Mesoscopic modeling-based multi-scale prediction method for hygrothermal aging performance of plant fiber/polylactic acid composite material
A composite material and plant fiber technology, which is applied in the direction of testing material strength, material thermal analysis, and material analysis by applying stable tension/pressure, which can solve the problems of ignoring fiber/matrix interface separation and multi-scale sufficient reaction analysis.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0026] The multi-scale prediction method for the moisture-heat aging performance of the plant fiber / polylactic acid composite material based on mesoscopic modeling of the present invention is further described in detail:
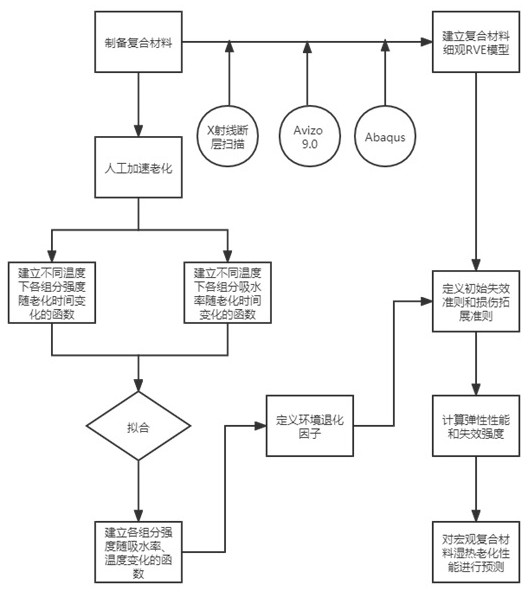
[0027] A multi-scale prediction method for hygrothermal aging properties of plant fiber / polylactic acid composites based on mesoscopic modeling, such as figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0028] 1) plant fiber / polylactic acid composite material preparation and aging test: the present invention selects jute fiber as filling phase, selects degradable polylactic acid as base material, jute fiber and polylactic acid particle are removed moisture in vacuum oven, with alkali / Silane coupling agent is processed jute fiber, and according to the ratio of 1:9 (ratio described in this embodiment is only to illustrate model establishment, the present invention is applicable to any ratio) jute fiber and polylactic acid particle are fully mixed to obtain jut...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com