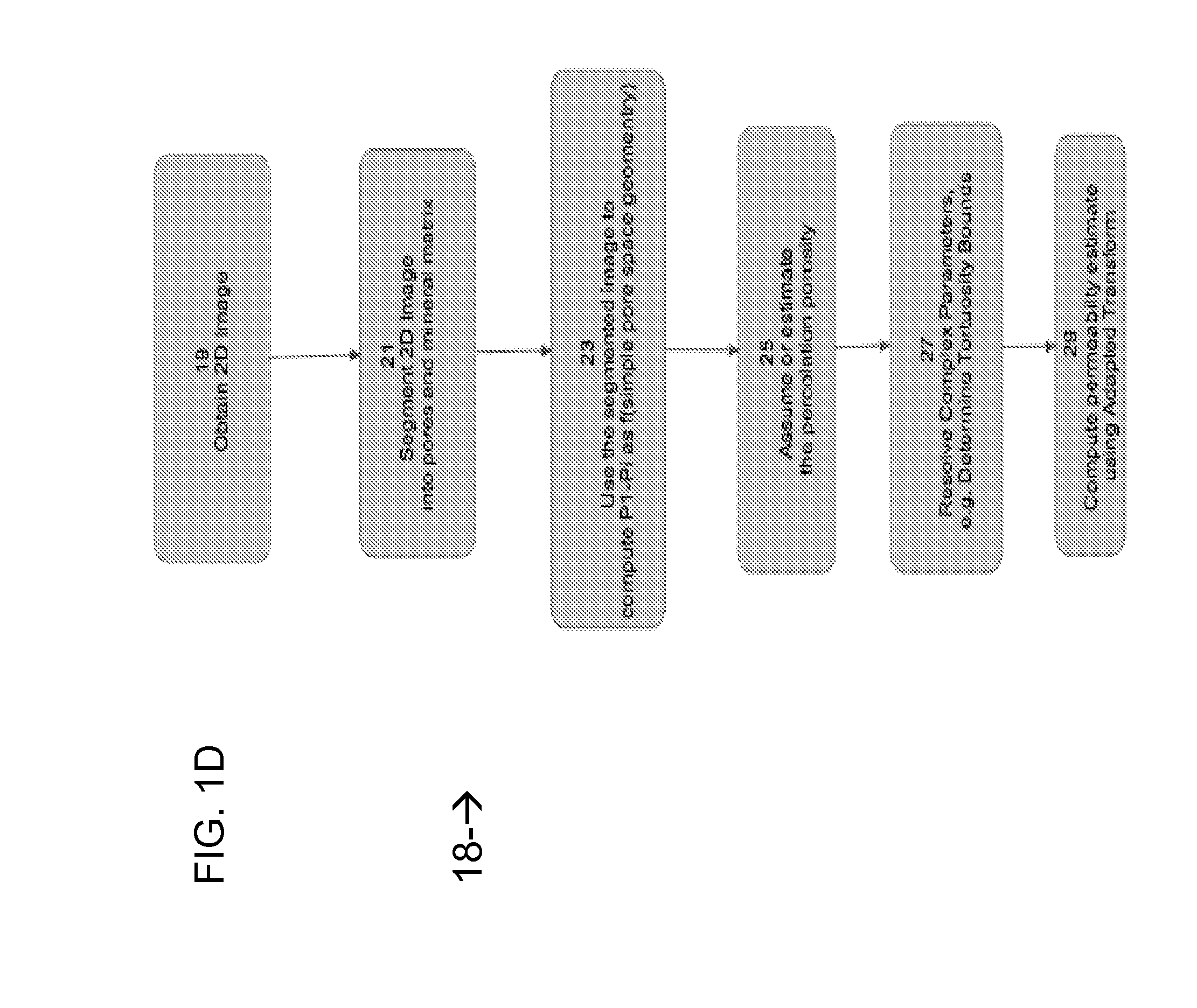
Method And System For Estimating Rock Properties From Rock Samples Using Digital Rock Physics Imaging
ActiveUS20130308831A1Effectively characterizeEfficiently estimating absolute permeability kSurveyImage analysisCapillary pressureGeophysics
A method is provided for efficiently characterizing rock traversed while drilling a borehole for hydrocarbon reservoir development. A rock sample can be obtained having a provenance of collection linked to a specific region of the borehole, which is scanned to obtain a 2D digital image that is segmented to pixels characterized as pore space and as mineral matrix and defining a boundary between them. A transform relationship, for example, a form of the Kozeny-Carman equation adapted for application to a 2D segmented image environment, can be applied to calculate the estimated value for a target rock property, which can be absolute permeability, relative permeability, formation factor, elasticity, bulk modulus, shear modulus, compressional velocity, shear velocity, electrical resistivity, or capillary pressure, and the estimated value is used to characterize the rock at that region of the borehole. This affords an opportunity to quickly and efficiently develop massive data directly characterizing extended regions of rock, whether traversed by the borehole in this or a related well. Computerized systems, computer readable media, and programs for performing the methods are also provided.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
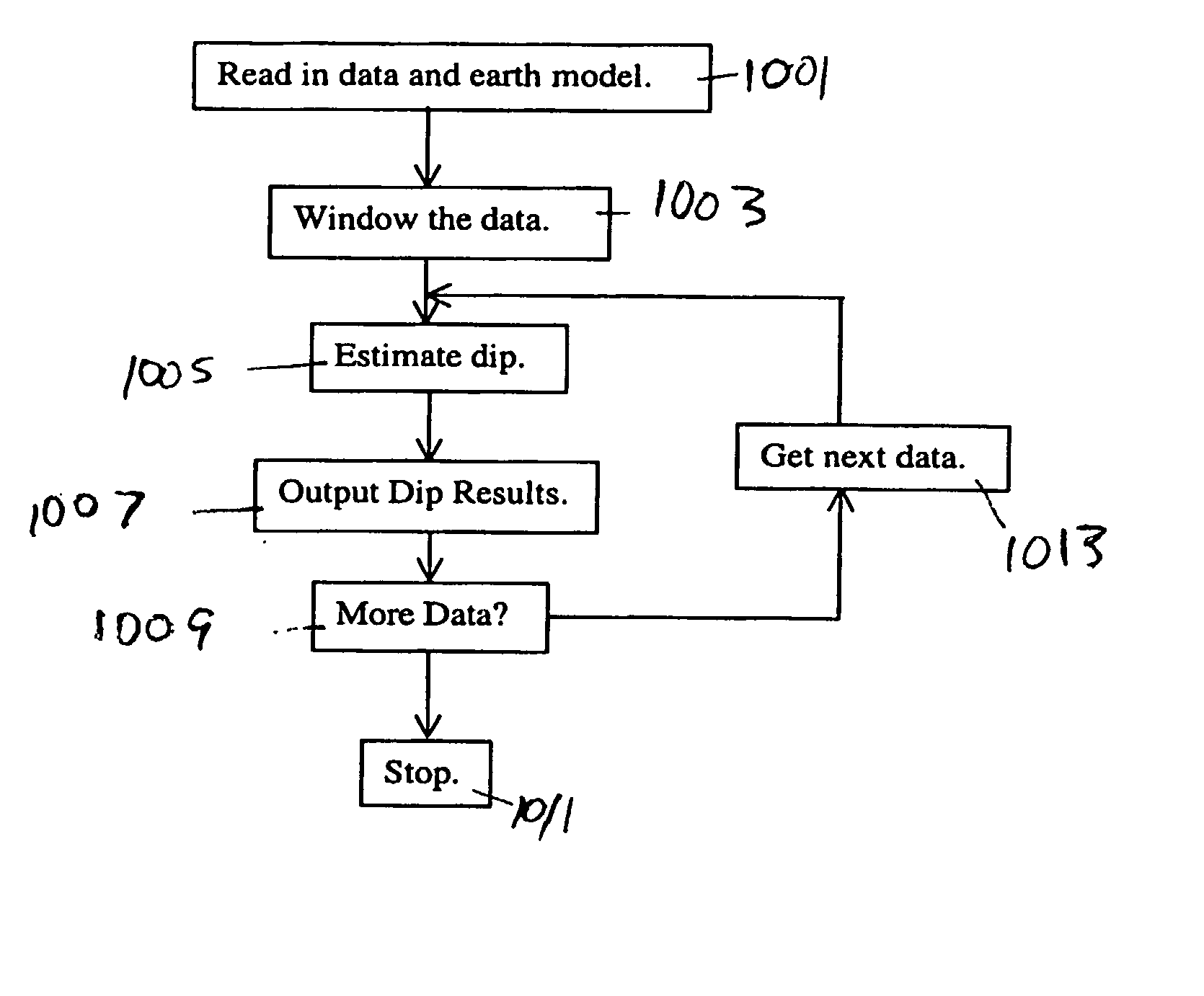
Method for joint interpretation of multi-array induction and multi-component induction measurements with joint dip angle estimation
InactiveUS20030028324A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismic signal processingCorrelation coefficientClassical mechanics
Data are acquired using multi-array logging tool in a borehole having an angle of inclination to a normal to the bedding plane of earth formations. The multi-array measurements are filtered using angle dependent filters to give a filtered curve corresponding to a target one of the multi-array measurements using angle dependent filters. Correlation coefficients are determined for a set of possible dip angles and a relative dip angle is estimated from the correlation coefficients. This dip angle estimate together with bed boundaries obtained from the multi-array measurements are used for inverting multi-component measurements alone or jointly with multi-array measurements to refine the relative dip angle interpretation and give horizontal and vertical formation resistivity.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Calibration method for representing dense sandstone pore size distribution by adopting nuclear magnetic resonance
InactiveCN104634718AMake up for the errorMake up for accuracyPermeability/surface area analysisNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceLarge pore
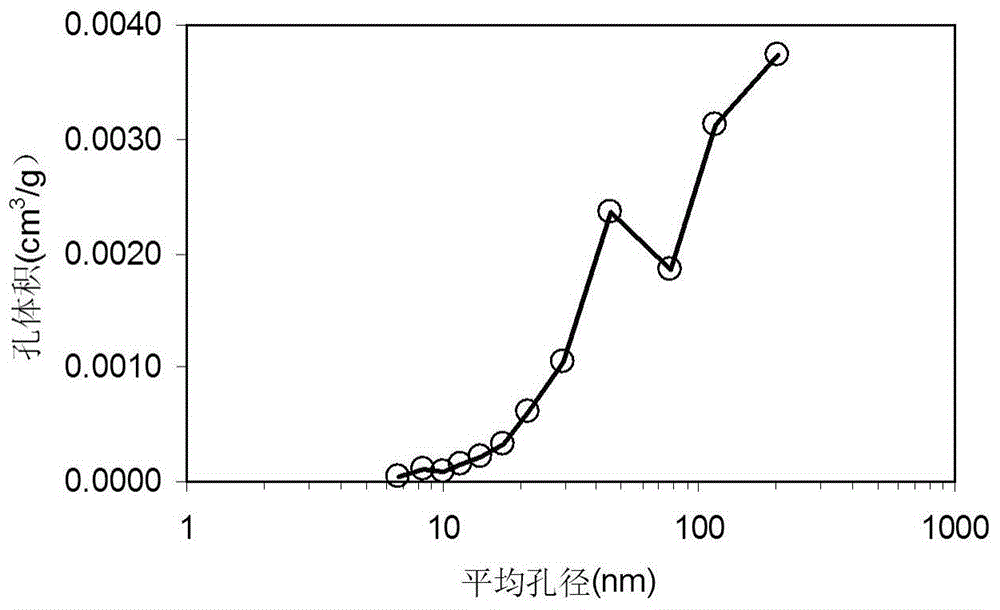
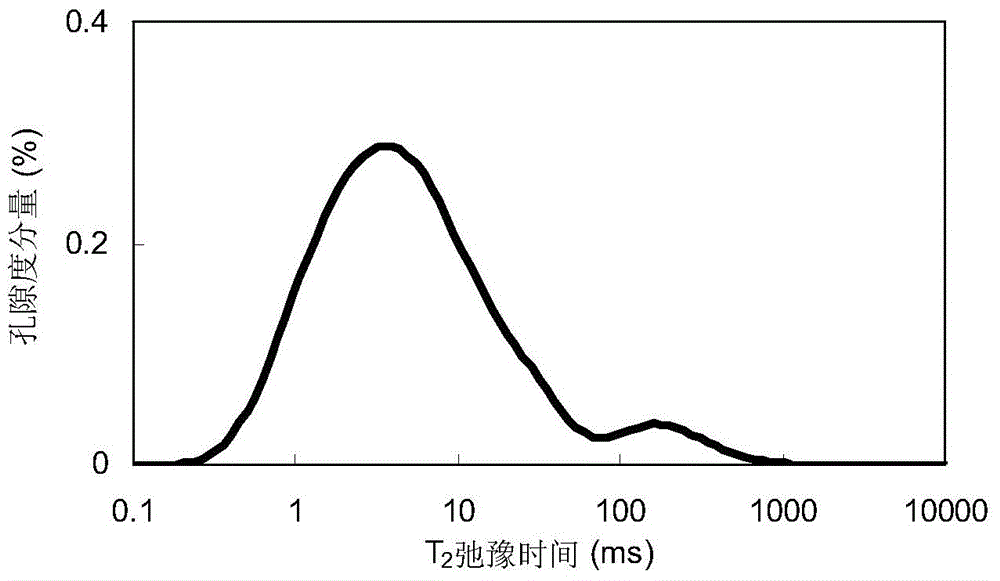
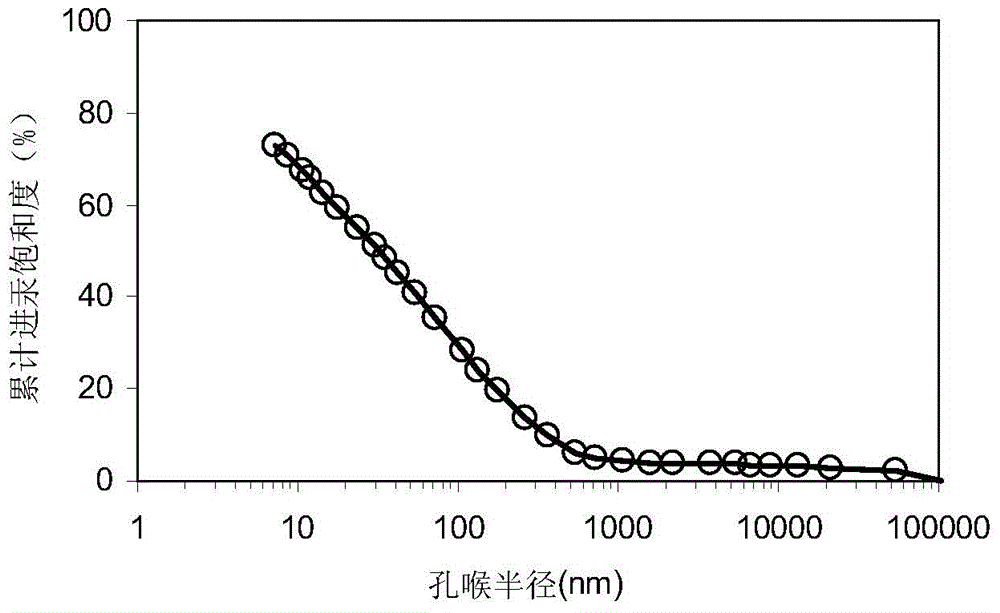
The invention relates to a calibration method for representing dense sandstone pore size distribution by adopting nuclear magnetic resonance; the method comprises the steps of measuring the rock porosity and the skeleton density; carrying out a low-temperature broken sample N2 absorption and desorption experiment, and carrying out a nuclear magnetic resonance test and a high pressure Hg injection test on a regular column sample in a saturated formation water state; converting pore volume obtained through N2 absorption into porosity components under different pore throat radiuses by using a capillary accumulated Hg inlet curve, and establishing a pore proportion summation curve by synthesizing low temperature N2-high pressure Hg injection; determining a best calibration coefficient by comparing the nuclear magnetic resonance pore proportion summation curves under the different C values to realize the conversion between nuclear magnetic resonance T2 spectrum and the pore throat radius; establishing a relation between parameters of the calibration coefficient C and a reflection pore-throat structure according to lithological characters; carrying out nuclear magnetic resonance conversion on dense sandstone reservoirs which are positioned in the same region and have the same lithological character. According to the method, the nuclear magnetic resonance T2 spectrum is calibrated by combining low temperature N2 absorption and a high pressure Hg injection experiment, and large pores, micropores and mesopores are calibrated, so that the distribution of different grades of pore sizes in dense sandstone can be effectively represented.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Glutenite comprehensive geologic modeling method
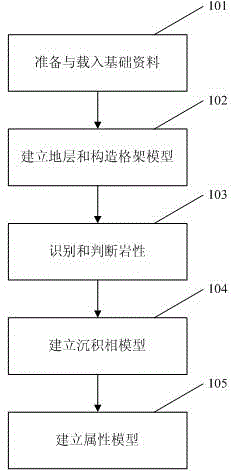
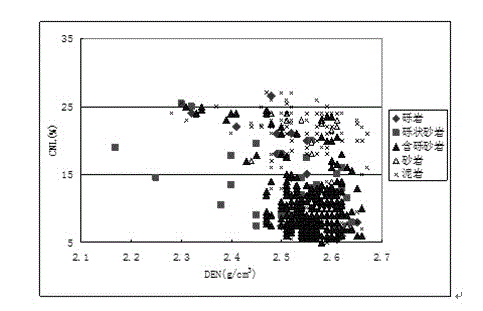
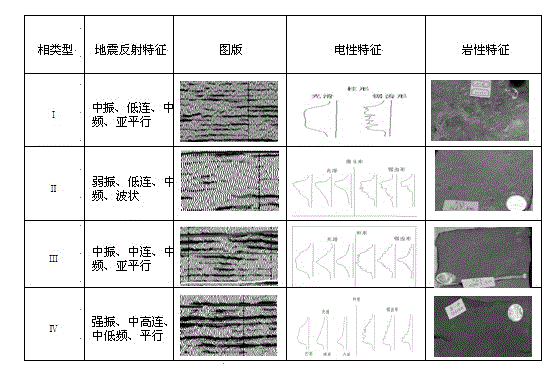
The invention provides a glutenite comprehensive geologic modeling method. The method comprises step1, performing analysis and arrangement on drilling well, earthquake, logging and stratigraphic correlation information to screen geologic model basic data; step2, building a stratum and tectonic framework model through single-well fine stratigraphic correlation, fine earthquake explanation and fine inter-bed and fracture system description; step3, recognizing and determining lithologic characteristics; step4, building a sedimentary facies model; step5, building an attribute model through a pore penetration model. By the aid of the method, the lithology identification accuracy is improved, and rapid division of the sedimentary facies is achieved through man-machine interaction.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Tight sandstone gas reservoir fracturing fluid damage experimental evaluation method
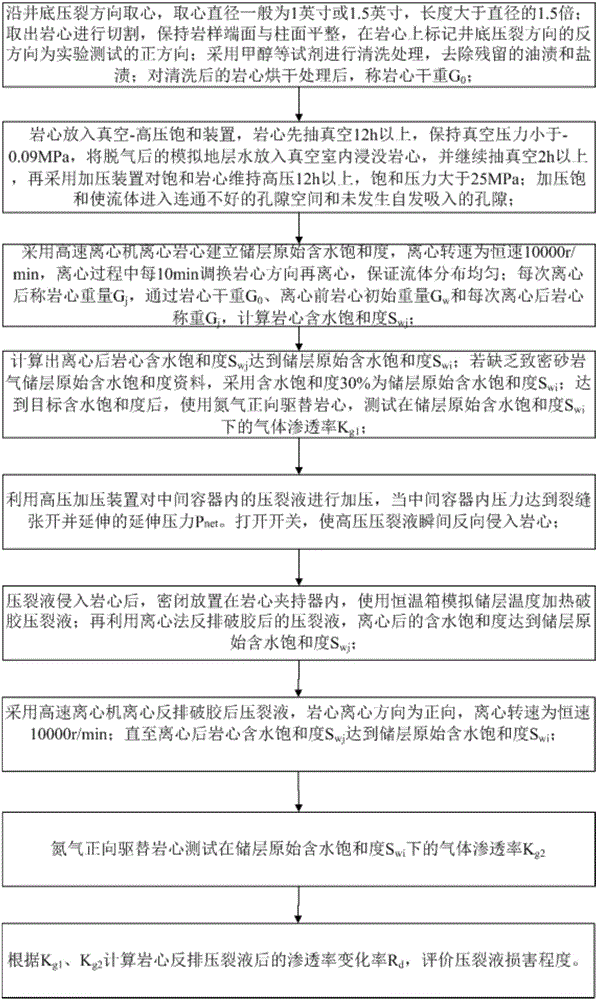
InactiveCN106153518AConforms to seepage characteristicsExperimental test pressure is smallPermeability/surface area analysisWeighing by absorbing componentRock coreFracturing fluid
The invention belongs to the field of oil-gas field development and relates to an experimental evaluation method for fracturing fluid damage in an unconventional tight sandstone oil-gas exploration and development process. The method includes: subjecting fracturing fluid to high-pressure instant reverse injection into a rock core, and simulating flow invasion damages of fracturing fluid in cracks in a continuous extension process after a stratum is fractured by the fracturing fluid; adopting a high-speed centrifuge to set up original water saturation of a reservoir; under the condition of the original water saturation of the reservoir, adopting nitrogen for testing permeability before and after injection of the fracturing fluid into the rock core, and judging fracturing fluid damage degrees according to gas log permeability change rate. By complete simulation of a fracturing fluid injection mode in a fracturing process, adoption of nitrogen for testing permeability accords with seepage characteristics of the tight sandstone gas reservoir, and defects of high experimental displacement pressure, long displacement time, large experimental data errors and the like are avoided.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
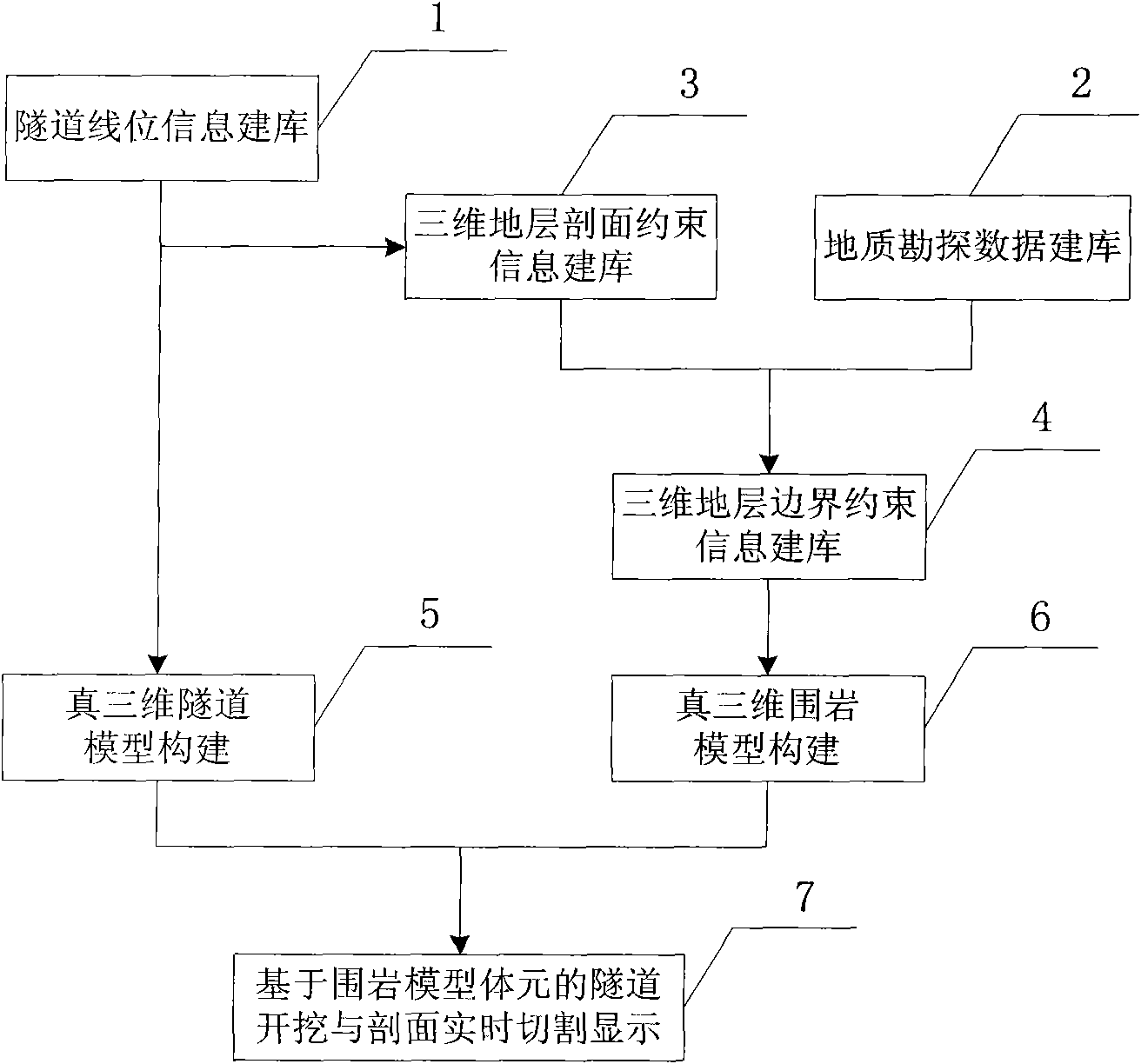
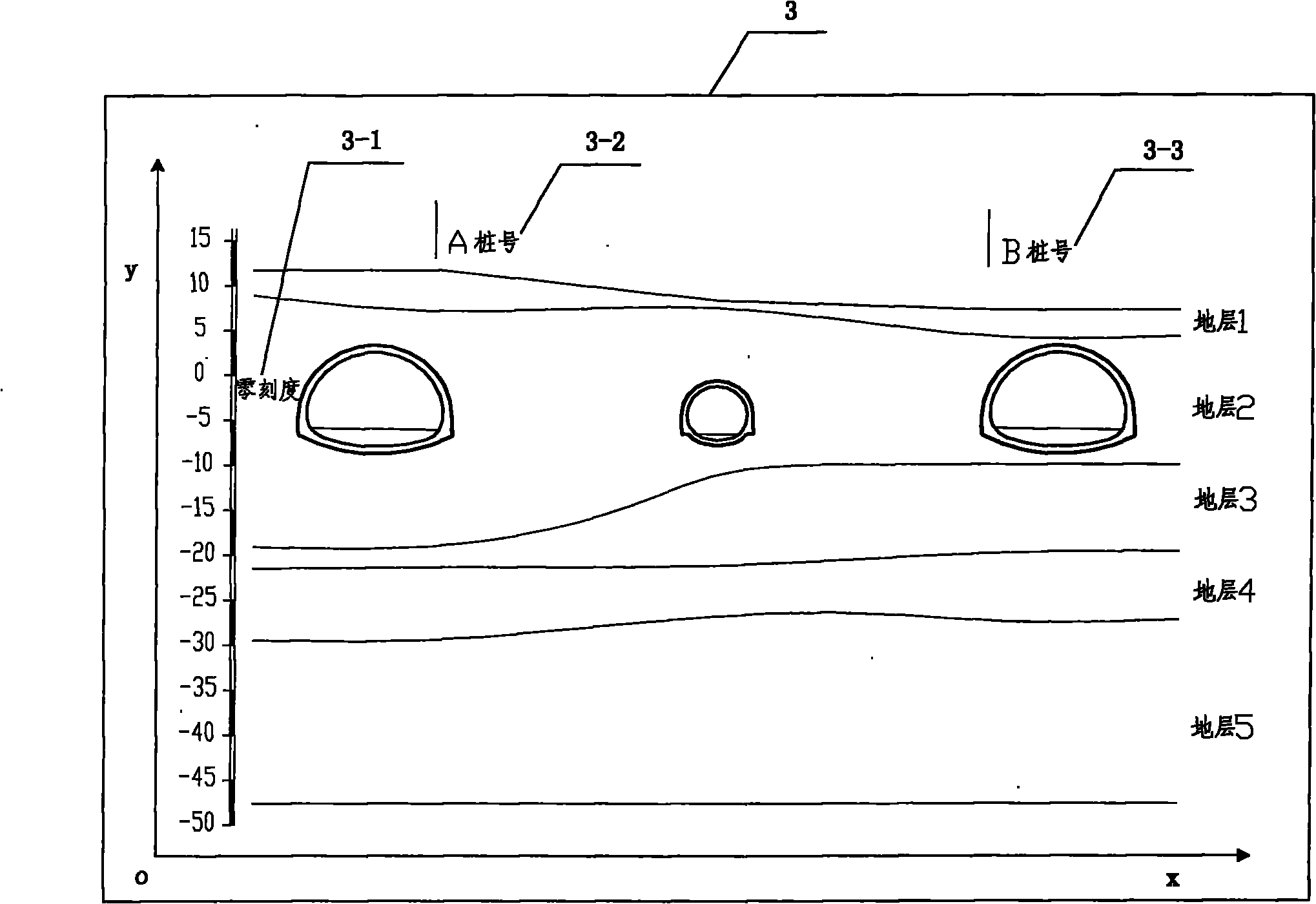
Method for fast establishing interactive tunnel and wall rock body three-dimensional models
ActiveCN101882171AFast refactoringOvercome time-consuming remodelingTunnelsSpecial data processing applicationsInformation repositoryClassical mechanics
The invention discloses a method for fast establishing interactive tunnel and wall rock body three-dimensional models, which comprises the following steps: A. tunnel line position information base establishment: collecting tunnel line position information and establishing a line position information base; B. geological exploration base establishment: carrying out standardized processing on hole drilling data obtained through geological exploration; C. three-dimensional stratigraphical profile constraint information base establishment: collecting three-dimensional stratigraphical profile constraint information; D. three-dimensional stratigraphical boundary constraint information base establishment: collecting self defined model establishing boundary; E. real three-dimensional tunnel model establishment: precisely establishing a tunnel three-dimensional model according to the information of tunnel line positions, the tunnel hole body outer cross section and the inner cross section; F. real three-dimensional wall rock model establishment: establishing a wall rock model according to the hole drilling and stratigraphical information; and G. tunnel digging and profile real-time cutting display based on the wall rack model body unit. The model establishing efficiency and precision of the tunnel simulation and digitalized design can be improved, the real-time cutting display of the tunnel passing through the wall rock and any vertical profile can be realized, and the fast reestablishment of the model can be realized.
