Viscosity-reducing pressure-driving method for deep low-permeability heavy oil reservoir
A viscous reduction technology for heavy oil reservoirs, applied in earthwork drilling, wellbore/well components, production fluids, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient energy supplementation, rapid production decline, etc., and improve the sweep coefficient and oil displacement efficiency , low cost, conducive to the effect of popularization and application
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
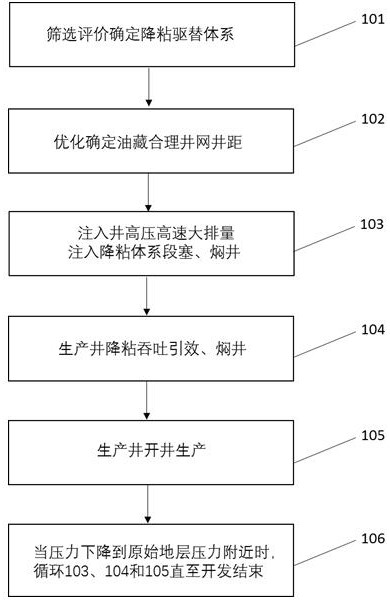
[0037] Such as figure 1 As shown, the viscosity reduction and pressure flooding method of the deep low-permeability heavy oil reservoir comprises the following steps:
[0038] Step 1. Screening and evaluation to determine the viscosity-reducing displacement system: take the viscosity-reducing rate and the reduction of oil / water interfacial tension as the main screening and evaluation indicators; the determined viscosity-reducing displacement system meets the following conditions: the organic chlorine content is 0.0%, and the appearance is a homogeneous liquid , no impurity, no irritating smell, pH value between 6.0-9.0; viscosity reducer and reservoir fluid are tested for compatibility, after compatibility, the viscosity reduction rate is not less than 90%, and the interfacial tension is 1×10 -1 Below mN / m.
[0039] Step 2: Optimizing and determining the well pattern and spacing of the reservoir for viscosity reduction and pressure flooding: according to the geological condit...
Embodiment 2
[0047] The viscosity-reducing pressure flooding method of the deep low-permeability heavy oil reservoir comprises the following steps:
[0048] Step 1. Screening and evaluation to determine the viscosity-reducing displacement system: take the viscosity-reducing rate and the reduction of oil / water interfacial tension as the main screening and evaluation indicators; the determined viscosity-reducing displacement system meets the following conditions: the organic chlorine content is 0.0%, and the appearance is a homogeneous liquid , no impurity, no irritating smell, pH value between 6.0-9.0; viscosity reducer and reservoir fluid are tested for compatibility, after compatibility, the viscosity reduction rate is not less than 90%, and the interfacial tension is 1×10 -1 Below mN / m.
[0049] Step 2: Optimizing and determining the well pattern and spacing of the reservoir for viscosity reduction and pressure flooding: according to the geological conditions and development status of th...
Embodiment 3
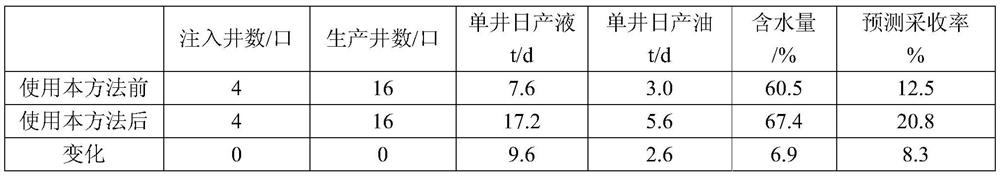
[0057] The Shasichunxia 3 sand formation in Wang 152 block of Wangjiagang Oilfield is deep low-permeability heavy oil. Exploration well Wang 152 in the work area was drilled in April 2011. Industrial oil flow was obtained in hot test, and then 6 evaluation wells were deployed and drilled. To break through the production capacity barrier, a variety of mining methods were adopted in the trial production process: conventional steam injection thermal recovery, fracturing reconstruction + steam injection thermal recovery, and viscosity reduction cold recovery huff and puff all failed to achieve a breakthrough in production capacity. In April 2020, the Wang 152-X6 well group carried out a viscosity reduction pilot test, which broke through the productivity barrier. The average daily oil production of a single well in the well group was 3.3t / d, which was 3 times that of the previous measures, and the production effect was significantly improved. In order to further efficiently produce...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com