Injectable hydrogels for vascular embolism
A hydrogel, medical technology, applied in the field of injectable hydrogel
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
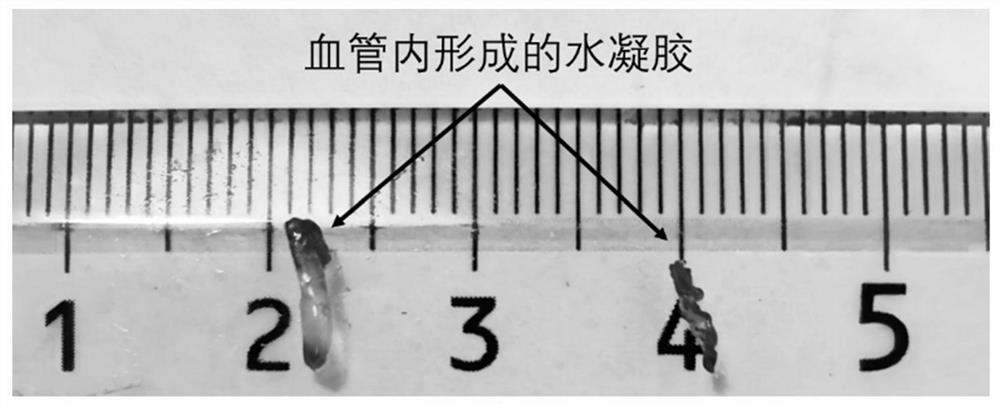
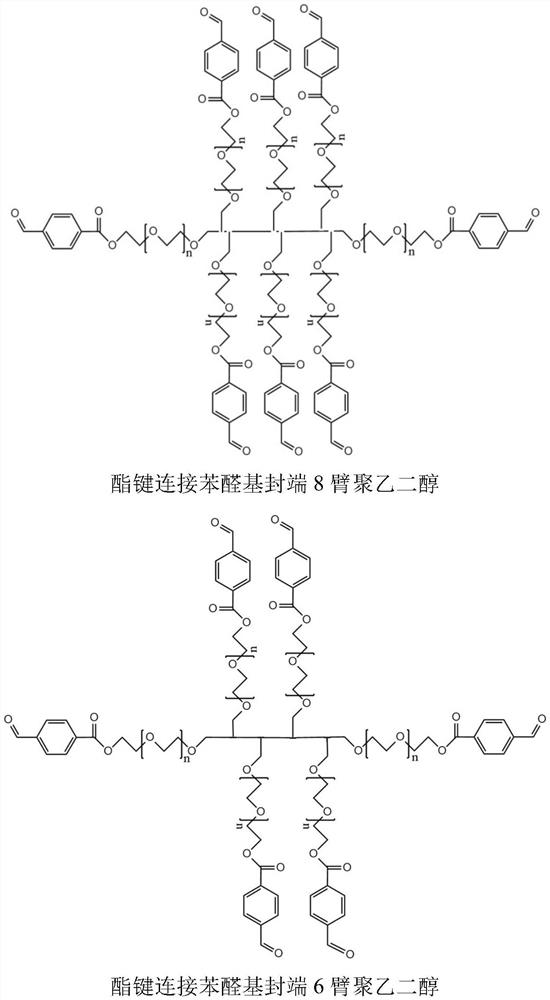
[0033] Example 1 The effect of the ratio of aldehyde groups to amino groups in the hydrogel on the intravascular gel-forming ability In order to test the intravascular gel-forming ability of different hydrogel formulations, this example uses a double syringe to inject two-component water The gel was injected into rat arteries, and the two-component hydrogel was formed by mixing liquid A and liquid B through a double syringe. First, 200 mg of ester bond-linked phenylaldehyde-terminated 8-arm polyethylene glycol (molecular weight: 15 kDa) was dissolved in 1 mL of phosphate buffer (pH 5.6) as liquid A. According to different molar ratios shown in Table 1, borax buffer (pH9.2) solutions with different contents of polylysine and polyethyleneimine (M.W.1.8K) were configured as B solution. A and B solutions were mixed and injected to obtain hydrogels, and hydrogel precursors of different formulations were injected into rat renal arteries to test the ability to form gels in blood vess...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Example 2 The ratio of aldehyde groups to amino groups in the hydrogel and the influence of PEG concentration on the vascular swelling rate of the gel The swelling rate of the gel in blood is very important for effective vascular embolism, and the swelling rate is too low (negative swelling) The hydrogel shrinks after gelling, which prevents the hydrogel from filling the blood vessel and effectively embolizing it. This example examines the swelling rate of the hydrogel in simulated blood, and the swelling rate of the gel meeting the embolism condition should be greater than 0.
[0038] According to the different final concentrations of polyethylene glycol shown in Table 2, different masses of ester-linked benzaldehyde-terminated 8-arm polyethylene glycol (molecular weight 15 kDa) were dissolved in 1 mL of phosphate buffer (pH 5.6 ), as liquid A. According to the different molar ratios shown in Table 2, the borax buffer (pH9.2) solutions with different contents of polyl...
Embodiment 3
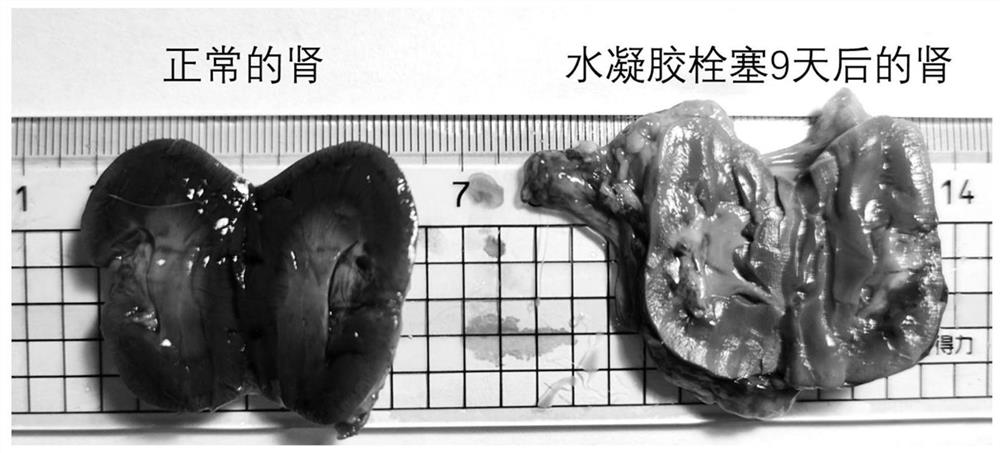
[0043] The stability of the gel in the blood is very important for effective vascular embolization, which needs to last for a period of time to achieve good results. When the gel stability time is too short, the time to form an effective embolism is too short, resulting in poor effect. The inventor's early research found that the molar ratio of the amino group of polylysine to the aldehyde group of polyethylene glycol affects the stability of the hydrogel (the amino group of polylysine and the 8-PEG-amide-BA aldehyde in the aqueous solution environment in vitro When the molar ratio of the base is greater than or equal to 0.4, the stability of the hydrogel exceeds one month), this example investigates the stability of the hydrogel in simulated blood. First, 200 mg of ester-linked benzaldehyde-terminated 8-arm polyethylene glycol (molecular weight: 15 kDa) was dissolved in 1 mL of phosphate buffer (pH 5.6) as liquid A. According to different molar ratios shown in Table 3, borax...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com