Owner:CCCC SECOND HIGHWAY CONSULTANTS CO LTD
Method For Indexing A Subsurface Volume For The Purpose Of Inferring Geologic Information
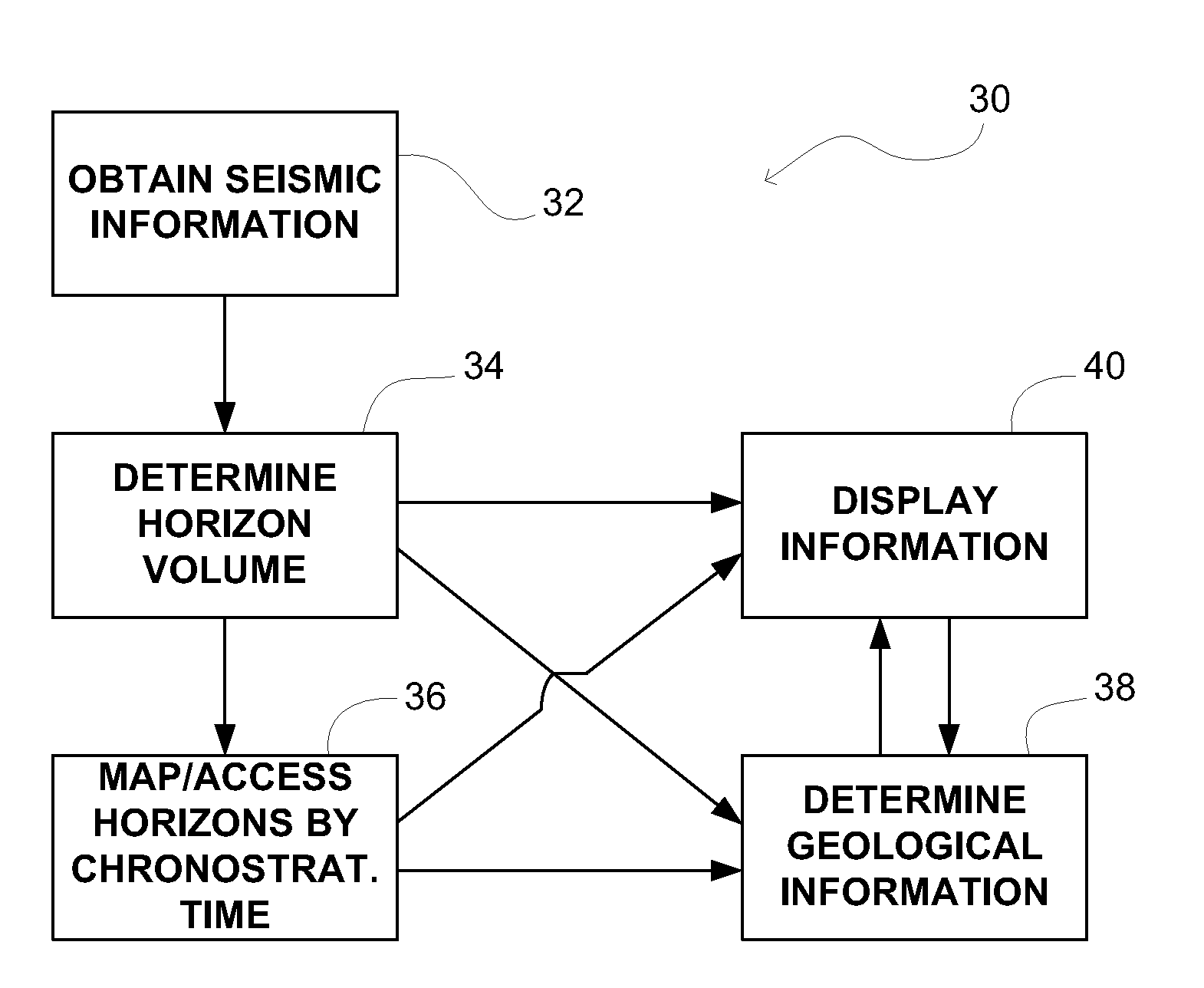
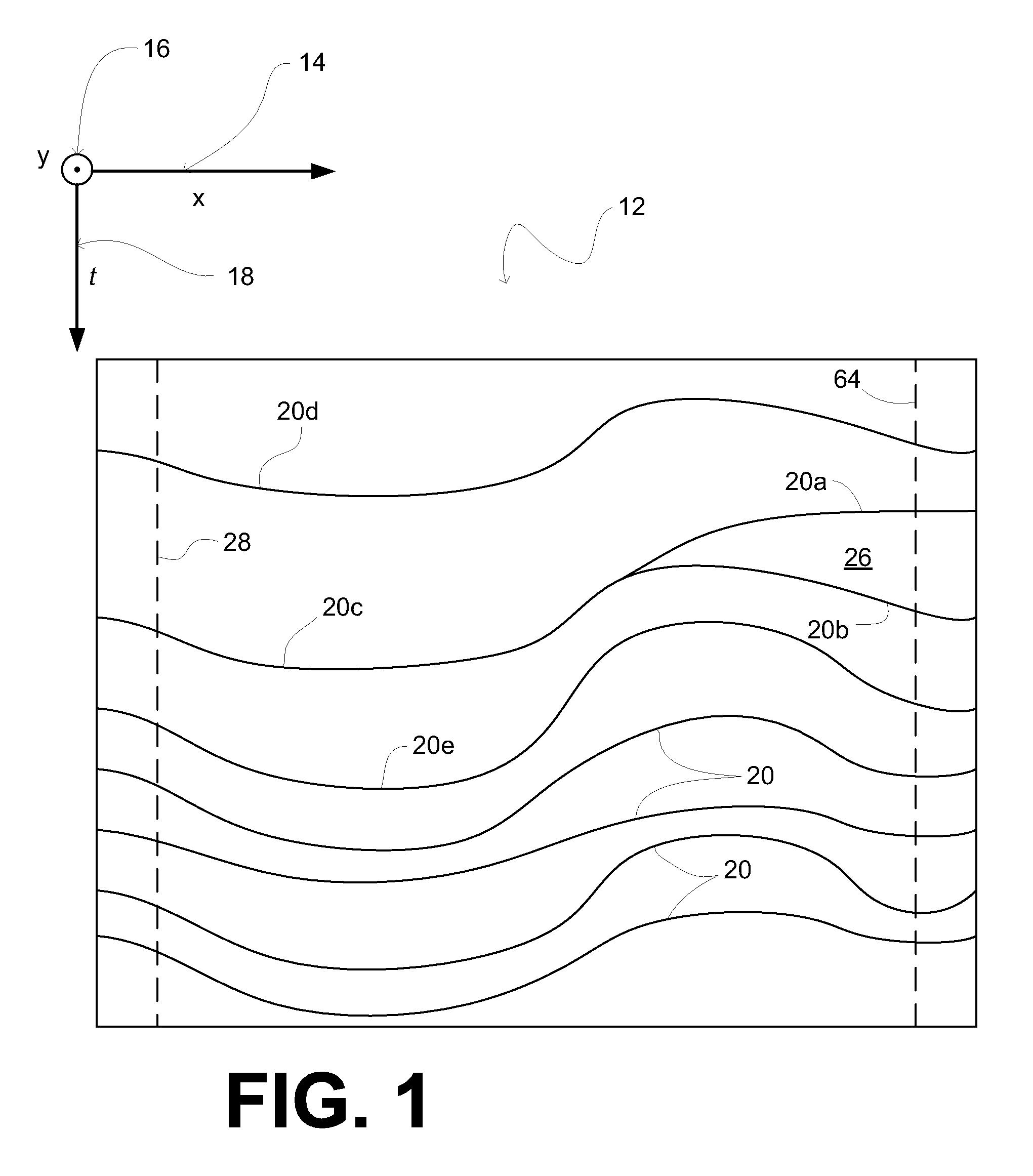
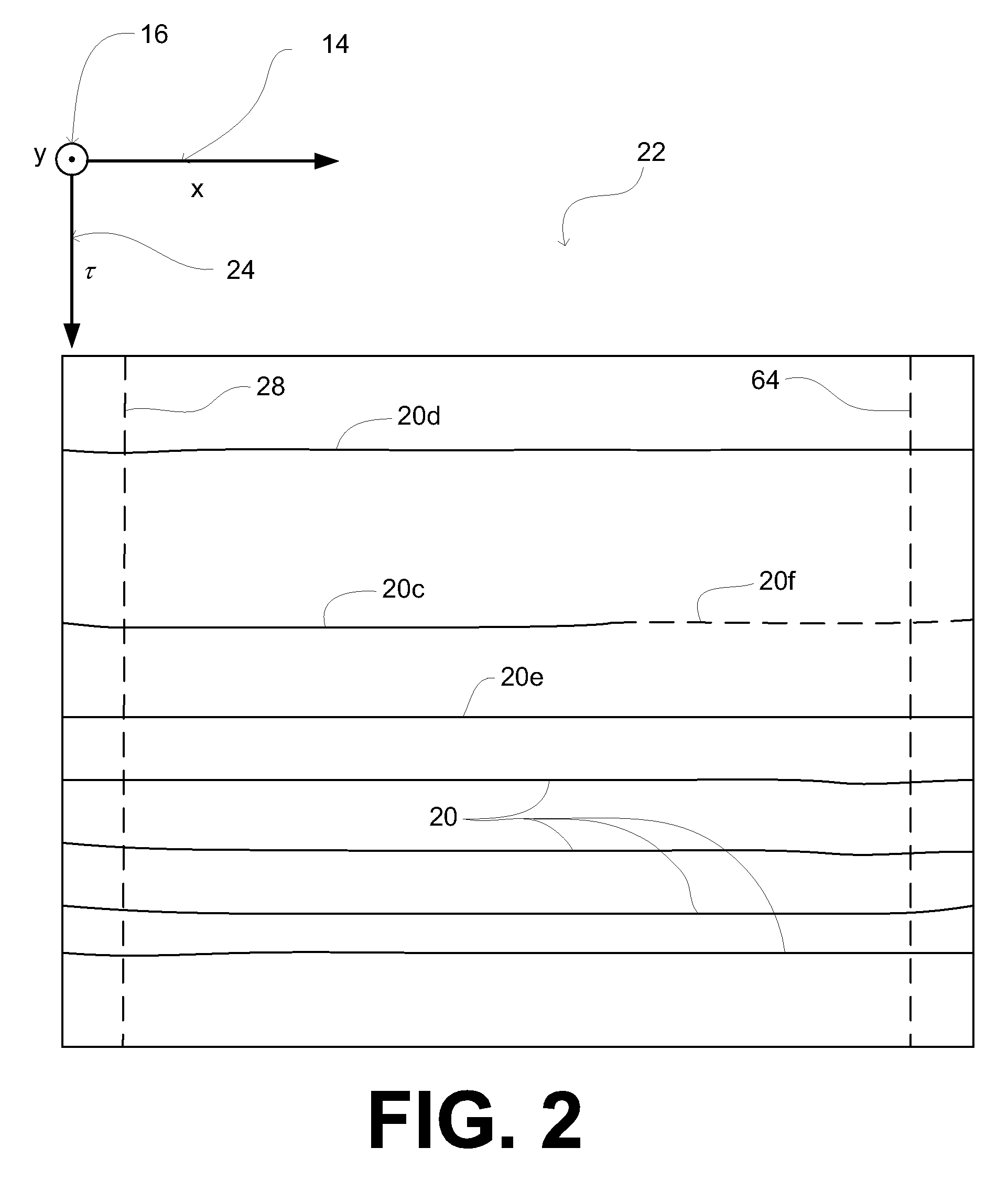
ActiveUS20090204332A1Seismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsHorizonClassical mechanics
A method of determining a horizon volume. In one embodiment, the horizon volume is determined from obtained seismic information, and maps the obtained seismic information onto a flattened volume such that in the flattened volume, horizons represented in the obtained seismic information are shifted to be substantially coplanar with a surface defined by the horizon volume as an estimate of a single chronostratigraphic time such that the parameters of the flattened volume include (i) a two-dimensional position in a surface plane, and (ii) a metric related to chronostratigraphic time.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
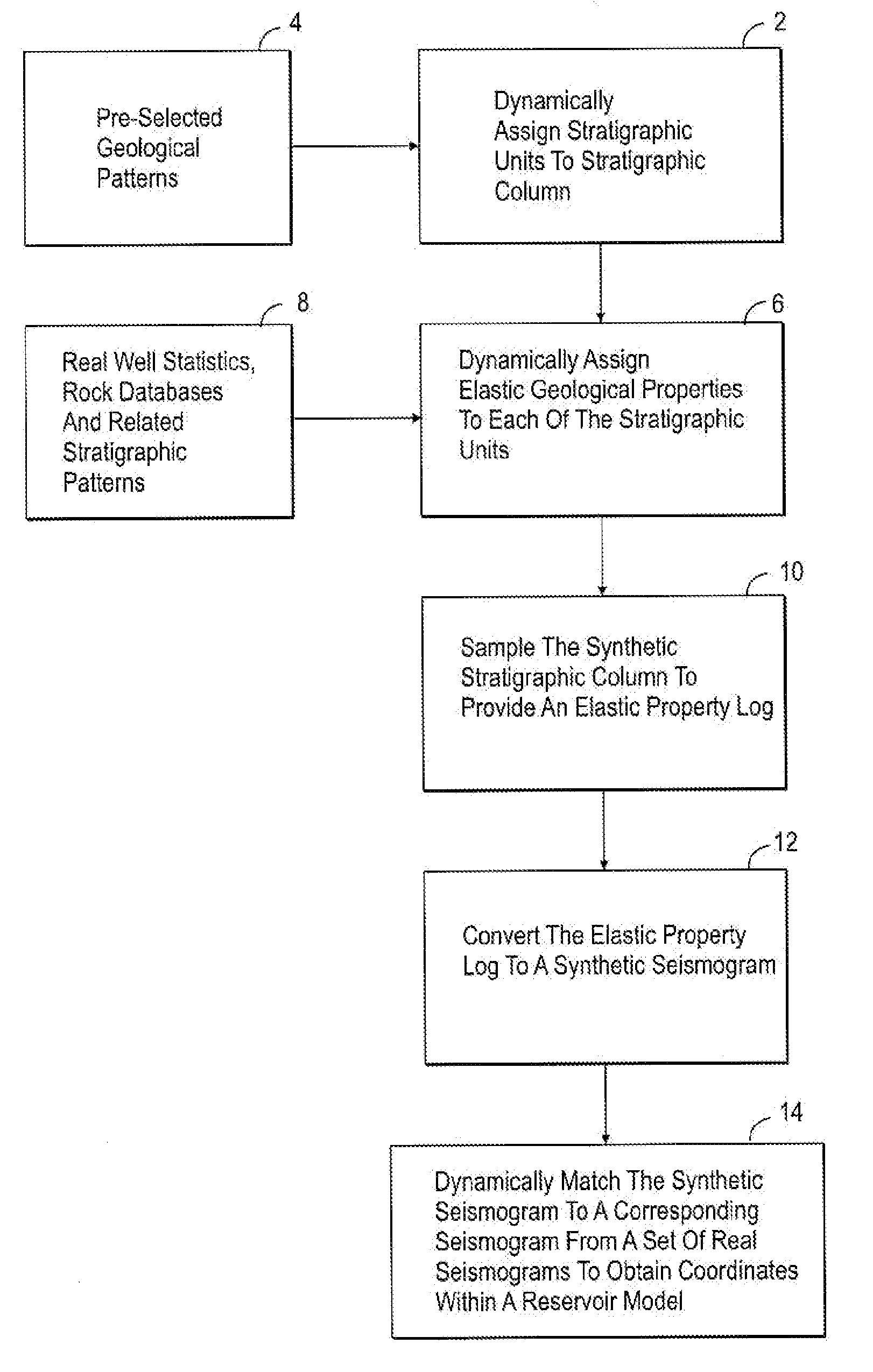
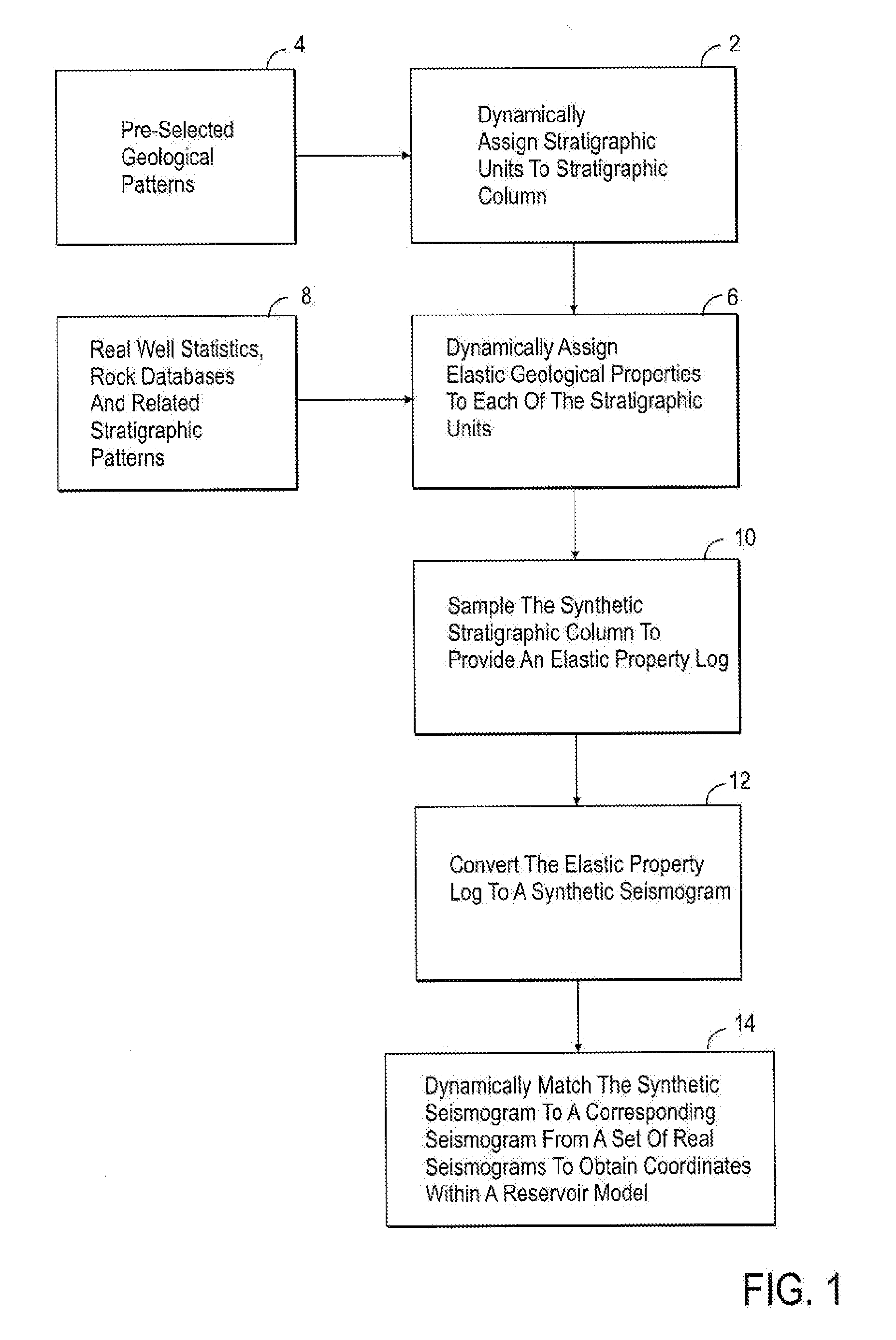
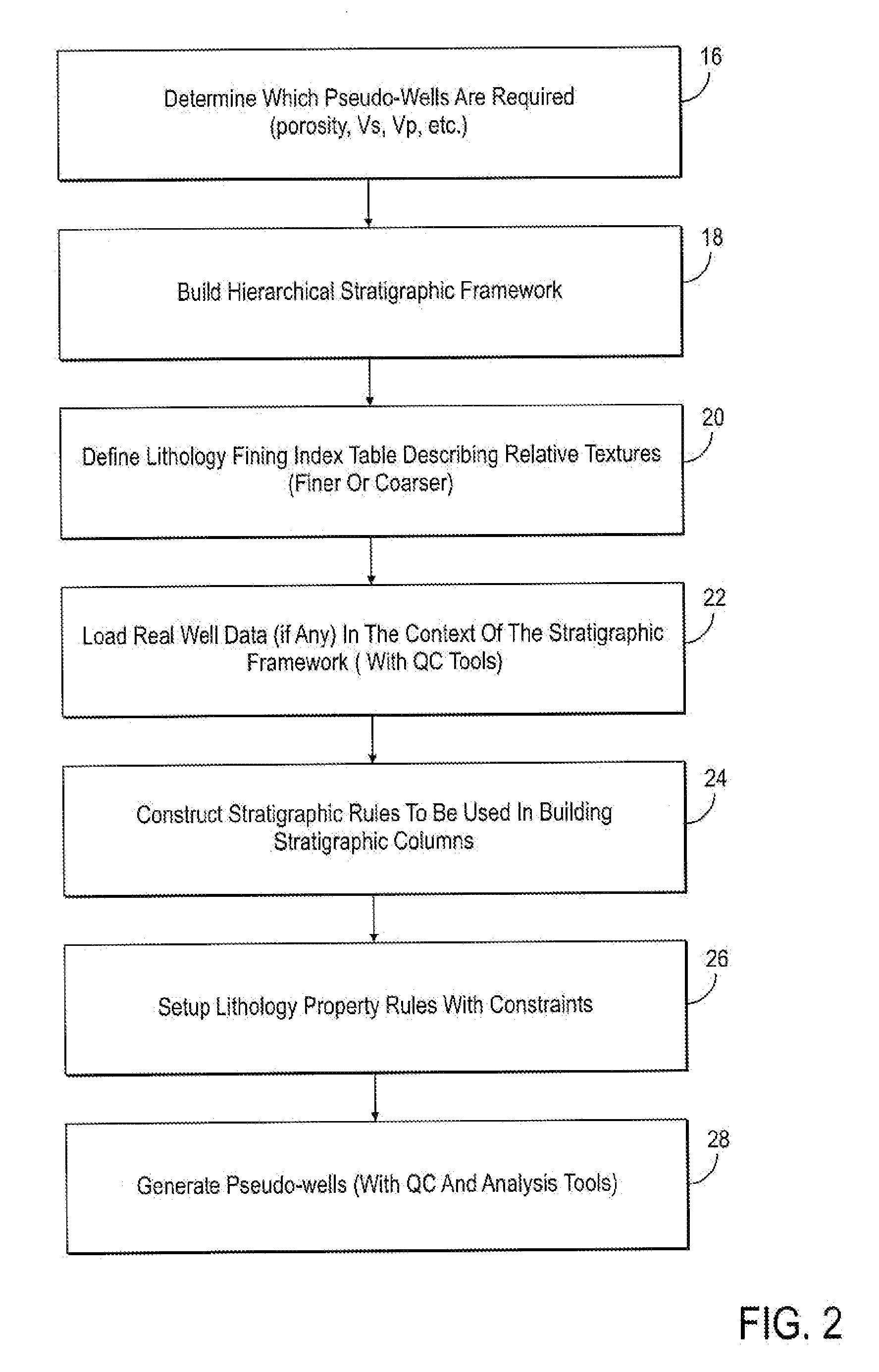
Method for generating reservoir models utilizing synthetic stratigraphic columns
ActiveUS20080195319A1Good estimateHigher elastic propertyElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismic signal processingCombined useStratigraphic column
The present invention incorporates the use of geophysical, geological and formation evaluation data to develop synthetic stratigraphic columns based on depositional rules and sedimentary stacking patterns. The present invention utilizes dynamic assignment and matching whereby the synthetic columns can be easily conformed throughout the reservation characterization process as geological data becomes available.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
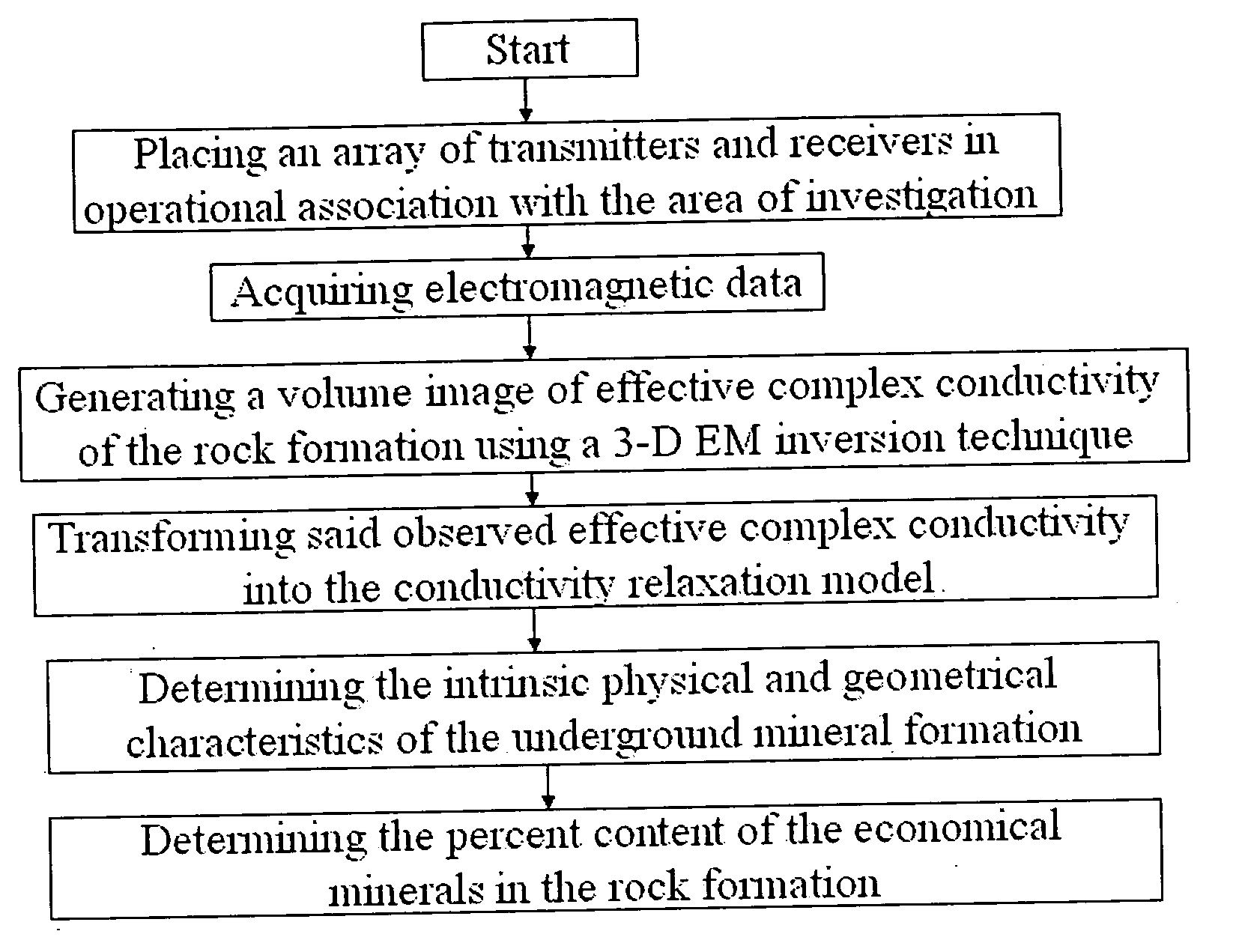
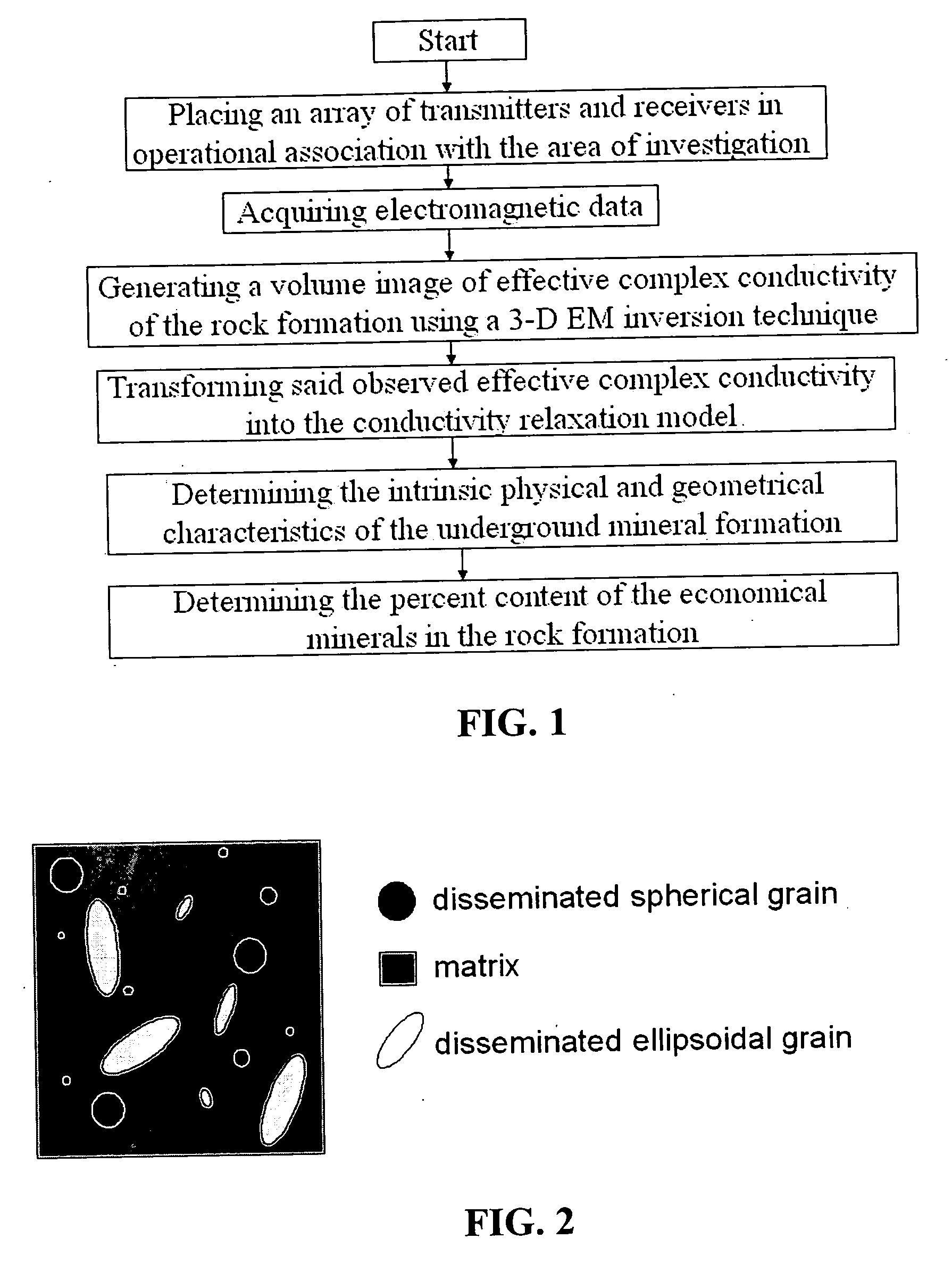
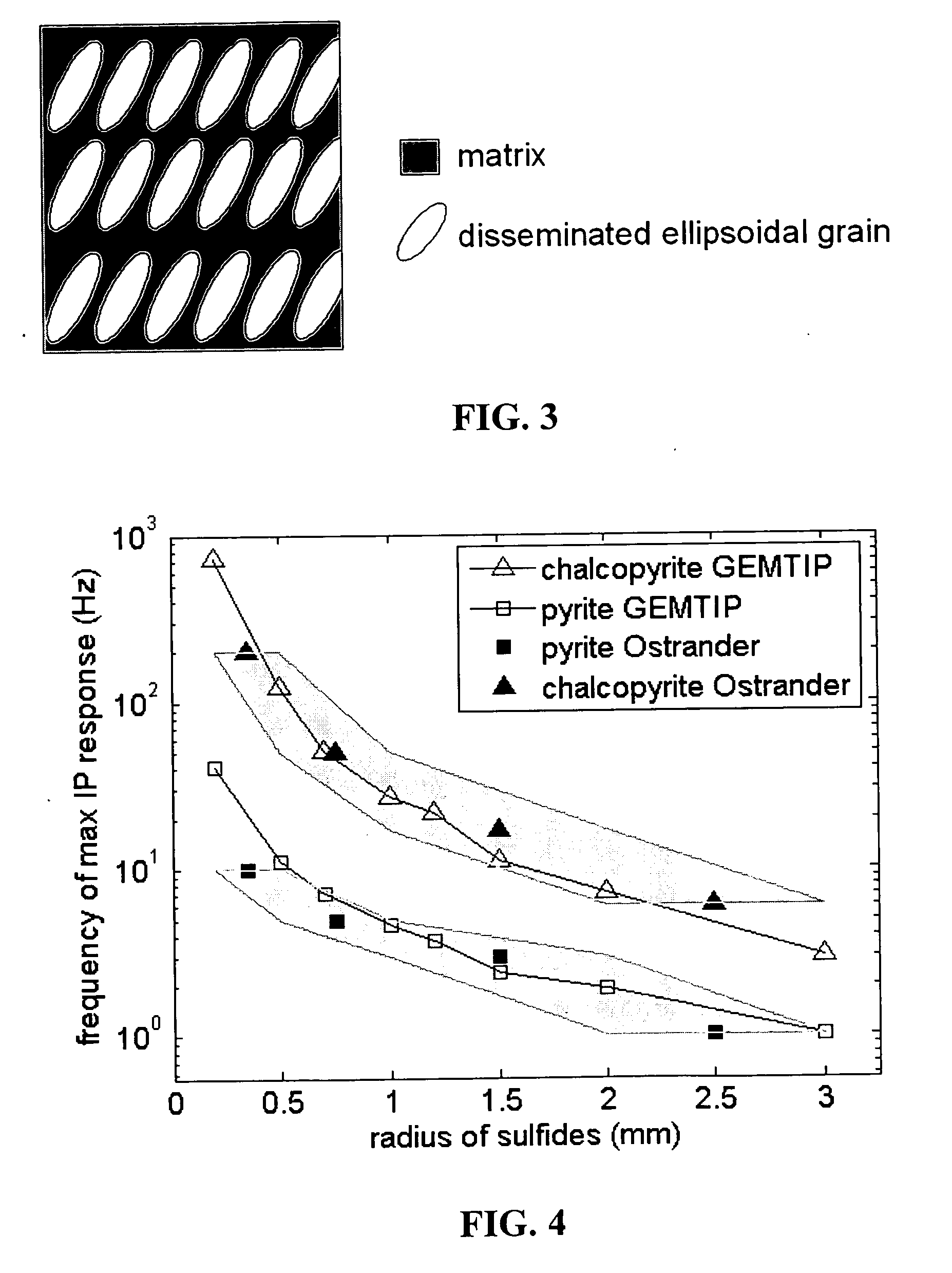
Geophysical technique for mineral exploration and discrimination based on electromagnetic methods and associated systems
ActiveUS20070061080A1Realistic representationElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismology for water-loggingAnalytical expressionsMicroscopic scale
Mineral exploration needs a reliable method to distinguish between uneconomic mineral deposits and economic mineralization. A method and system includes a geophysical technique for subsurface material characterization, mineral exploration and mineral discrimination. The technique introduced in this invention detects induced polarization effects in electromagnetic data and uses remote geophysical observations to determine the parameters of an effective conductivity relaxation model using a composite analytical multi-phase model of the rock formations. The conductivity relaxation model and analytical model can be used to determine parameters related by analytical expressions to the physical characteristics of the microstructure of the rocks and minerals. These parameters are ultimately used for the discrimination of different components in underground formations, and in this way provide an ability to distinguish between uneconomic mineral deposits and zones of economic mineralization using geophysical remote sensing technology.
Owner:THE UNIV OF UTAH +1
Processing of stratigraphic data
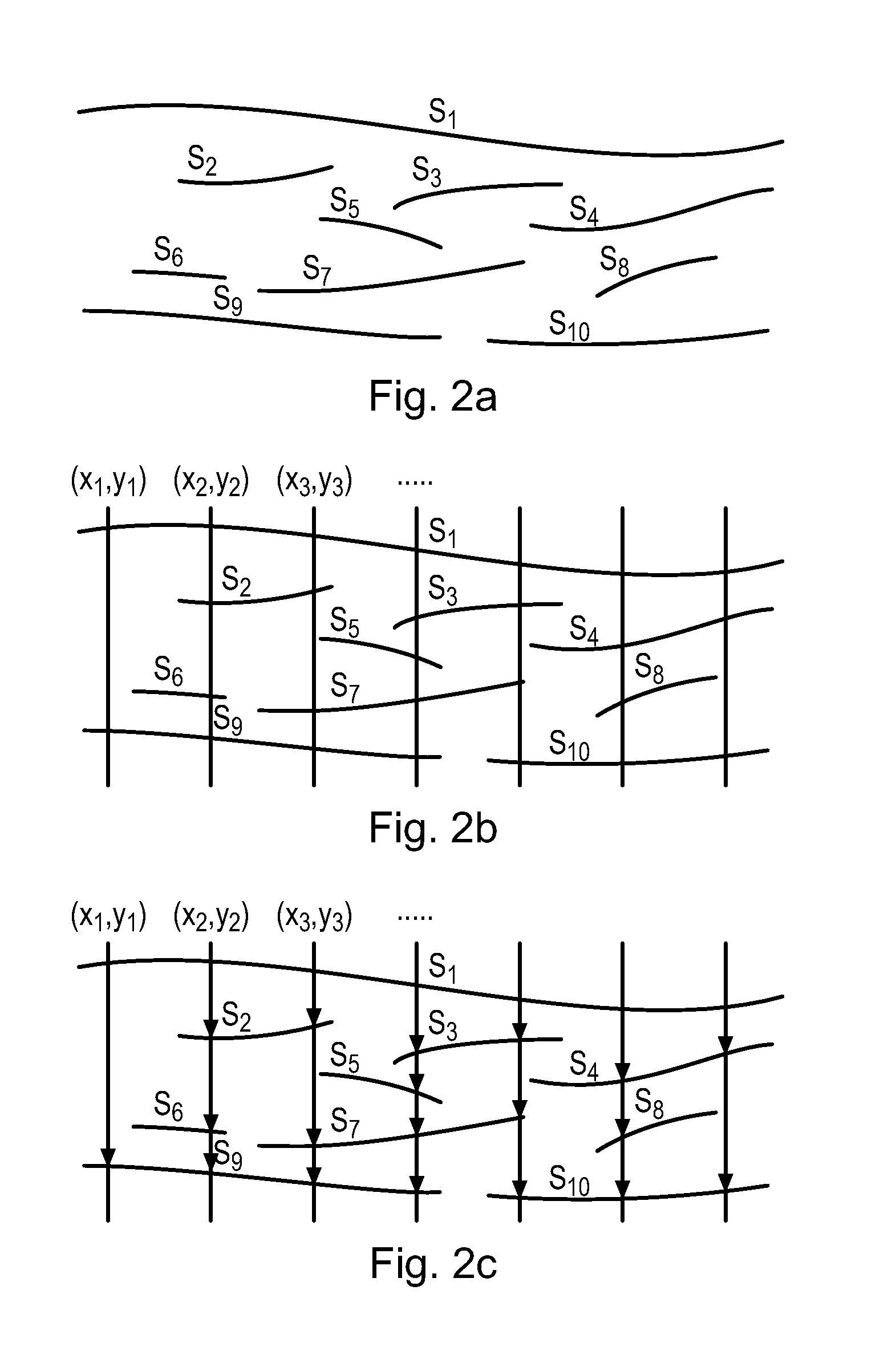
ActiveUS8219322B2Avoid confictDescribe wellDigital variable displayNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementAssiseGeophysics
A method of processing stratigraphic data comprising a plurality of stratigraphic features, such as horizon surfaces, within a geological volume is provided. The method includes the steps of: extending a plurality of spaced sampling traces through the volume to traverse the stratigraphic features; and assigning the stratigraphic features respective relative geological ages. On each sampling trace, the relative geological age of each stratigraphic feature traversed by the sampling trace in the direction from geologically younger to geologically older stratigraphic features is increased in relation to the relative geological age of its preceding stratigraphic feature, under the condition that each stratigraphic feature takes the same relative geological age across all the sampling traces by which it is traversed.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
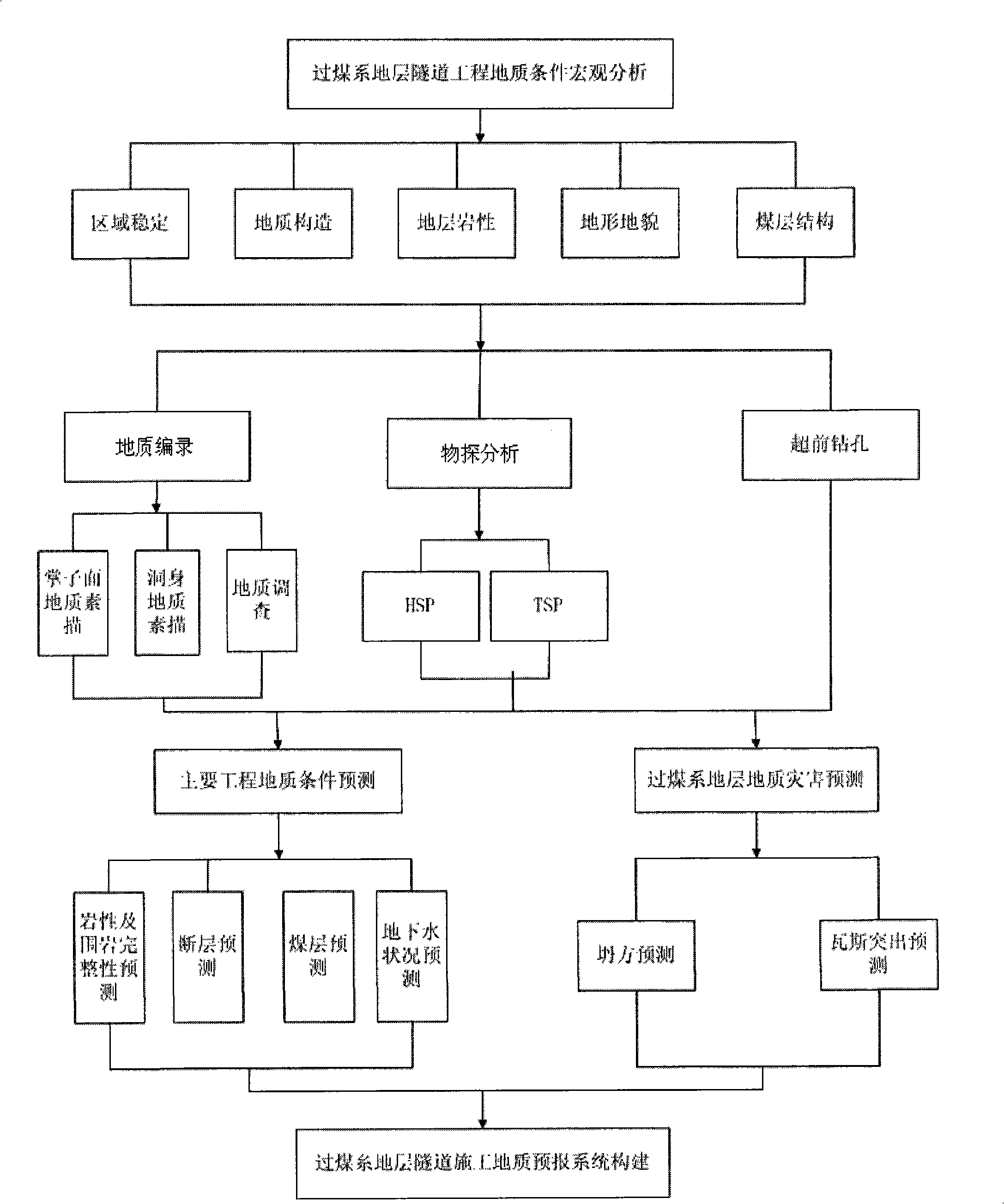
Geological prediction system for constructing tunnel passing through coal measure strata
ActiveCN101526629ADetection using electromagnetic wavesAcoustic wave reradiationCoal measuresGeomorphology
The invention discloses a geological prediction system for constructing a tunnel passing through coal measure strata. The condition of the tunnel passing through the coal measure strata is specifically analyzed in a way of geological record, geophysical prospecting analysis or advance borehole according to specific condition based on macroscopic analysis which is adopted in sequence; the obtained information is classified so as to predict the geological condition of a main job and the geologic hazard of the coal measure strata; and the correlative information and data are used for completing the construction of the geological prediction system for constructing tunnel passing through coal measure strata. The invention provides a system for perfectly and exactly predicting the geology for constructing the tunnel passing through coal measure strata.
Owner:CHINA RAILWAY NO 2 ENG GRP CO LTD
Fast and fine geological orientation method for shale gas horizontal well
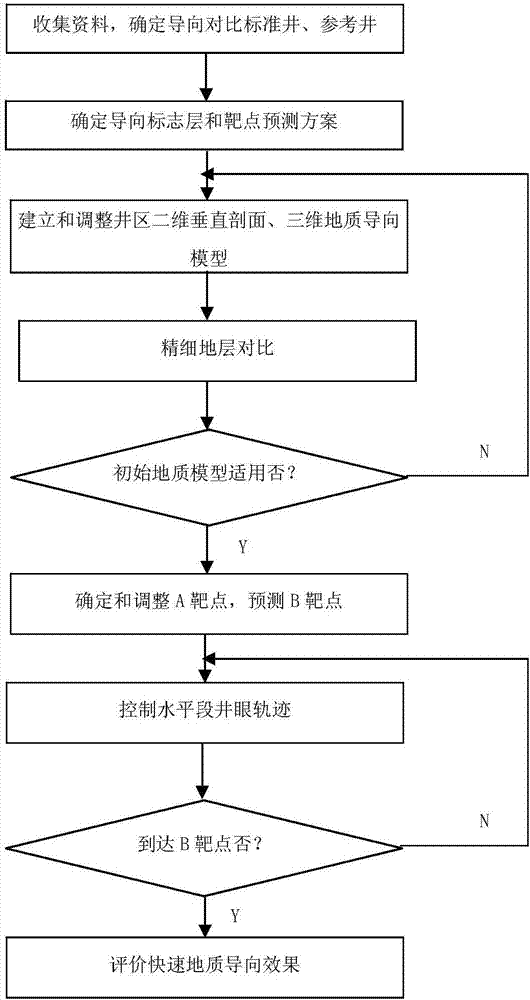
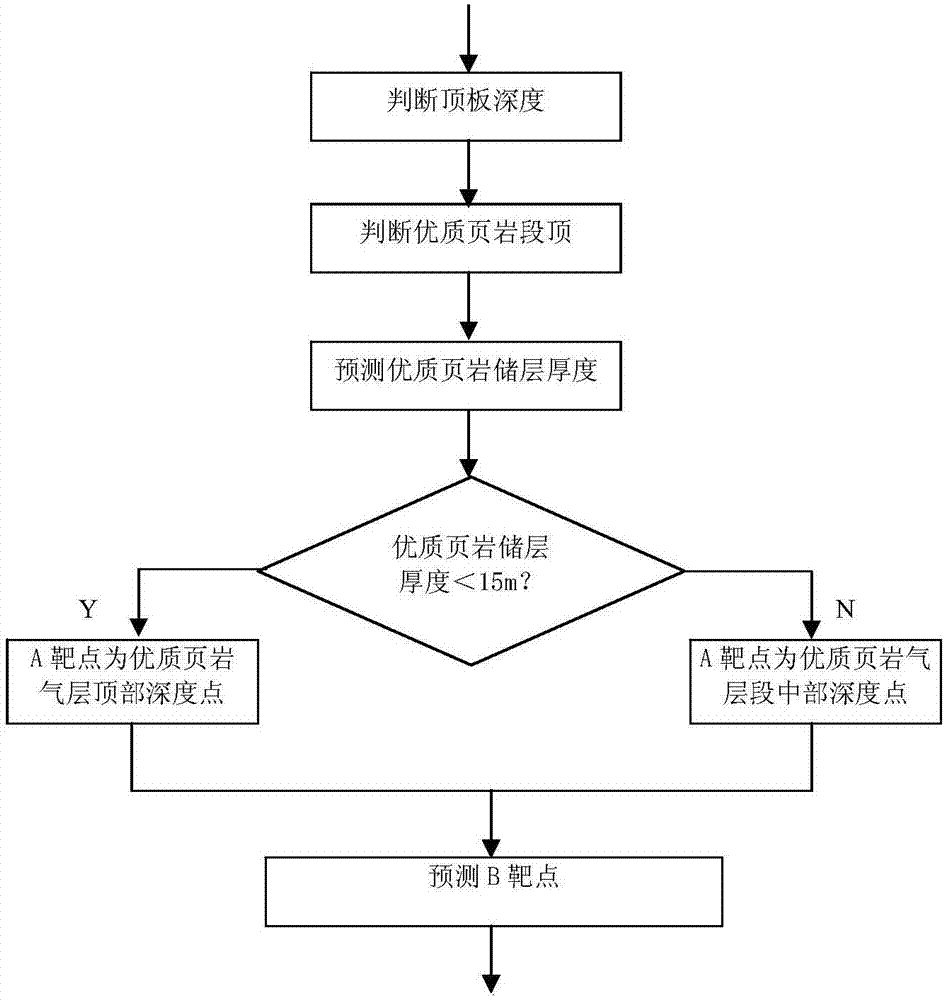
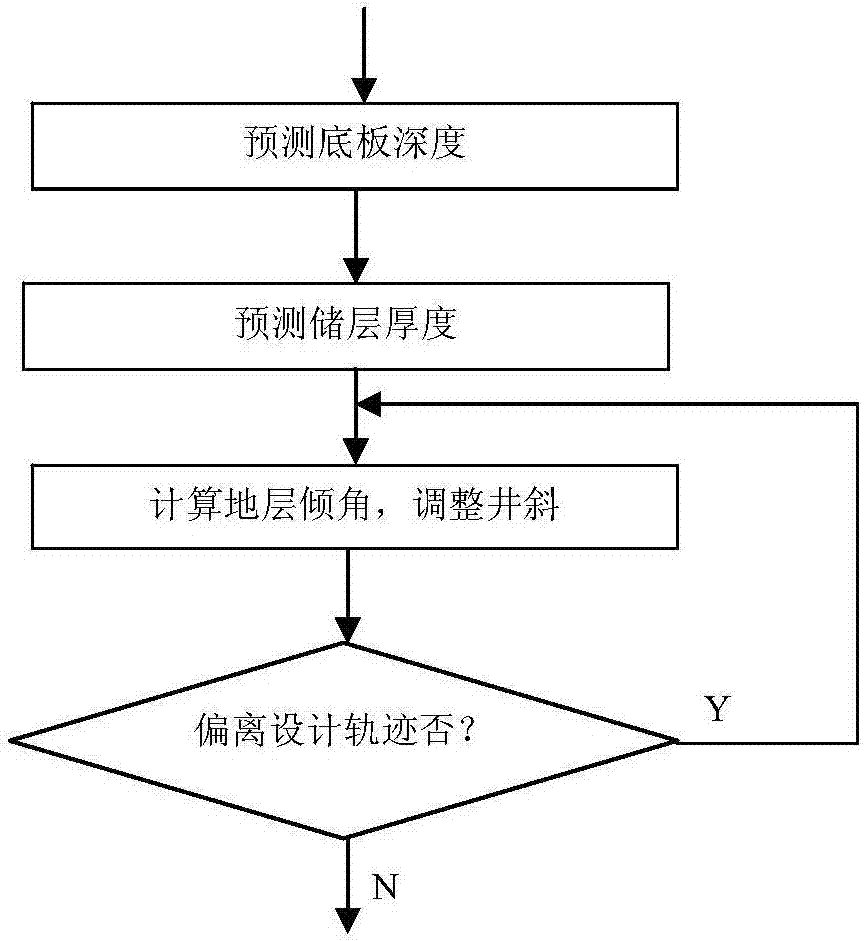
The invention relates to a fast and fine geological orientation method for a shale gas horizontal well. Materials are collected, an orientation comparing standard well and a reference well are determined, and an orientation sign layer and a target spot predicting scheme are determined; a well zone two-dimensional geological orientation model and a well zone three-dimensional geological orientation model are built and regulated, and a two-dimensional vertical section and the three-dimensional geological orientation model of a well to be oriented are amended in time; by means of the characteristics of lithological characters, well deflection, while-drilling gamma and the like of the well to be oriented, the standard well and the reference well, stratum comparing is conducted; the position where a drill is located is judged through three figures, one table and the like; whether the position where the drill is located is in a high-quality shale gas layer section or not is evaluated while drilling; whether an initial geological model is applicable or not is judged; through an equal-thickness comparing method a target spot A is determined and regulated, a target spot B is predicted, and a track of a borehole in a horizontal section is controlled; and the pass-through rate of a high-quality shale gas layer is calculated according to the statistic drilling-meeting thicknesses of a shale reservoir and a high-quality shale reservoir, whether the track is controlled to reach the target spot B or not is judged, and the fast geological orientation effect is evaluated. Fast orientation is achieved, the application range is wide, and application and popularization are easy.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +3
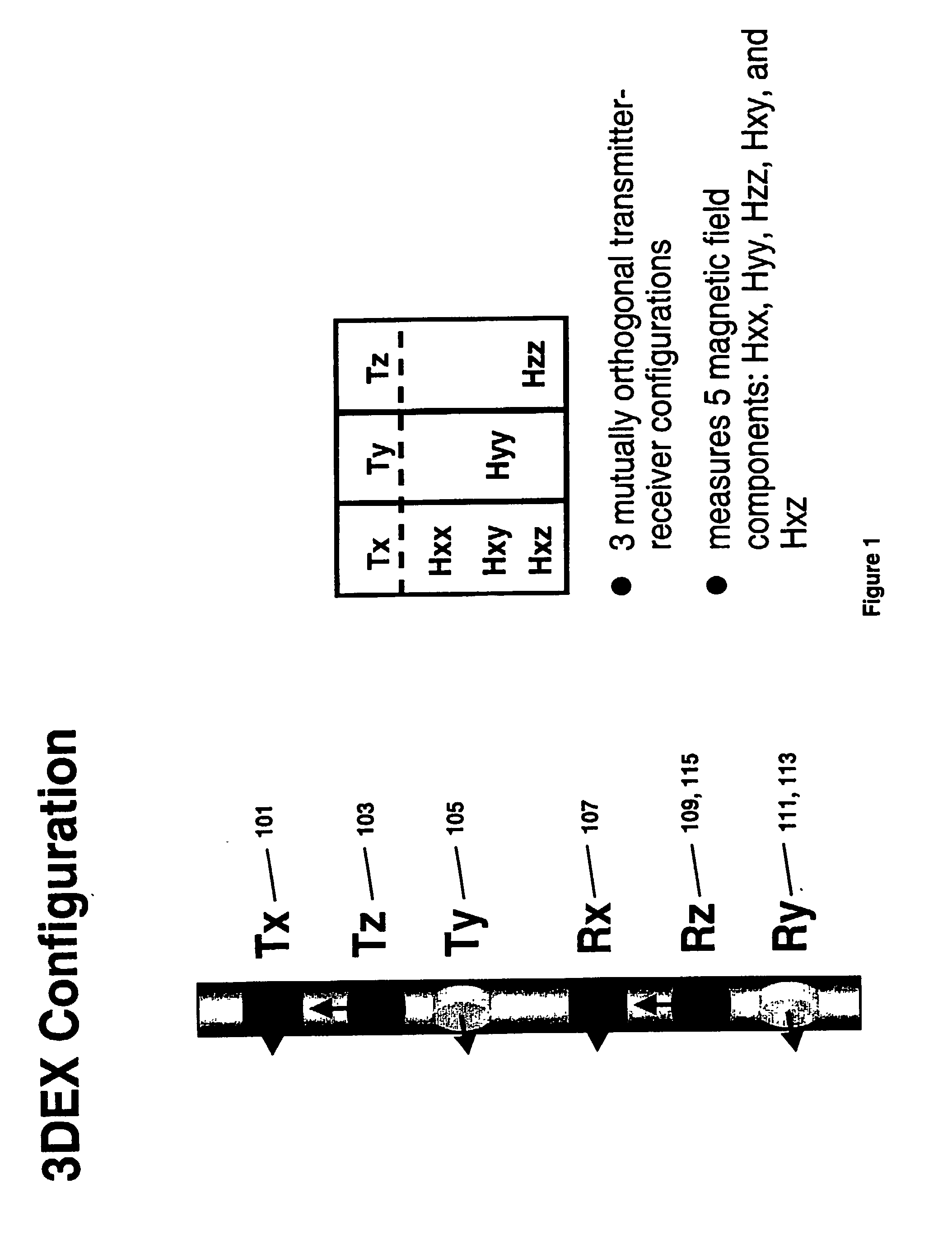
System and method for determining formation fluid parameters
ActiveUS20050246151A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismic signal processingGeomorphologyFormation fluid
A method for determining a parameter of interest of a formation fluid, comprises moving a tool attached to a tubular member along a borehole in a subterranean formation. The tool is used to determine a formation fluid pressure and a formation fluid temperature at predetermined locations along the borehole and calculating a formation fluid density along the borehole therefrom. A density of a reference fluid is determined along the borehole and is related to the formation fluid pressure and the formation fluid temperature. The parameter of interest of the formation fluid is determined at a predetermined location from a comparison of the corresponding formation fluid density and the reference fluid density at the predetermined location.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
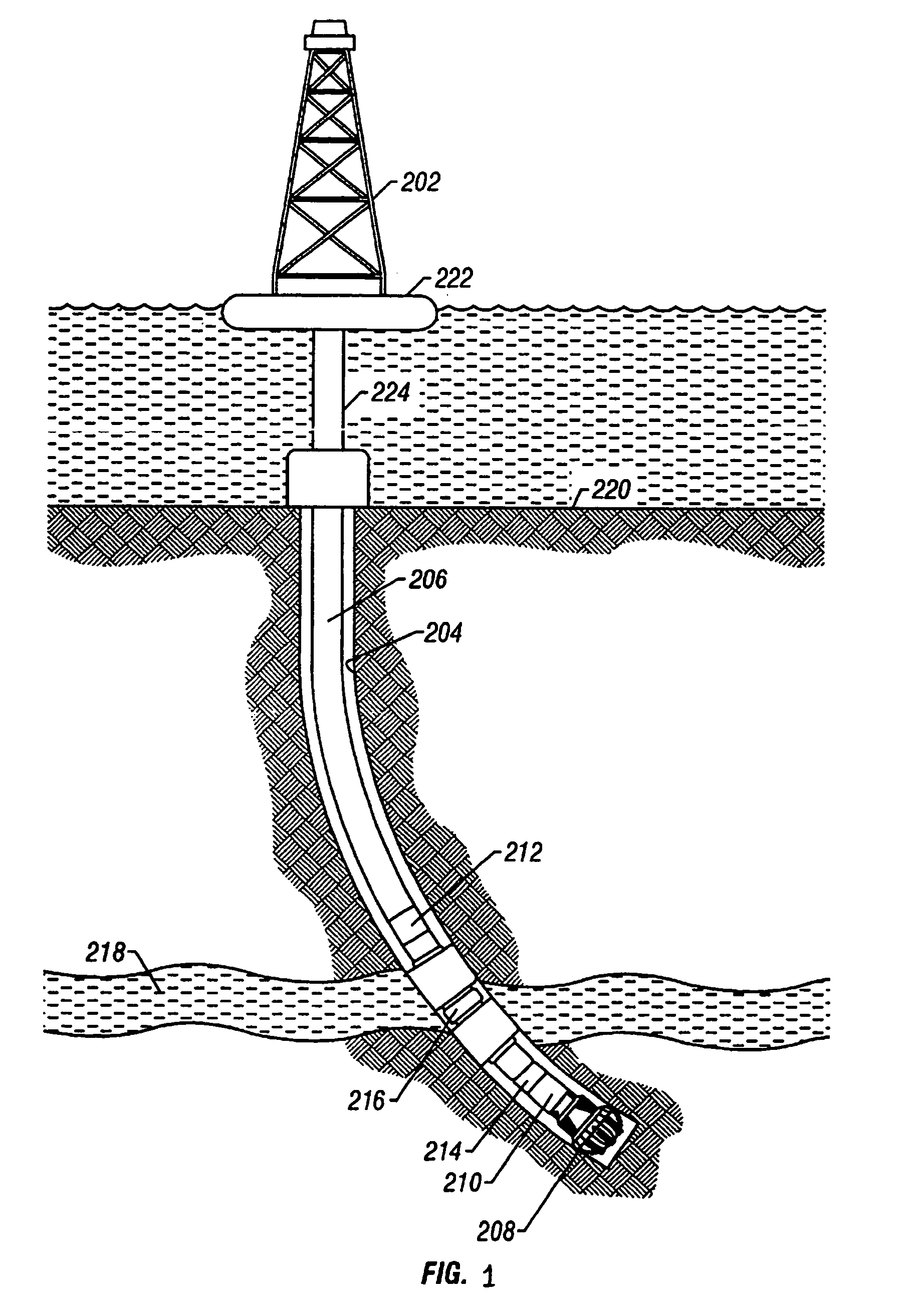
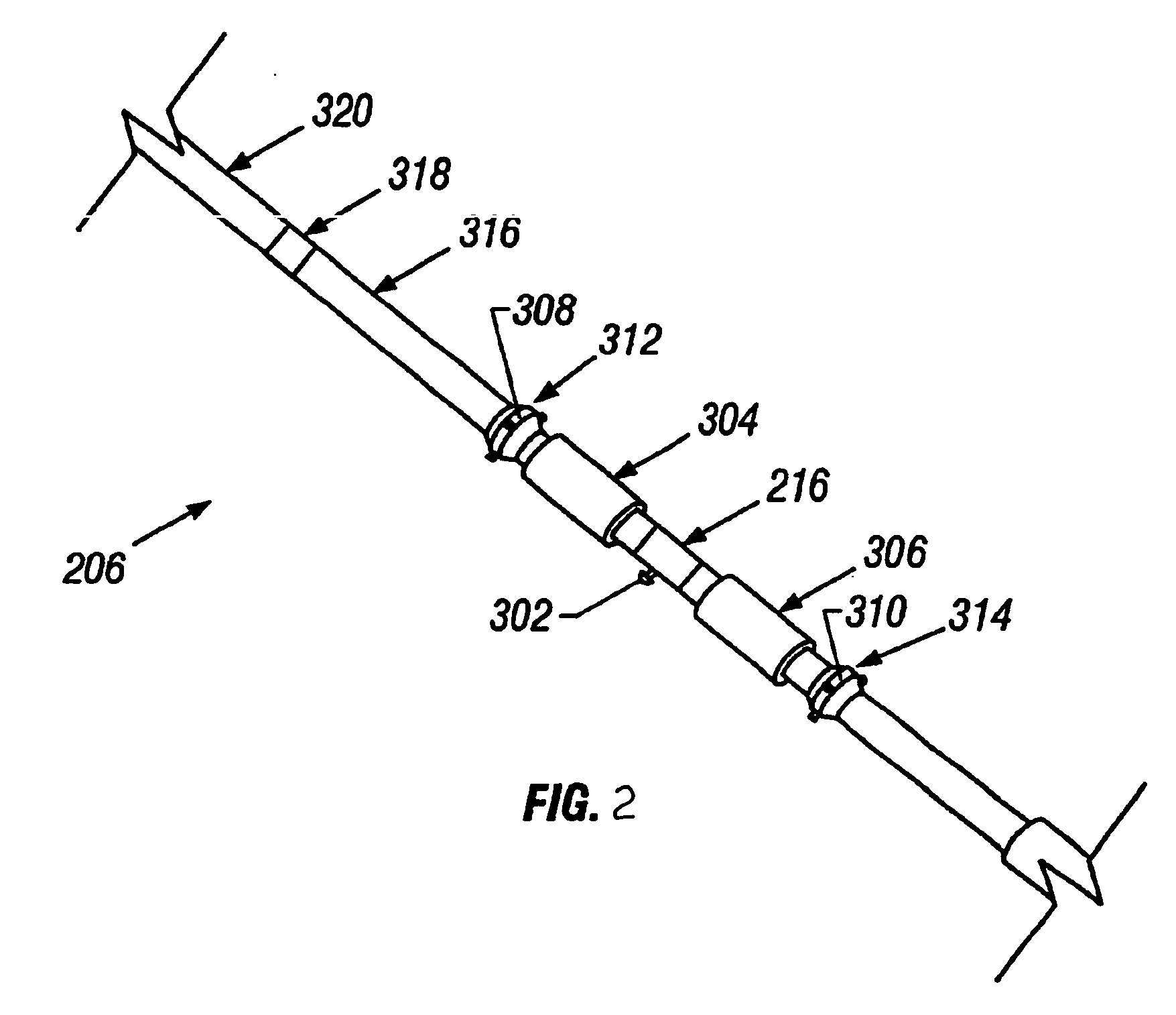
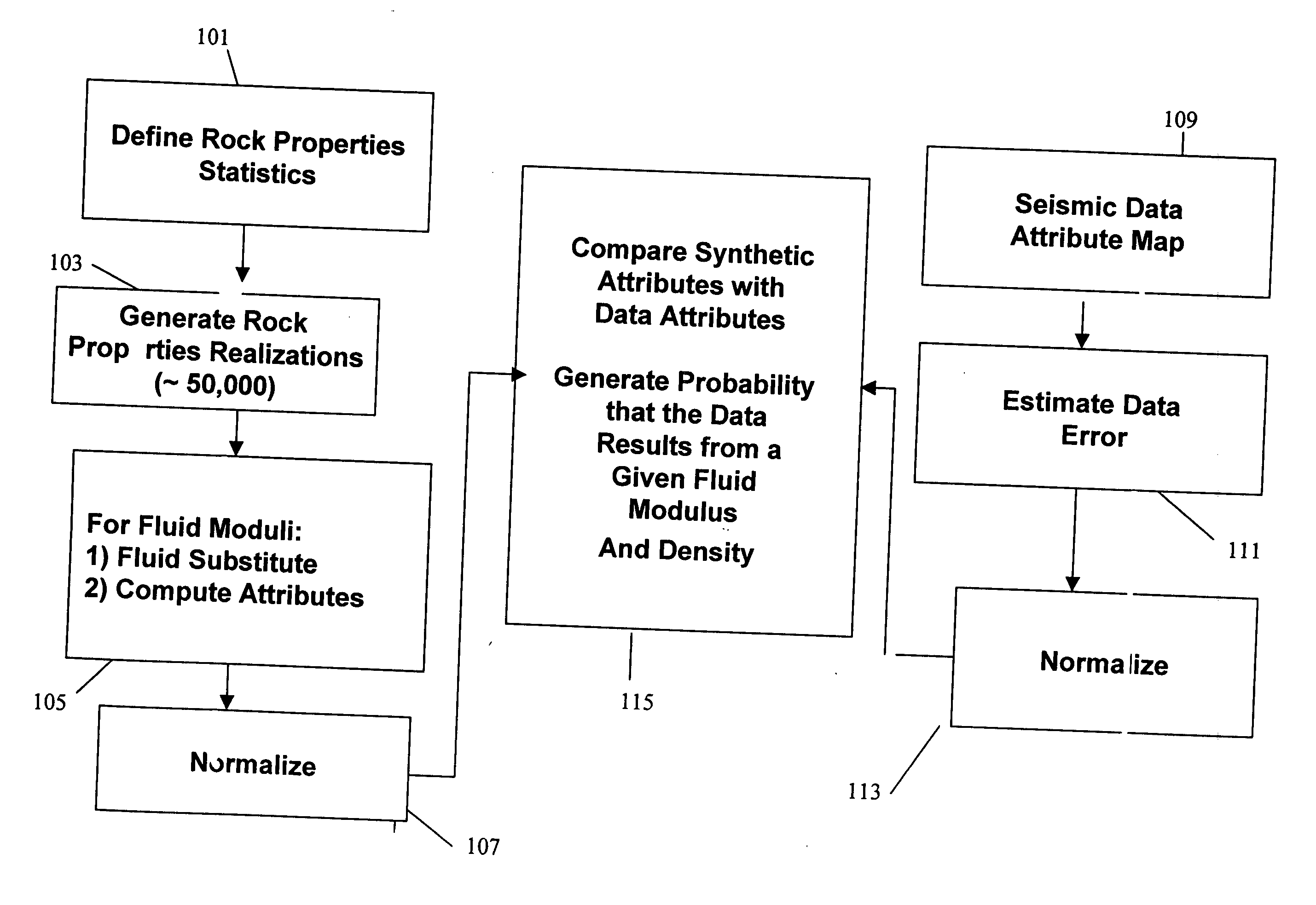
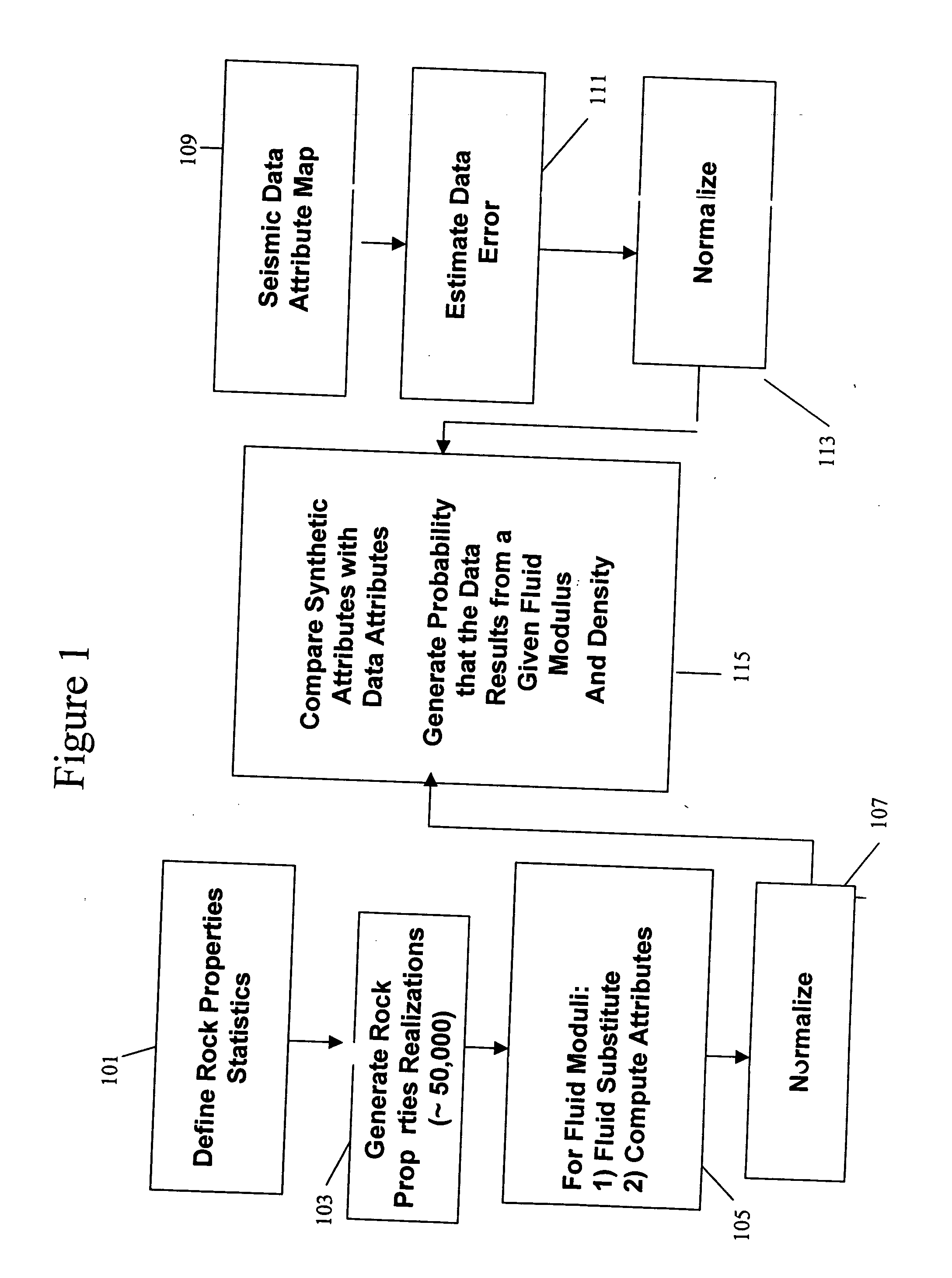
Determination of fluid properties of earth formations using stochastic inversion
ActiveUS20050007876A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismic signal processingSeismic attributeTest region
A method of determining a fluid property in a subsurface region of interest of an earth formation uses measurements of seismic attributes on seismic data. For a test region, a plurality of realizations of rock properties are specified, and for each of the realizations and a selected value of a fluid property, the seismic attribute is modeled. This defines a probability density function (PDF). Comparison of the PDF of the model output with the PDF on the measured seismic data is used to determine the likelihood of the selected fluid property.
Owner:GAS TECH INST
Automatically generating method of pinchout geological body three-dimensional complex profile
InactiveCN102651143ARealize 3D visualization expressionTroubleshoot auto-painting issues3D modellingTriangulationGeological section
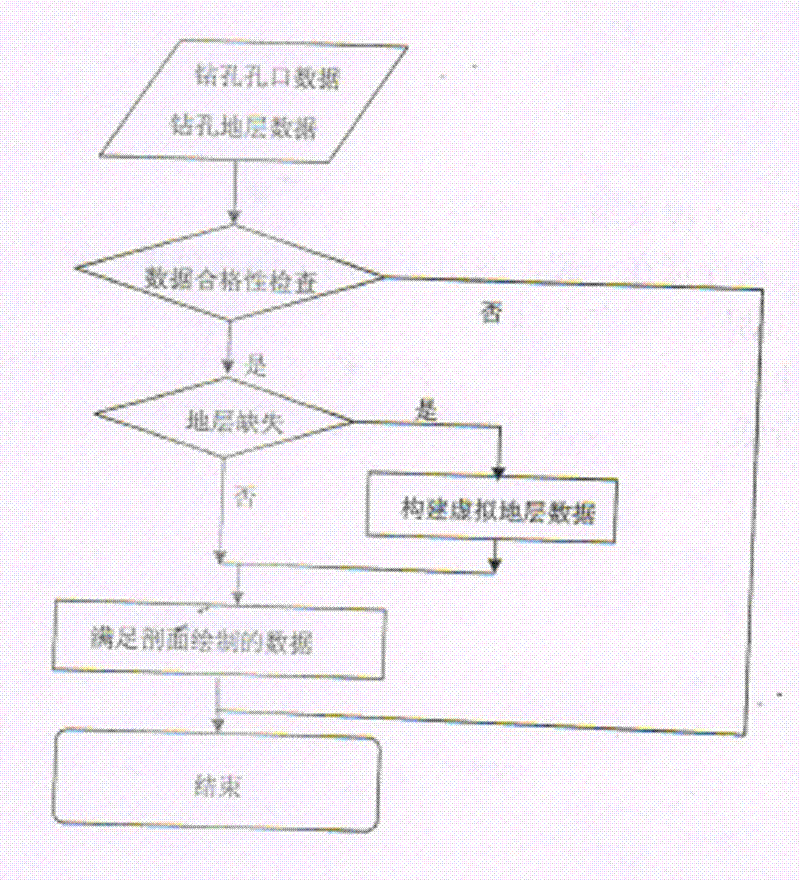
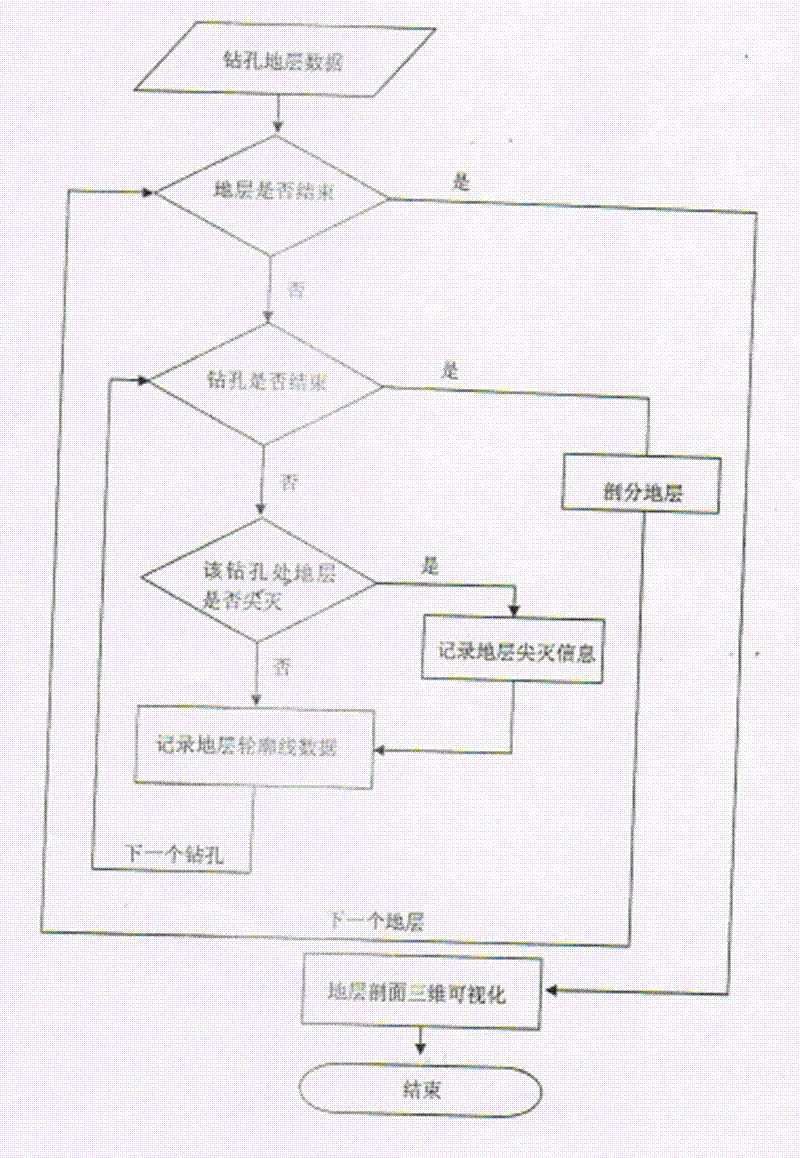
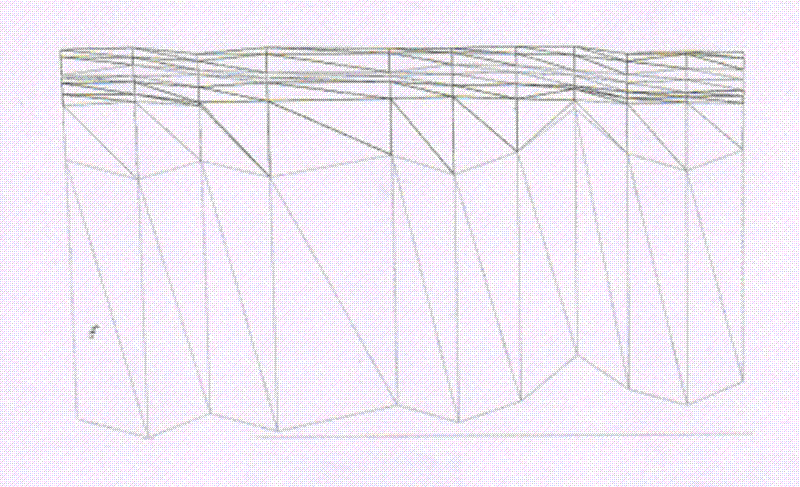
The invention provides an automatically generating method of pinchout geological body three-dimensional complex profile, which performs virtual supplementation to missed stratigraphic data in drilling holes by starting from processing the data of the drilling holes and according to the space distribution of the data of the drilling holes. The method comprises the following steps of extracting the data of the drilling holes in the same layer according to a one-to-one corresponding rule of the stratum of the drilling holes, and combining the data into a profile line of the stratum; performing triangulation based on the upper and lower stratum points of the stratum formed by adjacent two drilling holes according to the extracted profile line of the stratum, thereby realizing three-dimensional visual expression for the stratigraphic section. According to the method provided by the invention, the automatic drawing problem of complex three-dimensional section is solved; the workload for hand drawing geological profile can be greatly reduced; the method is based on the stratum information of the drilling hole to identify the pinchout situation, so that the efficiency for space analysis and decision making can be improved; molding of complex geological body three-dimensional section can be adapted, and the method can be widely promoted and used in the three-dimensional geo-science modeling.
Owner:中冶沈勘工程技术有限公司 +1
Methods of downhole testing subterranean formations and associated apparatus therefor
Methods and apparatus are provided which permit well testing operations to be performed downhole in a subterranean well. In various described methods, fluids flowed from a formation during a test may be disposed of downhole by injecting the fluids into the formation from which they were produced, or by injecting the fluids into another formation. In several of the embodiments of the invention, apparatus utilized in the methods permit convenient retrieval of samples of the formation fluids and provide enhanced data acquisition for monitoring of the test and for evaluation of the formation fluids.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
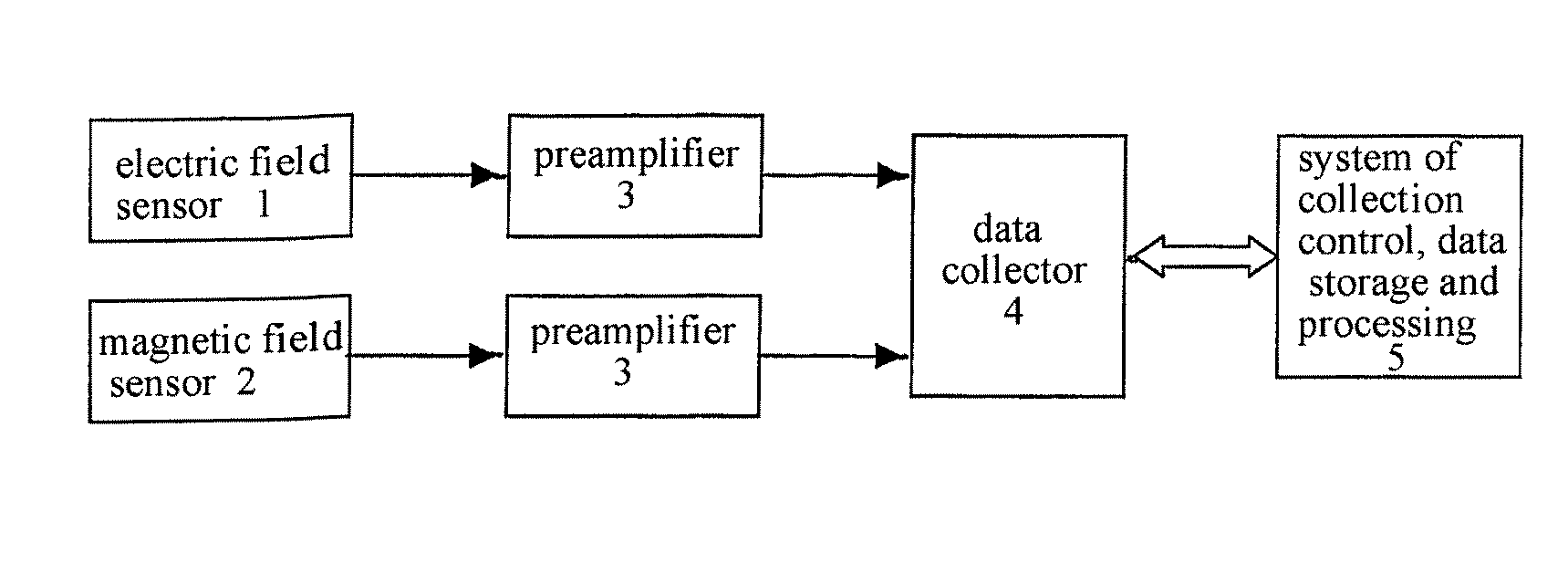
Method and Apparatus for Measuring the Resistivity of Electromagnetic Waves of the Earth
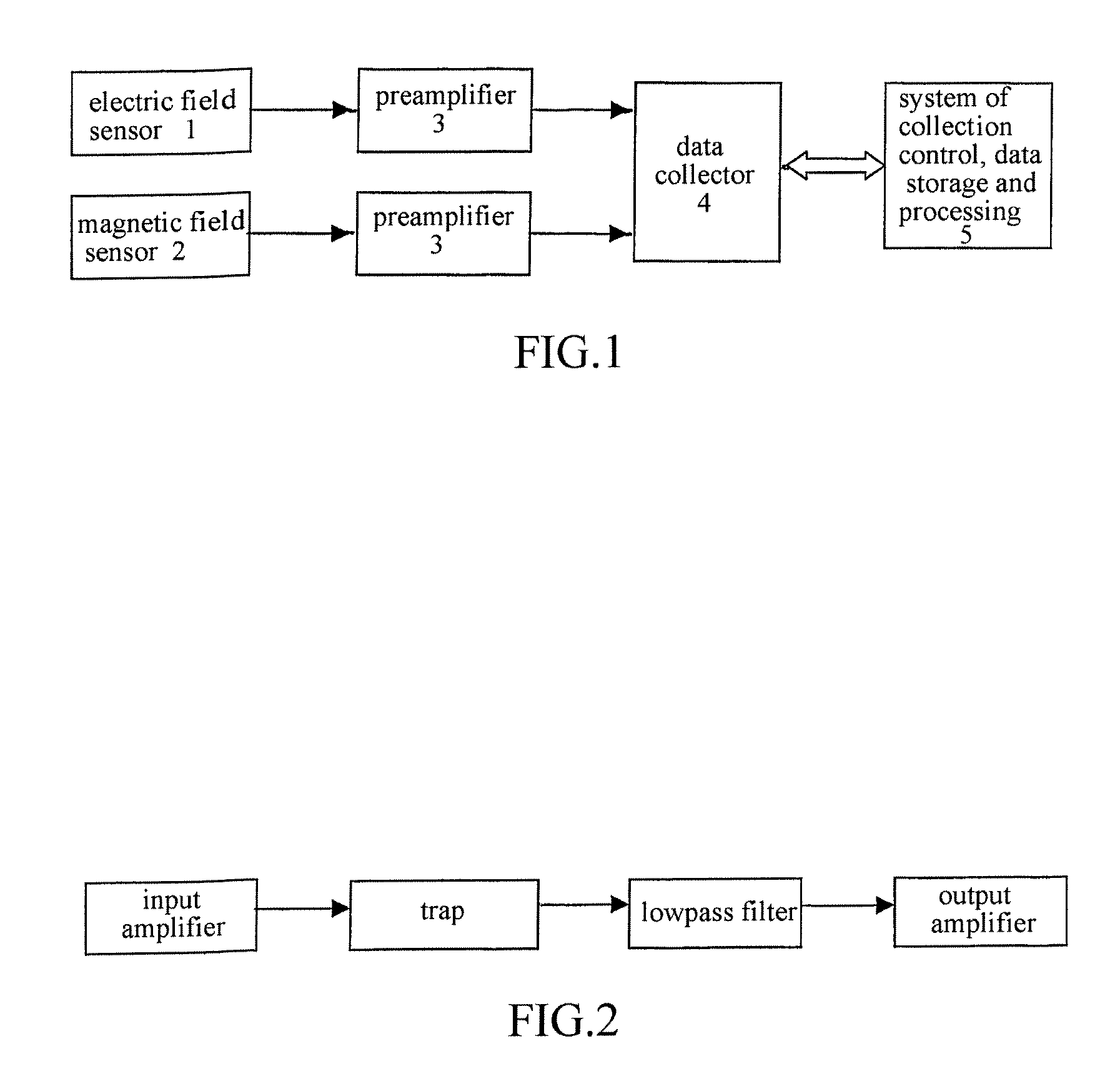
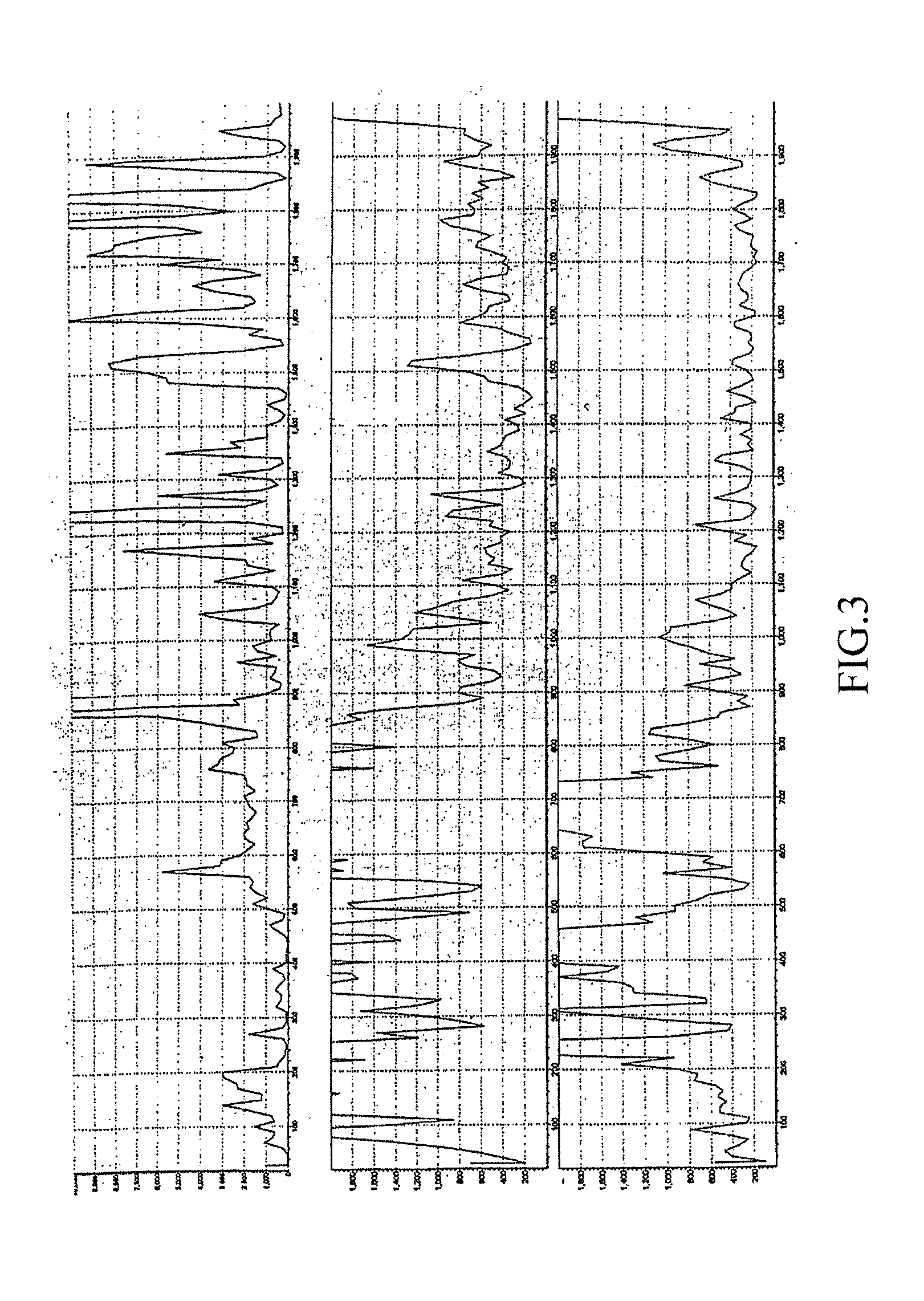
ActiveUS20080228401A1Improve accuracyImprove efficiencyElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismology for water-loggingContinuous measurementElectric field sensor
Disclosed is a method and apparatus for measuring the electromagnetic wave resistivity of earth formations. The disclosed method and apparatus use an electric field sensor, a magnetic field sensor in conjunction with a data collecting system to obtain data samples from strata, determine certain parameters associated with the data samples, such as a depth coefficient and a surface-layer depth coefficient, establish an observational reference frame based upon an equation defined by the stratum depth (H) and propagation frequency (F) and an equation defined by the electromagnetic wave resistivity (ρ) and stratum depth (H), and utilize the reference frame to record results from a data collecting, controlling, storing and processing system configured for continuously measuring the electromagnetic wave resistivity of earth formations. Compared with the conventional method where the multi-variable theory and formula is used for determining the stratum depth and / or thickness, the presently disclosed method uses actual data to determine the relationship between the stratum depth (H) and propagation frequency (F), which makes the resistivity of earth formations the only variable to be measured and thus significantly improves the accuracy of depth measurements. In addition, the disclosed apparatus provides almost real-time data processing of the collected data samples to produce a changing curve of the measured electromagnetic wave resistivity corresponding to any changes in the stratum depth. The disclosed method and apparatus can be directly applied in the field of mineral exploration, and it will reduce the number of well drills and improve the efficiency of mineral exploration.
Owner:ZHOU RENAN +1
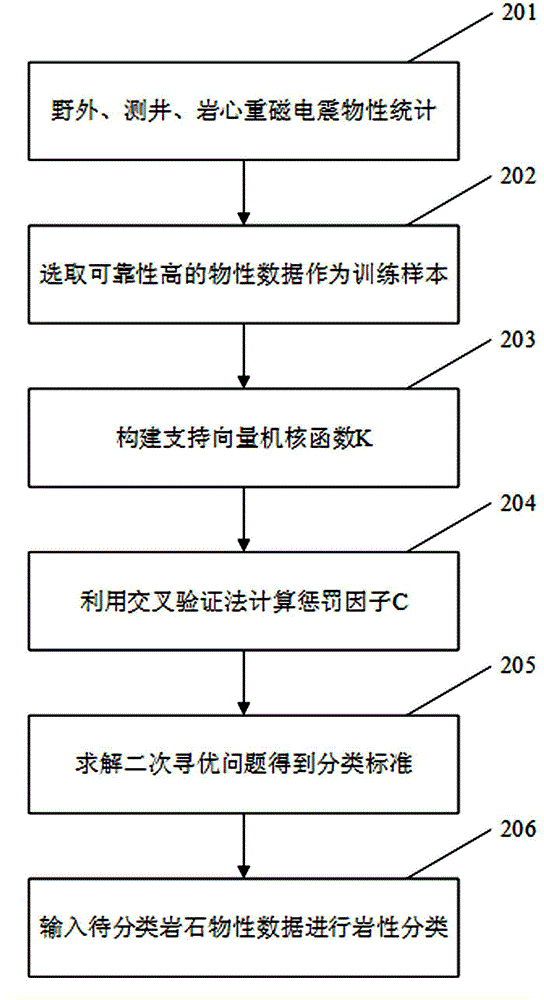
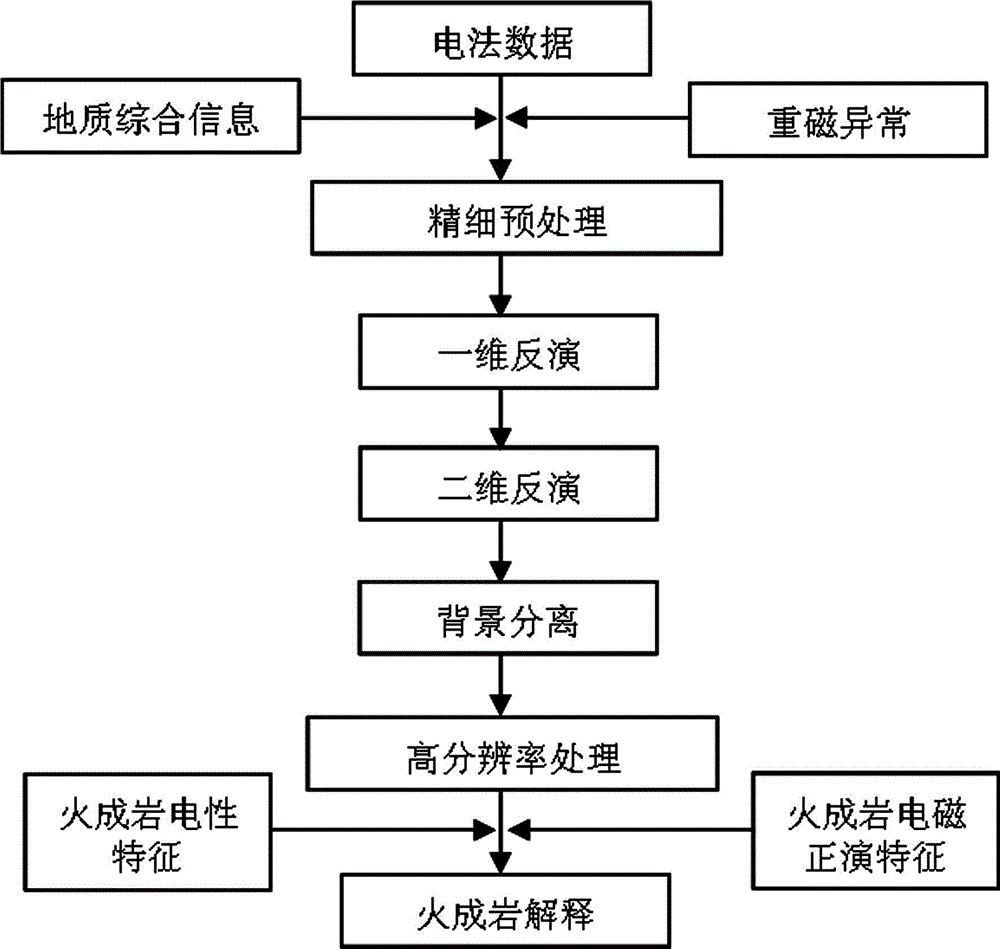
Method for comprehensive recognition of igneous rocks by employing gravity, magnetism, electromagnetism, and earthquake data
InactiveCN105005097AHigh recognition reliabilityGeological measurementsDistribution frameIgneous rock
The invention discloses a method for comprehensive recognition of igneous rocks by employing gravity, magnetism, electromagnetism, and earthquake data. The method includes steps: building templates of different igneous rocks and stratum physical properties; performing forward modeling of gravity, magnetism, electromagnetism, and earthquake, and making clear of response characteristics and rules; performing gravity and magnetism anomaly extraction of the planes of the igneous rocks and weak anomaly enhancement processing, and explaining and dividing distribution zones and range of the planes of the igneous rocks; performing electrical and seismic profile data igneous rock target processing explanation and making clear of the distribution rule of the igneous rocks in the vertical direction; performing combined inversion of gravity, magnetism, electromagnetism, and earthquake data profile, and building a vertical distribution frame of the igneous rocks; developing three-dimensional inversion of the physical properties of the igneous rocks with gravity and magnetism anomalies by employing the profile combined inversion result and drilling data as the constraint condition and with the combination of plane distribution of the igneous rocks; and recognizing the space distribution and lithological and lithofacies distribution rules of the igneous rocks in a comprehensive manner with the combination of physical property combined characteristics of different igneous rocks according to the three-dimensional distribution of the physical properties. According to the method, comprehensive recognition of the igneous rocks is realized by employing various data, and the reliability is higher compared with the recognition of the igneous rock by employing single data.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
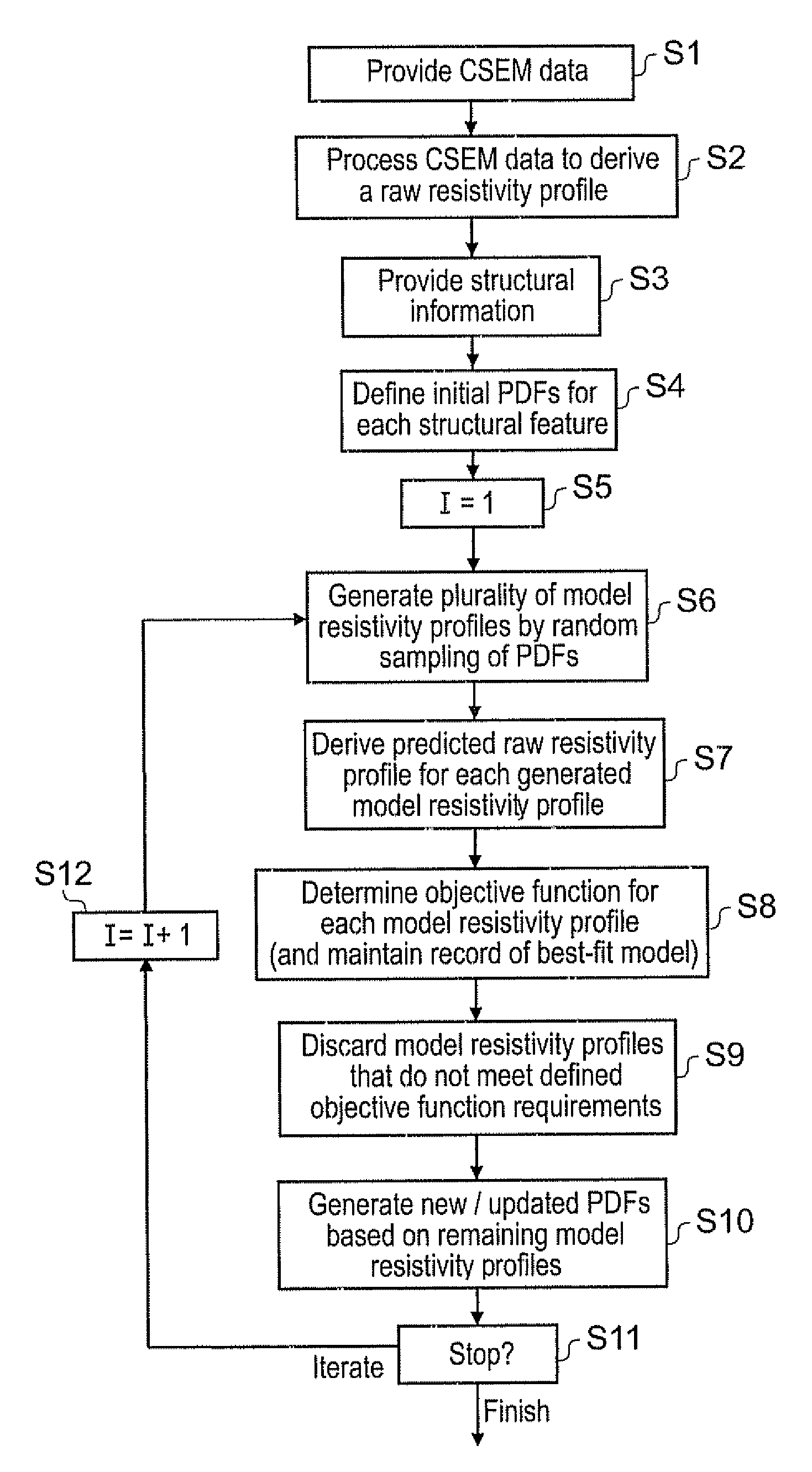
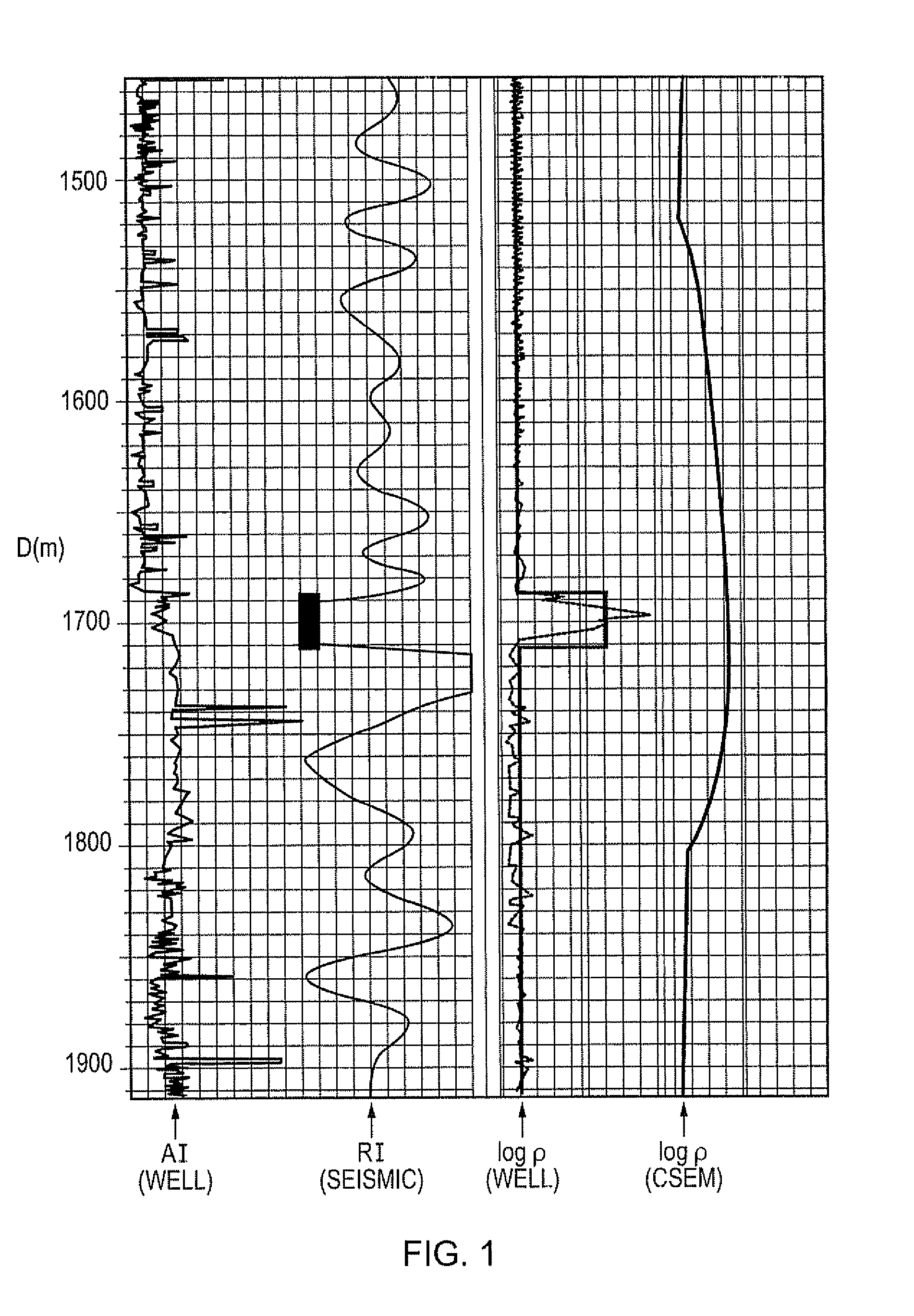
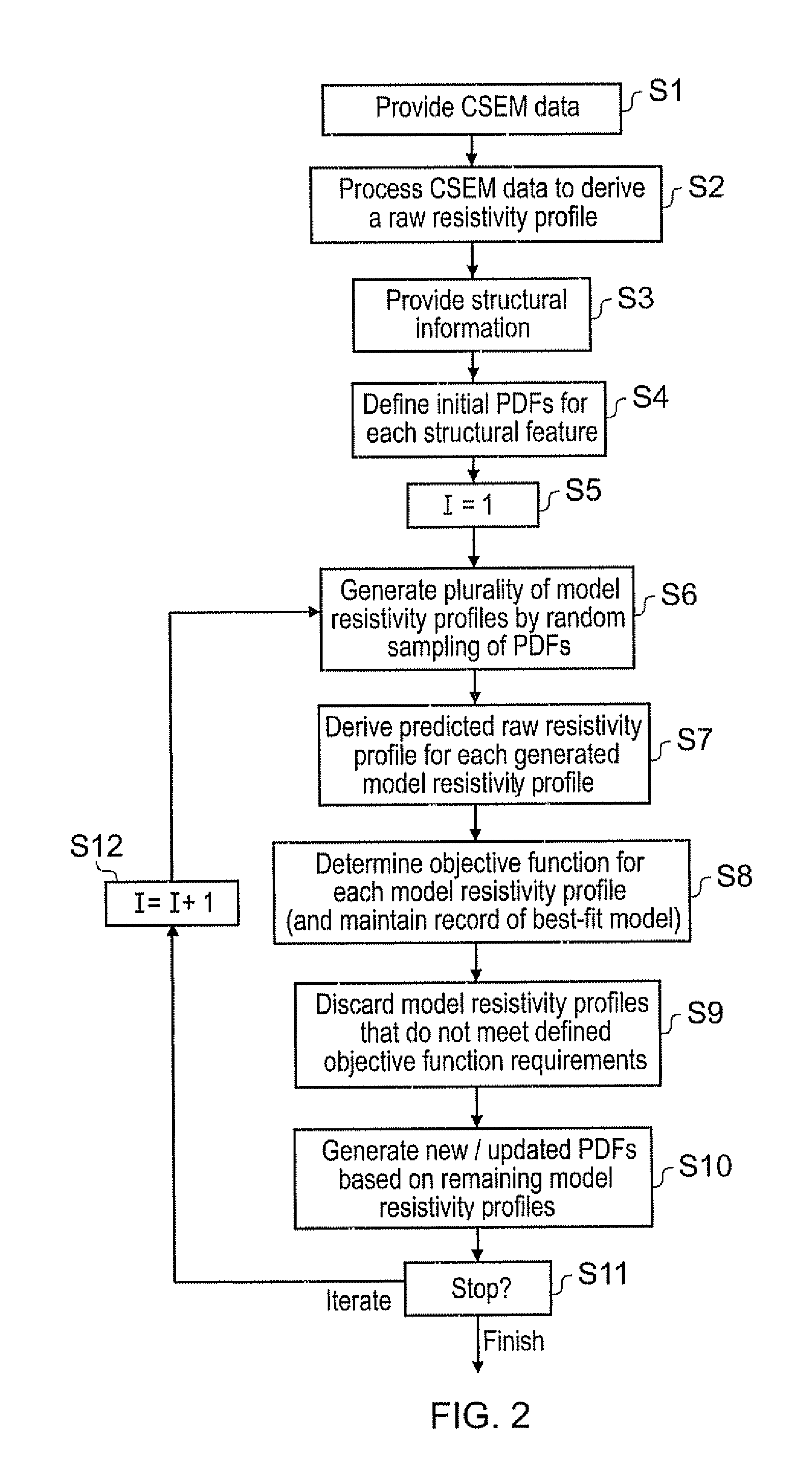
Geophysical surveying
ActiveUS20090306895A1Increase valueImprove spatial resolutionElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismology for water-loggingSeismic surveyNormal density
A method of analysing controlled source electromagnetic (CSEM) survey data to determine probability density functions (PDFs) for values of an electromagnetic parameter at locations in a subterranean region of interest is provided. Structural features in the subterranean strata are identified, e.g. from seismic survey data. An initial PDF for values of the electromagnetic parameter is then assigned to each feature. Models lo specifying values for the parameter in each structural feature are generated by sampling the PDFs. A subset of the models are deemed acceptable based on an acceptance criterion. The PDF for each feature is modified based on values for the parameter in the subset of accepted models to generate replacement PDFs for each feature. The process may be iterated a number of times to generate final PDFs for values of the electromagnetic parameter in the structural features identified in the subterranean region of interest.
Owner:PGS GEOPHYSICAL AS
Method and appartus for transforming a stratigraphic grid
A method of transforming an input stratigraphic grid SGrid which represents a region including one or more geological discontinuities is now disclosed. At least one target cell that is local to one or more geological discontinuities is transformed by displacing at least one target vertex of the target cell of the input SGrid in a selected direction that: i) is selected to approximate a local tangent of the reference horizon; and ii) is oriented from the target vertex to a representative manifold representing one of the geological discontinuities and / or an intersection between two or more of the geological discontinuities. A magnitude of a displacement by which the target vertex is moved is determined according to a non-Euclidian distance between the target vertex of the target cell of the input SGrid and the representative manifold.
Owner:ASPEN PARADIGM HLDG LLC +1
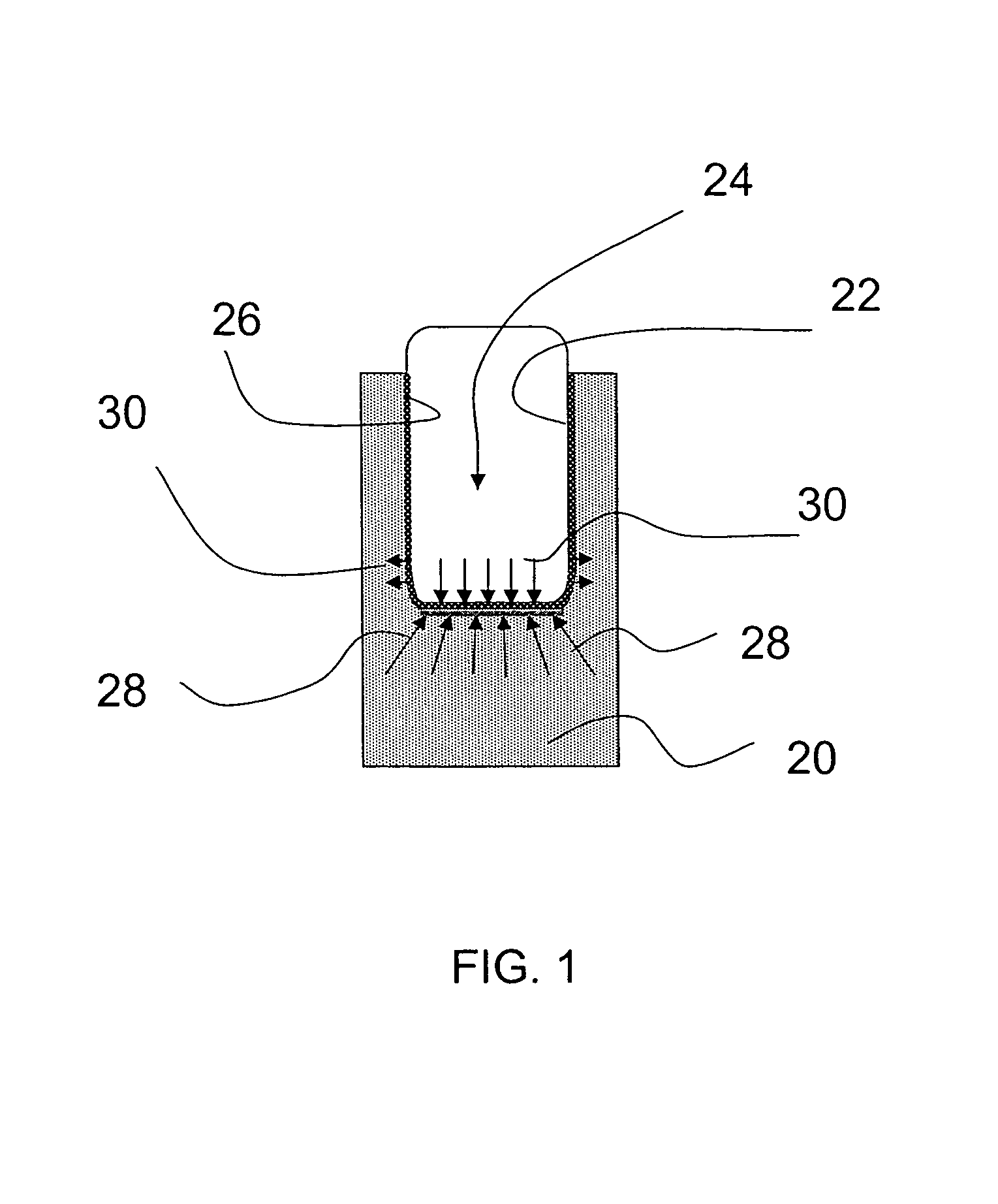
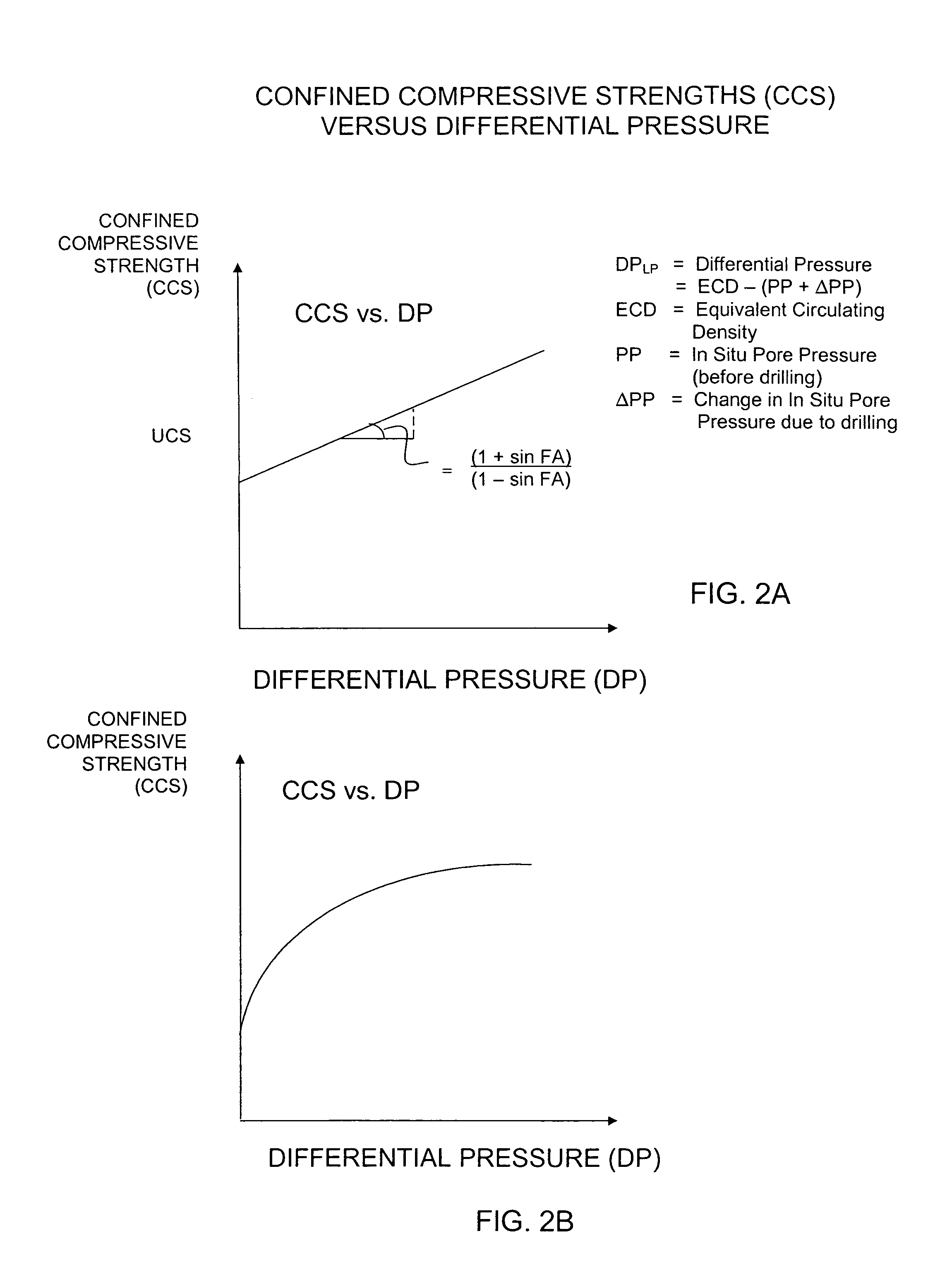
Method for estimating confined compressive strength for rock formations utilizing skempton theory
InactiveUS7555414B2Improve accuracyElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyStress concentrationWell drilling
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
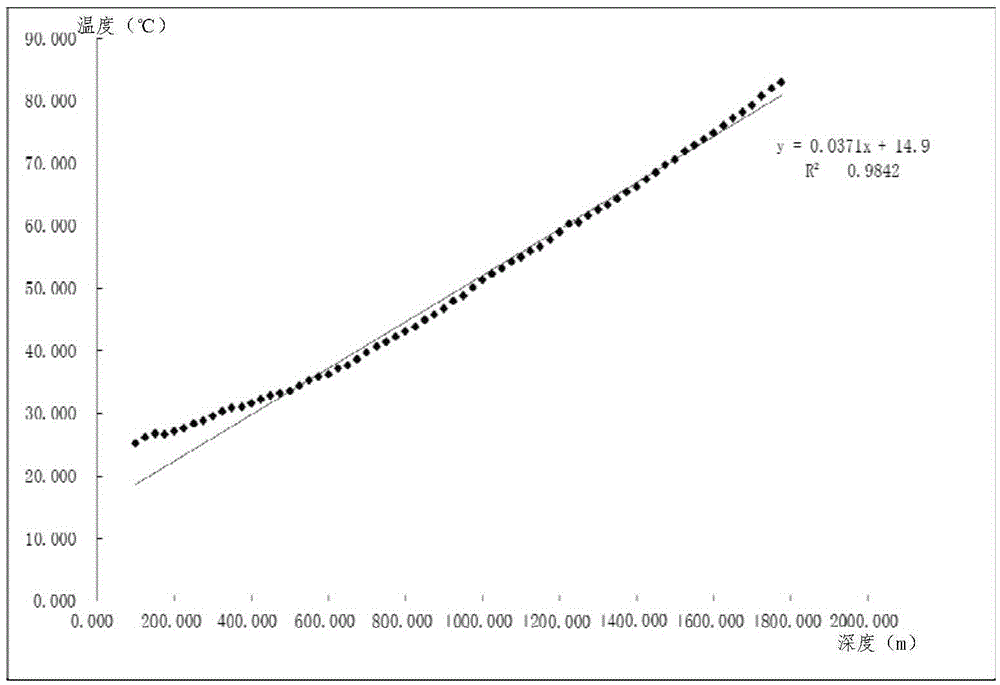
Sectional type ground temperature gradient fitting method based on stratigraphic unconformity surface
InactiveCN105652342AAccurate responseOvercoming the problem of insufficient ability to identify ground temperature anomaliesDetection/prospecting using thermal methodsComplex mathematical operationsGround temperatureEngineering
The invention discloses a sectional type ground temperature gradient fitting method based on a stratigraphic unconformity surface. The method comprises the steps of: 1) determining the distribution and burial depth of the stratigraphic unconformity surface, obtaining temperature measurement data, and drawing a ground temperature curve with the temperature and the burial depth respectively serving as a transverse coordinate and a longitudinal coordinate; 2) in the range of 0-100 m downward from the stratigraphic unconformity surface, selecting the most bending part of the ground temperature curve as a ground temperature gradient critical surface, and dividing the ground temperature curve into an upper cure and a lower curve; 3) carrying out linear fitting respectively on temperature measurement data corresponding to the upper curve and the lower curve, and obtaining an upper straight line and a lower straight line, wherein the gradients thereof are respectively the ground temperature gradients of a shallow stratum and a deep stratum and reflect the practical ground temperature field of a temperature measurement well area. The method is characterized in that according to the development characteristics of stratums in different areas, the ground temperature gradients above and below the ground temperature gradient critical surface are independently fitted, so that the ground temperature gradients of upper and lower stratums are obtained, the ground temperature field characteristics of new and old stratums are really reflected, and a reliable basis is provided for oil and gas and geothermal resources exploration, development and utilization.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
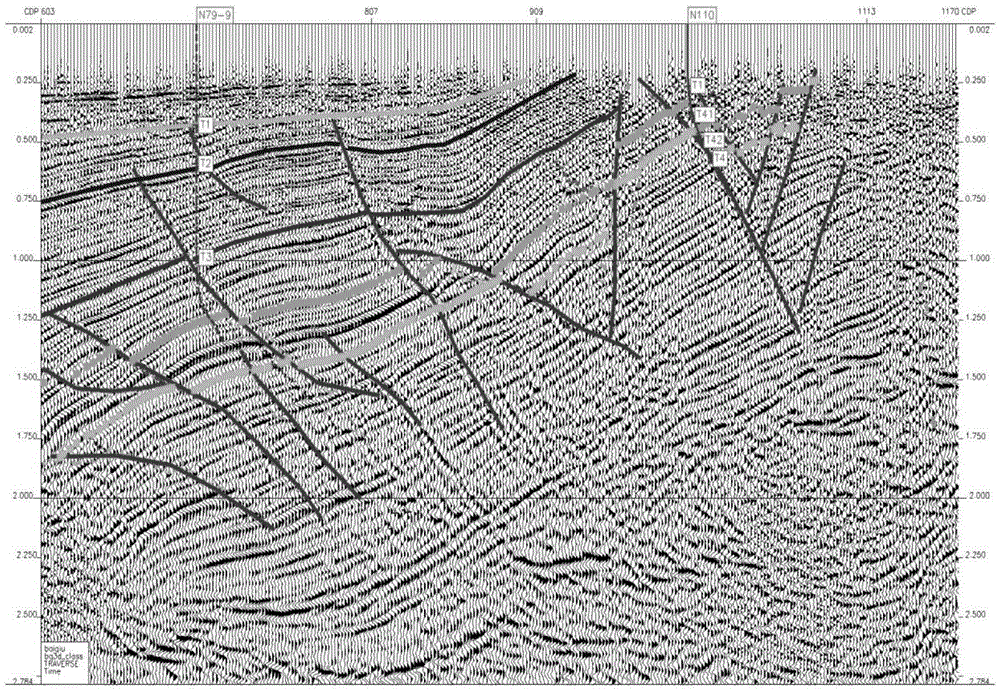
Identification method and system for complex basin edge super-stripped belt subtle trap boundary
InactiveCN104049275AAccurate descriptionFine characterizationSeismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsGeomorphologyWell logging
The invention discloses an identification method and system for a complex basin edge super-stripped belt subtle trap boundary. The identification method includes the following steps that firstly, structural features of a plane of unconformity are analyzed and defined with data of earthquakes, well drilling, well measuring, well logging and the like as the basis; secondly, a geologic model is designed, forward modeling of earthquake responses is conducted, instantaneous phase earthquake attributes are extracted along the stratum, and a stratum super-stripped line for earthquake identification is depicted; thirdly, a geologic model capable of reflecting the super-stripped concept of the stratum is selected, earthquake forward modeling is conducted, and main factors affecting an error distance are defined; fourthly, an error distance formula under the stratum super-stripped condition is established; fifthly, the stratum subtle strap boundary is described according to the stratum super-stripped line and the error distance for the earthquake attribute identification. According to the identification method and system for the complex basin edge super-stripped belt subtle trap boundary, the position of the super-stripped line for earthquake identification can be accurately described, the subtle trap boundary is quantitatively identified based on an extrapolation formula built through multi-model forward modeling, an oil-gas accumulation boundary can be easily and accurately determined, and the oil exploration risk can be effectively lowered.
Owner:中国石油化工股份有限公司胜利油田分公司勘探开发研究院西部分院
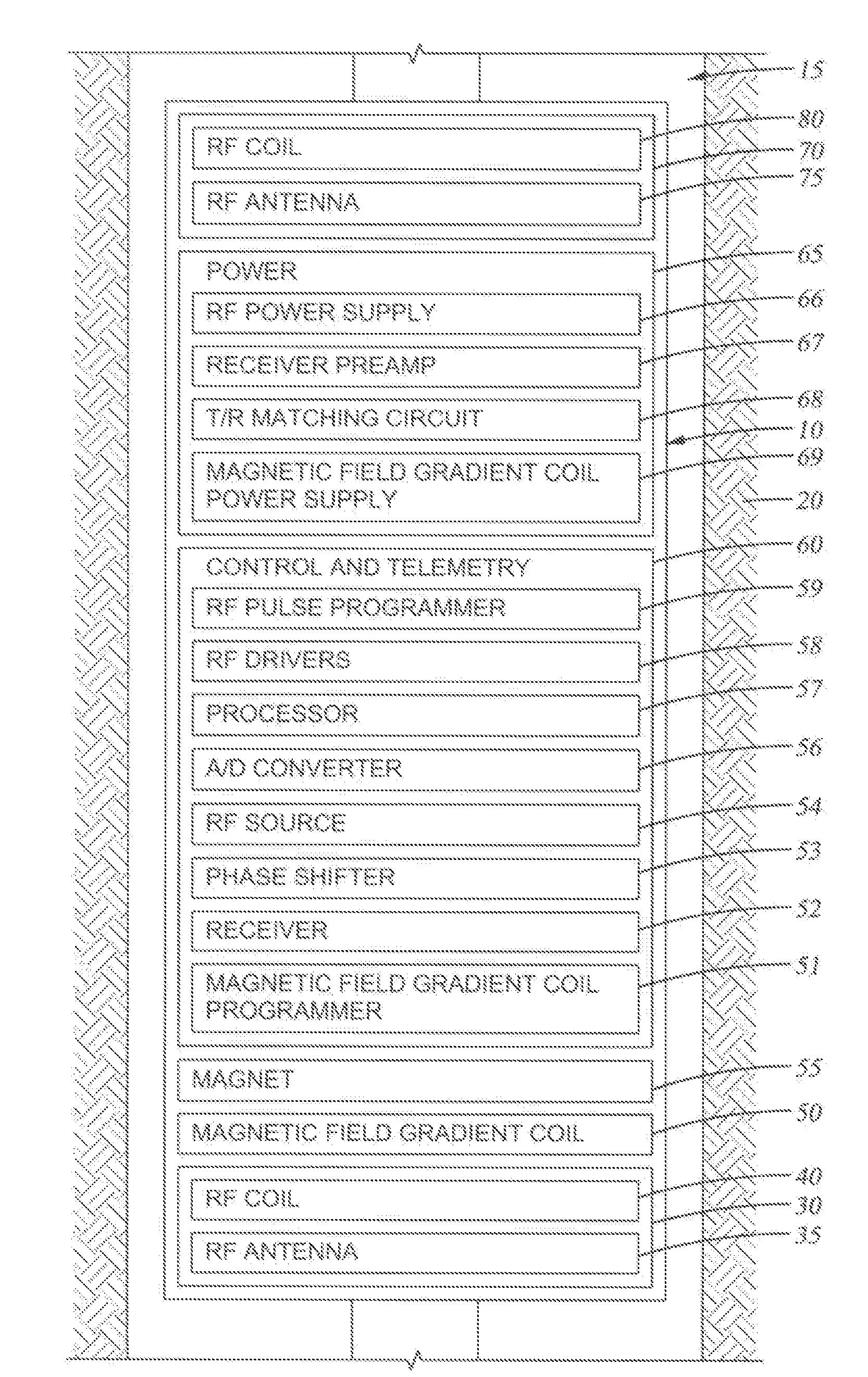
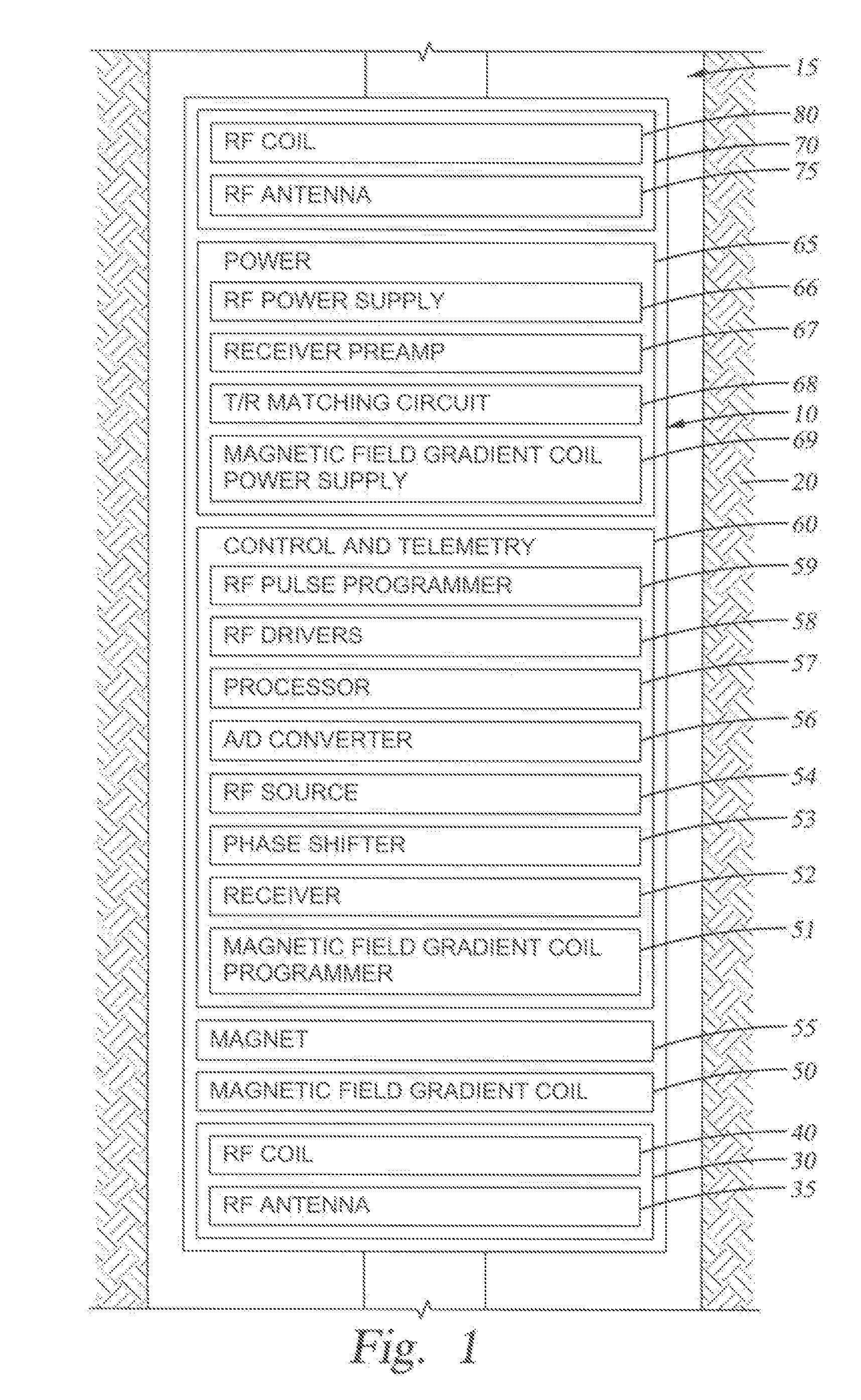
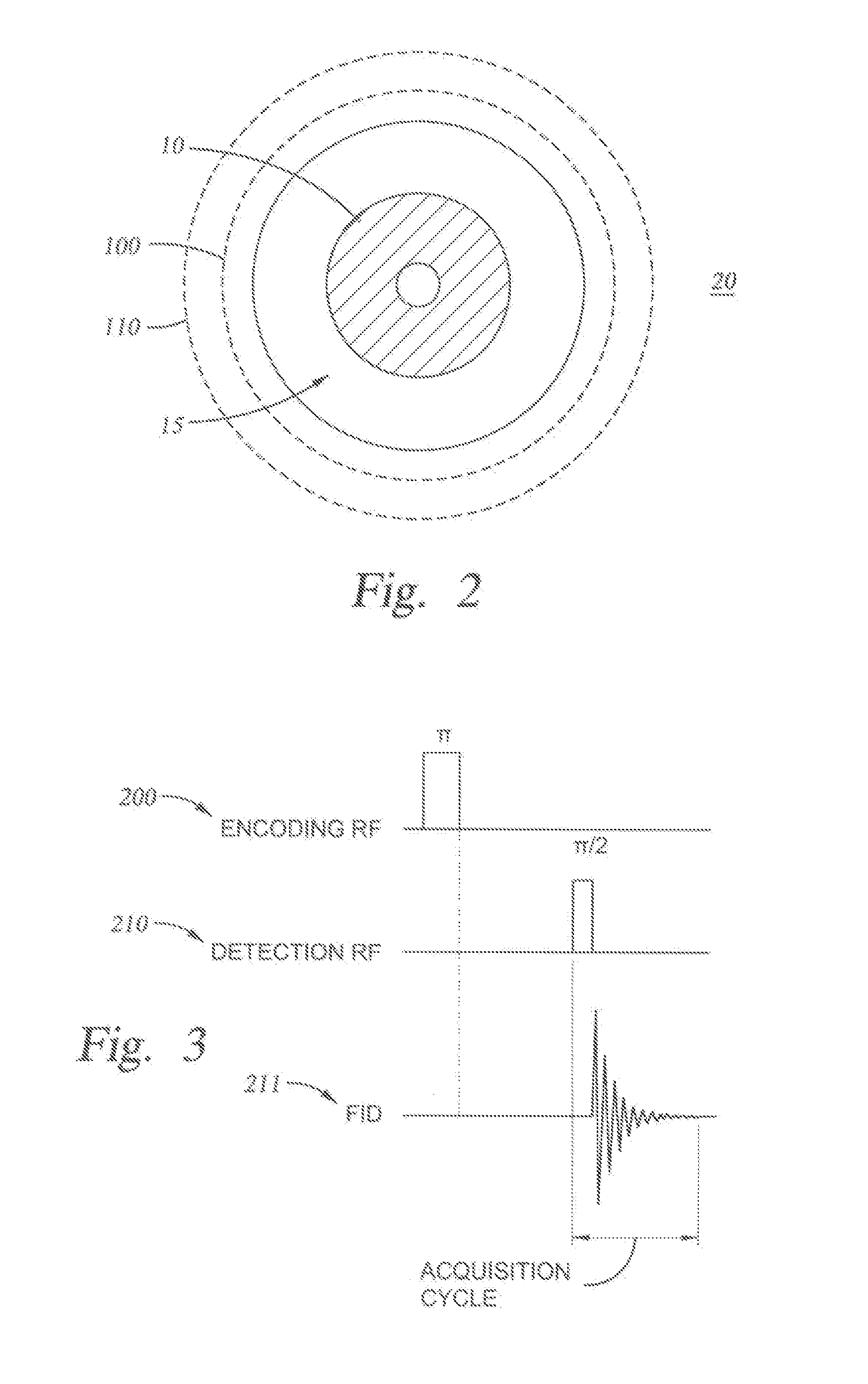
System and Method for Downhole Time-of-Flight Sensing, Remote NMR Detection of Fluid Flow in Rock Formations
ActiveUS20080136409A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingDetection using electron/nuclear magnetic resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceMagnetic resonance technique
A system and method for measuring fluid flow in a wellbore in an earth formation using time-of-flight (TOF) sensing and remote detection nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) techniques, by applying a magnetic field to the formation to polarize spins present in a portion of the formation, providing an encoding shell in the formation, selecting an encoding volume from the encoding shell, applying an encoding signal to excite the spins in the encoding volume, introducing a time delay to the encoding signal, providing a detection shell in the formation, applying a detection signal to the detection shell, detecting an NMR signal generated by the migration of spins from the encoding shell to the detection shell, and collecting TOF data corresponding to time elapsed from when a spin is encoded to when the spin reaches the detection shell.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
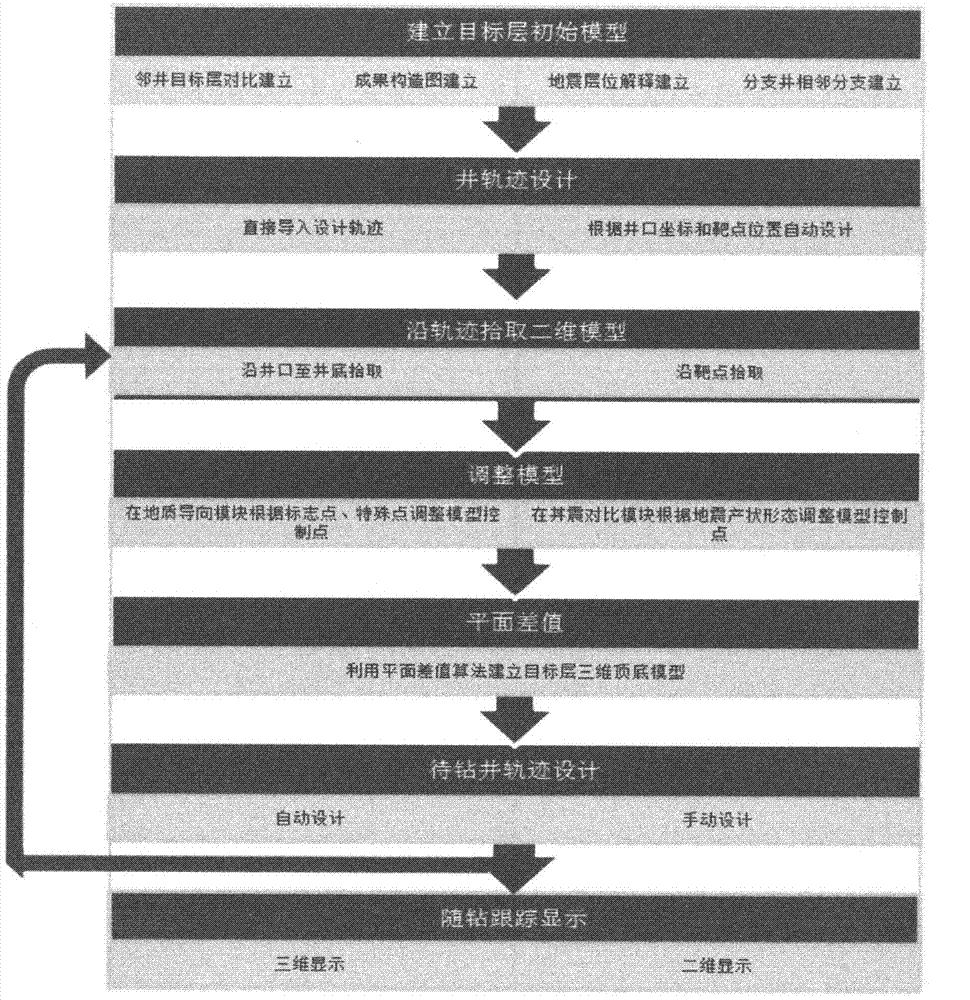
Horizontal well geosteering analysis method for designing track of well to be drilled through dynamic modeling during drilling
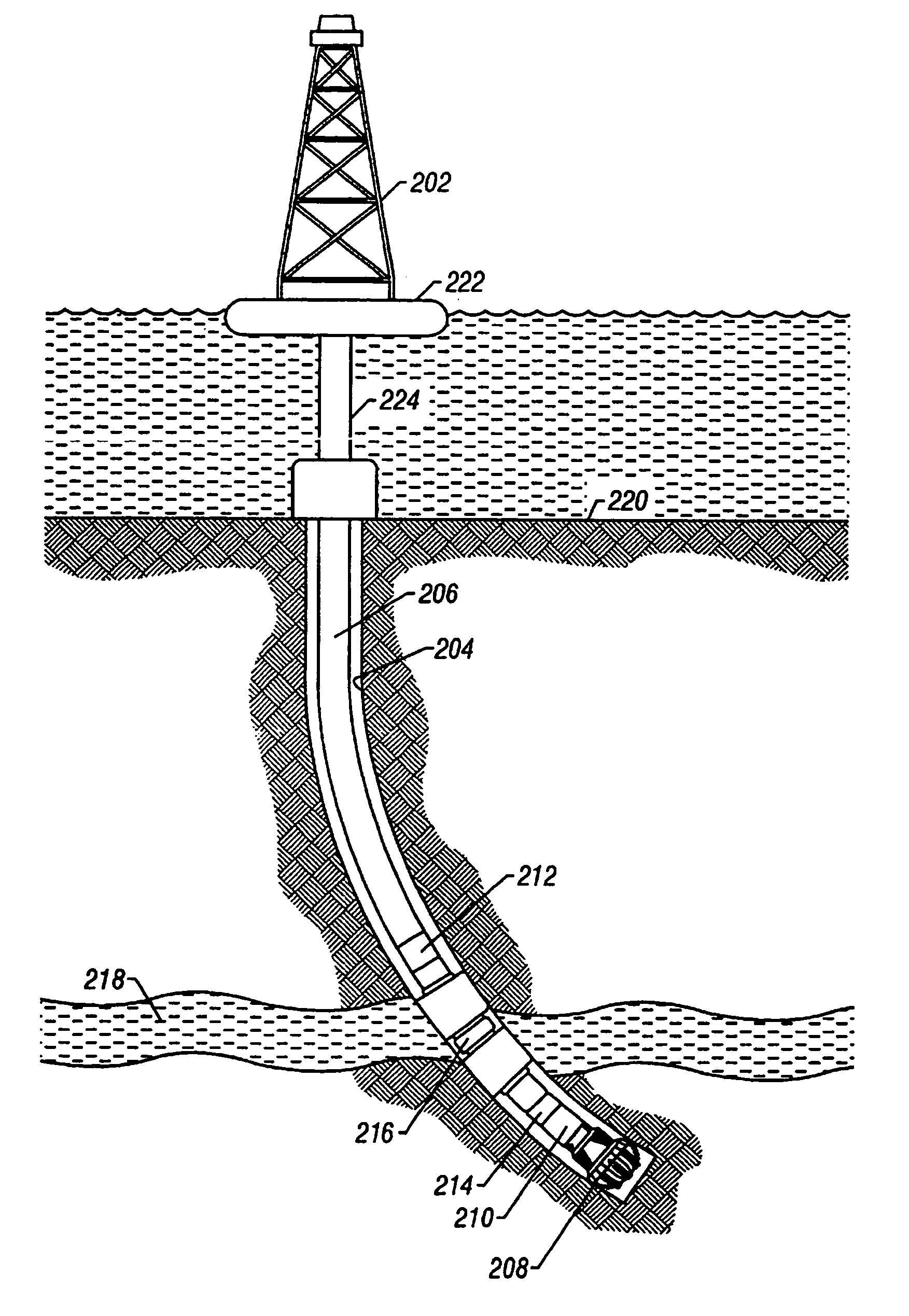
InactiveCN103774989ACognition objectiveImprove target rateDirectional drillingSpecial data processing applicationsGeosteeringHorizontal wells
The invention relates to a geosteering method for dynamic modeling during drilling and dynamic adjustment of the track in the process of horizontal well drilling of oil drilling. According to the solution, computer software is used, mutual multi-well comparison is carried out on target layer hierarchical data, target layer result structural maps, earthquake target layer pickup and multilateral well target layer data, and a plane difference algorithm is used, so that a target layer initial three-dimensional geological model is built; a two-dimensional geological model is extracted according to the track of a horizontal well which is being drilled, the direction of a drill bit is adjusted according to the spatial relation between the drilling track and the two-dimensional geological model, the vertical depth between the top and the bottom of the portion, arranged on each key point, of a target layer is obtained during drilling according to the electronic logging characteristics or the gasometry characteristics of special key points encountering a drill, such as a marker layer, a landing point, a bottom outlet, a bottom inlet, a top outlet, a top inlet and a special layer in the target layer, and the thickness uniformity principle, the three-dimensional geological model is adjusted, a two-dimensional geological model is extracted according to the track of the horizontal well which is being drilled, and the hole deviation angle of the drill bit is modified according to the dip angle provided by the two-dimensional geological model; the process is repeated, and it is ensured that the drilling direction of the drill bit is kept to be within the controllable range all the time. The hit rate and the drilling-encounter ratio of well drilling are improved, the drilling cycle is shortened, and drilling efficiency is improved.
Owner:刘俊
Method of constructing a geological model
Method of constructing a geological model of a subterranean formation formed of at least two sedimentary beds.On the basis of sparse measurements of the geometry of boundaries of beds of a subterranean formation carried out on a grid, values of the geometry of each bed at any point of the grid are calculated according to at least the following steps: a succession of coarser and coarser grids is defined, constructed on the basis of the grid of interest; then, proceeding from the coarsest grid to the grid of interest, the geometry of the boundaries of each bed is determined by solving an inverse problem initialized with the result obtained for the previous coarser grid. Next, on the basis of the completed geometry of each boundary of beds on the grid of interest, the geological model of the formation is constructed.Application especially to the exploration and exploitation of oilfields.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
A simulation method of single fracture propagation based on quasi-continuous geomechanical model
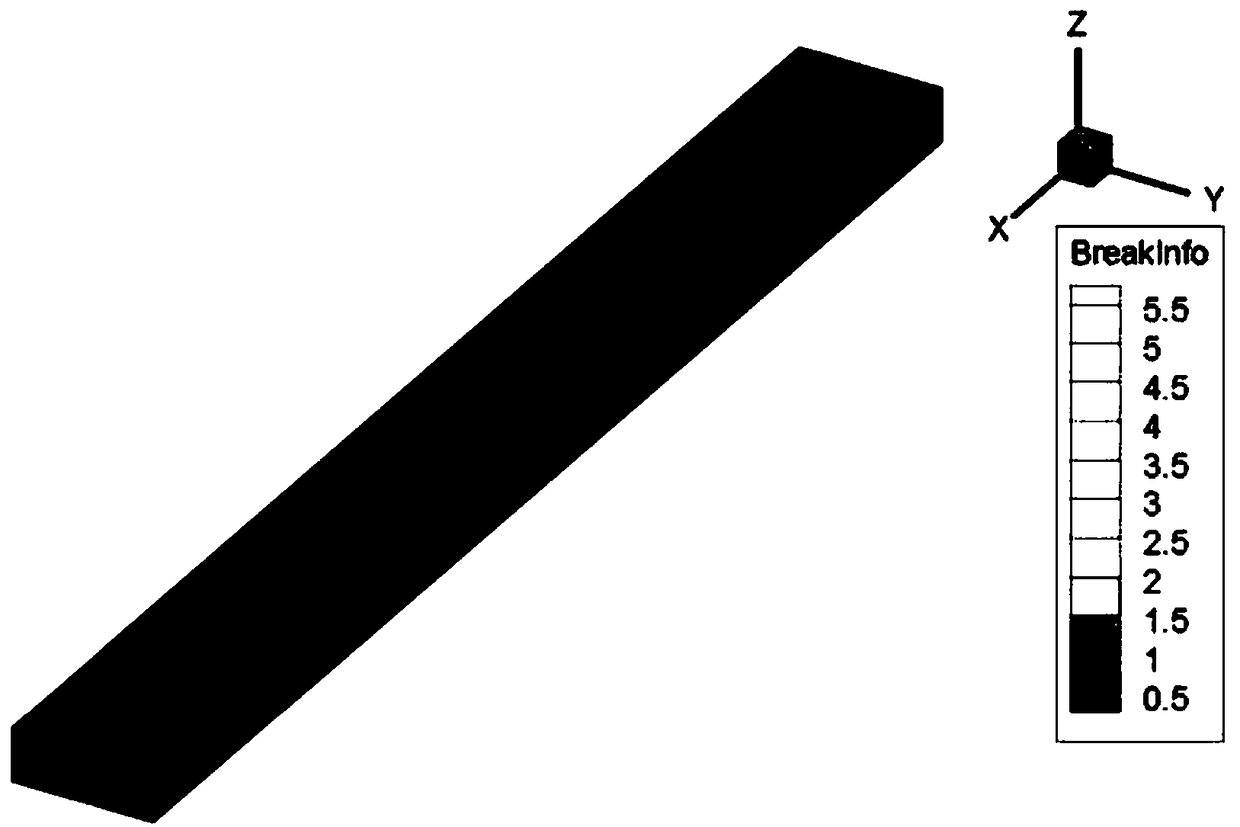
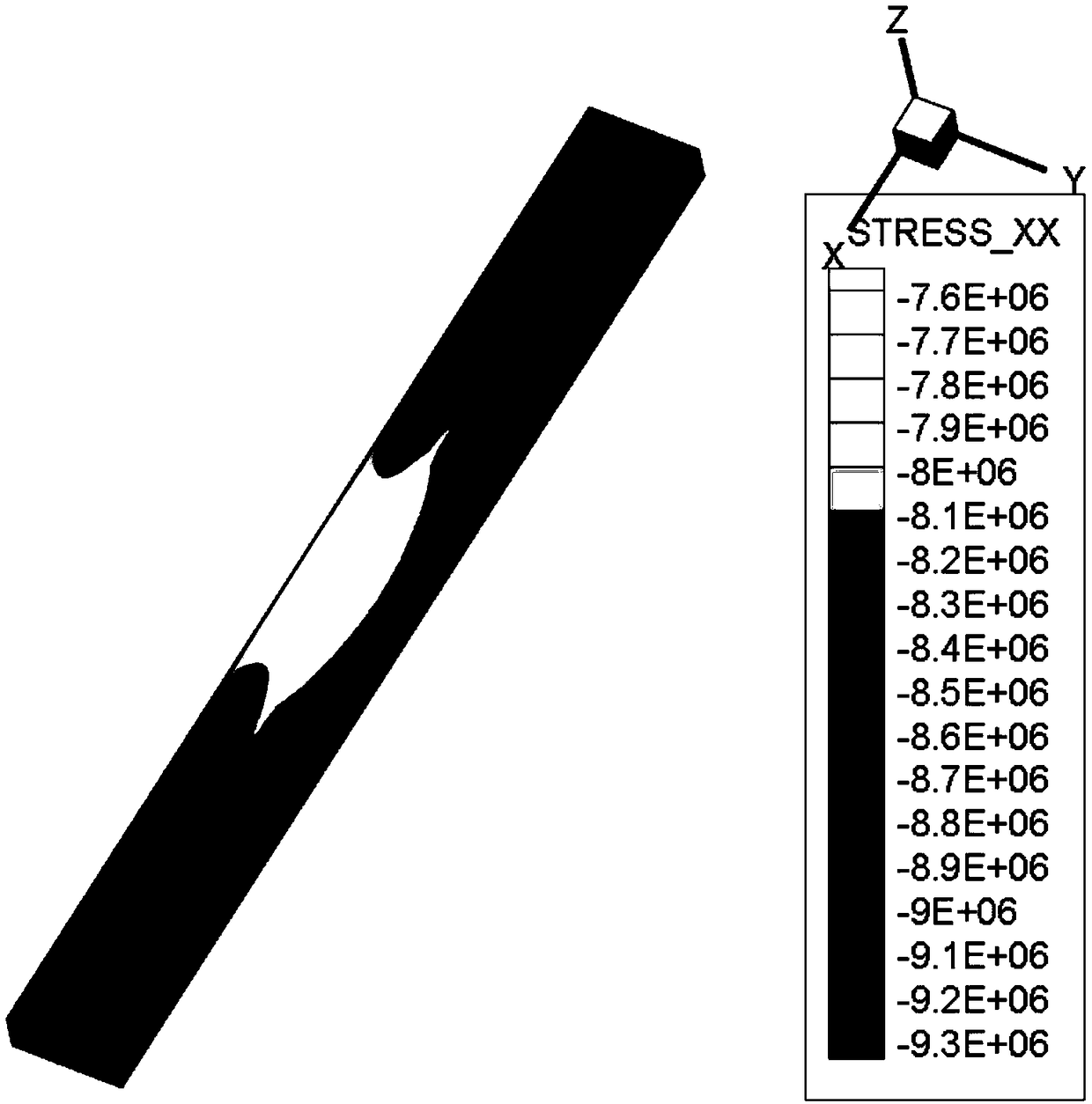
ActiveCN109241588AImprove reliabilityEasy to set upDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsStress strengthHydraulic fracturing
The invention discloses a simulation method of single propagation expansion based on a quasi-continuous geomechanical model, which comprises the following steps: acquiring geological parameters, including three-dimensional geological information and rock physical property information; Correcting petrophysical information; Establishing three-dimensional geological model of stratum; establishing FEMfluid-solid coupling model; obtaining the pressure field, displacement field, stress field and strain field of the three-dimensional geological model by solving the fluid-solid coupling equations ofthe finite element method; judging whether cracks are produced or not according to the stress strength criterion; obtaining The fracture width, permeability matrix and flexibility matrix, and then calculating the influence of fracture on pressure field and displacement field. The simulation of single fracture propagation based on quasi-continuous geomechanical model is realized. The invention hasthe advantages of quick solution, high accuracy and good reliability, and effectively solves the problem of dynamic display of fractures in the process of hydraulic fracturing simulation.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Method and device for determining the resistivity in a geological formation crossed by a cased well
InactiveUS20060015258A1Good precisionHigh resistivityElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismology for water-loggingEnvironmental geologyGeometric factor
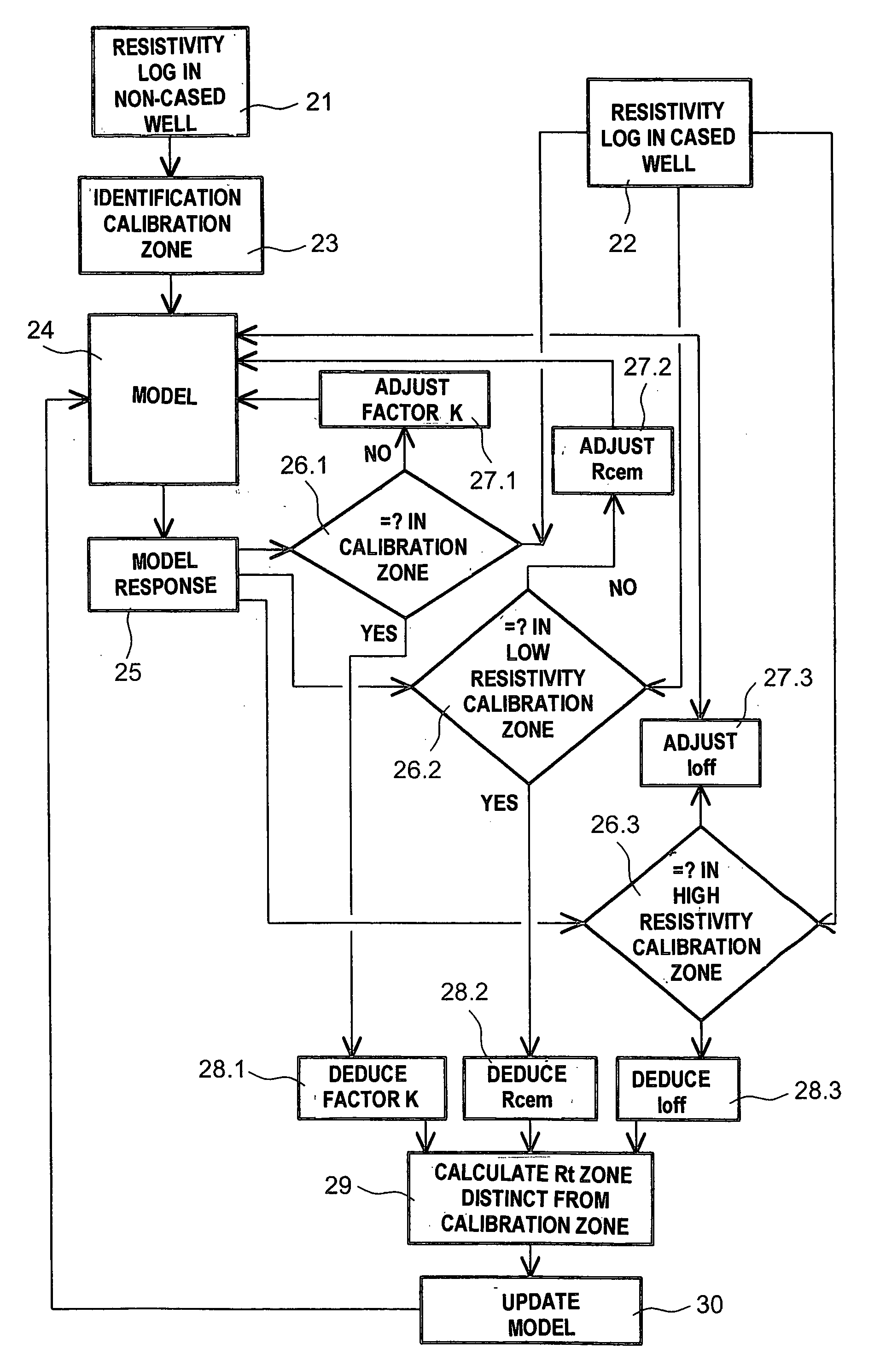
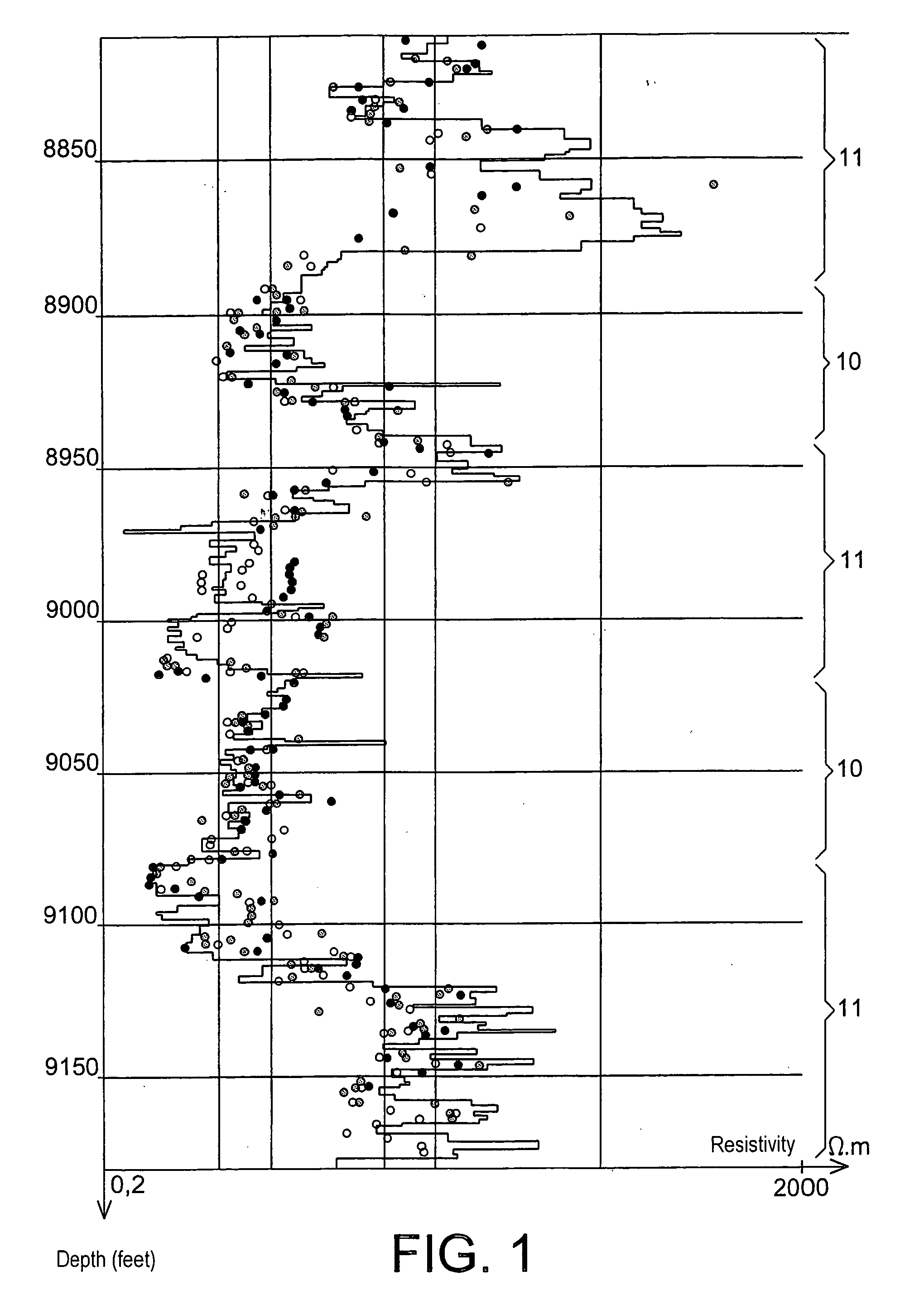
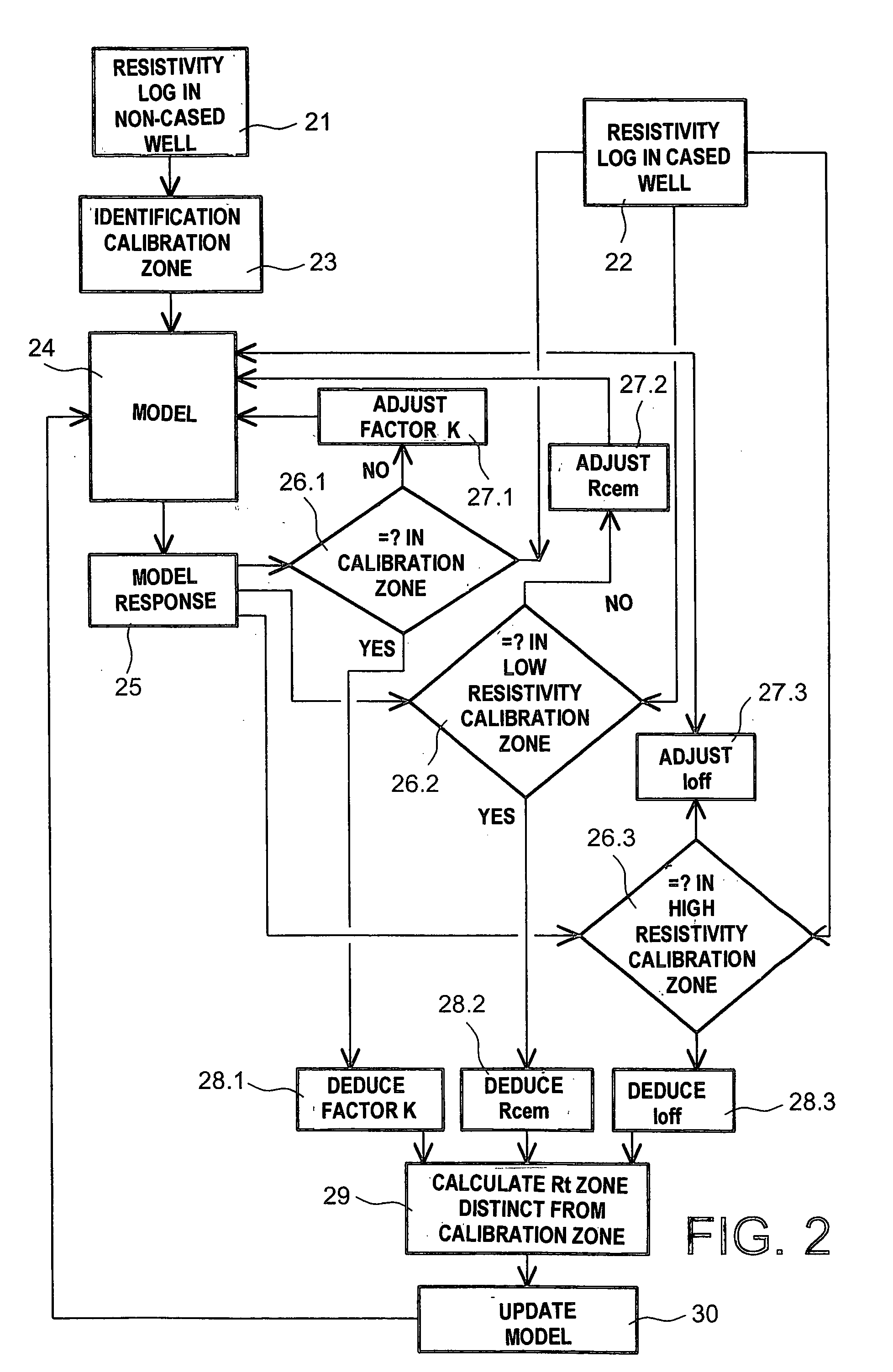
The invention concerns a method for determining the resistivity in a formation crossed by a cased well, in which one carries out at least one resistivity log in the cased well and one uses the results of at least one resistivity log in the non-cased well, carried out in the same well previously, in order to, in at least one zone (10) of the formation in which the resistivity has not changed between the cased and non-cased condition, deduce the value of a geometric factor k conditioning the resistivity and for determining, by means of said geometric factor k and the log in the cased well, the resistivity in at least one zone (11) different to the calibration zone, in which the resistivity has varied between the non-cased condition and the cased condition.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Seismic sedimentology interpretation method based on frequency-scale matching
ActiveCN103217714ASolving sediment characterization challengesEasy to operateSeismic signal processingPetroleum explorationSedimentology
The invention discloses a seismic sedimentology interpretation method based on frequency-scale matching, and belongs to the field of petroleum exploration and development. The seismic sedimentology interpretation method comprises the following steps: (1) loading post-stack seismic data, (2) carrying out phase switching, obtaining a phase seismic data body with the angle of 90 degrees, (3) confirming the average thickness of a main exploration target sand body according to well-point analysis, (4) confirming the tuning frequency of the target sand body, (5) processing the seismic data in a fractional frequency mode, obtaining a fractional frequency seismic data body reflecting the target sand body, (6) manufacturing strata slices of the fractional frequency data body, (7) interpreting the strata slices, obtaining plane distribution and evolution of the target sand body, (8) when sand bodies with various thickness levels exist, carrying out operations on the sand body at each level according to the step (4) to the step (7), (9) combining the interpretation results of the slices with the same depth of various fractional frequency bodies, and interpreting characteristics and evolution of research area sedimentary microfacies. The seismic sedimentology interpretation method based on the frequency-scale matching is used for interpretation of the thin-layer sedimentary characteristics under a seism vertical resolution ratio, remarkably improves thin-layer sedimentary seismic interpretation accuracy and is wide in application prospect.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com