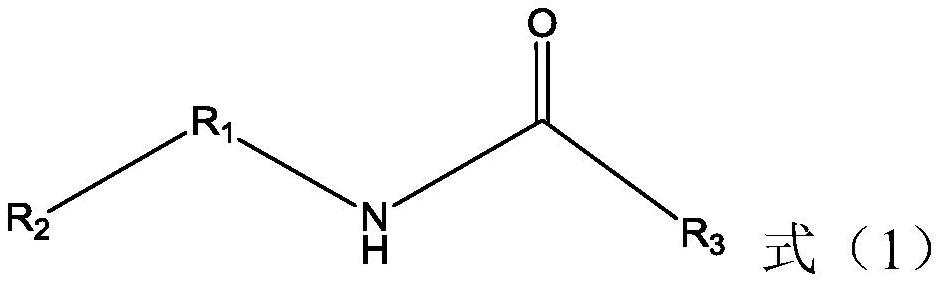
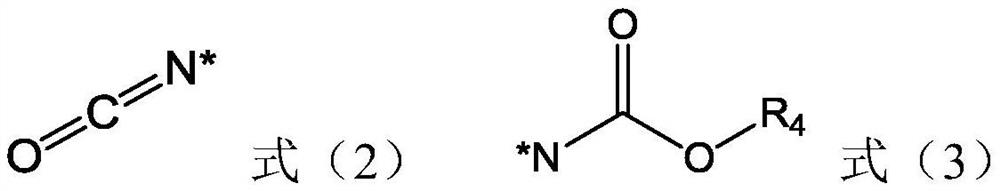
Lithium ion battery
A lithium-ion battery, carbon number technology, applied in secondary batteries, secondary battery repair/maintenance, circuits, etc., can solve problems such as poor performance of lithium-ion batteries
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example 1-7
[0120] Under 25 DEG C, the raw material compound A in Table 1 and the raw material compound B were carried out amidation reaction with the molar ratio of 1:1 respectively for 10 hours, and triethylamine was used as the acid-binding agent in the reaction (triethylamine and the raw material compound A The molar ratio is 1.5:1), and compound 1, compound 2, compound 3, compound 4, compound 6, compound 7 and compound 12 were prepared by column chromatography purification after the reaction.
[0121] Table 1
[0122]
[0123]
[0124]
Embodiment 1
[0135] 1) Preparation of electrolyte
[0136] Mix ethylene carbonate (EC), diethyl carbonate (DEC) and ethyl methyl carbonate (EMC) according to the mass ratio EC:DEC:EMC=1:1:1, and then add lithium hexafluorophosphate (LiPF 6 ) to a molar concentration of 1mol / L, and then adding compound 1 of 0.001% by weight of the total mass of the electrolyte;
[0137] 2) Preparation of positive electrode
[0138] The cathode active material LiNi 0.8 co 0.1 mn0.1 o 2 , the conductive agent conductive carbon black Super-P, carbon nanotubes (CNT) and the binder polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) are uniformly mixed according to the weight ratio of 96.5:1.5:0.5:1.5, and then they are dispersed in N-formaldehyde base-2-pyrrolidone (NMP) to obtain the positive electrode slurry; apply the positive electrode slurry evenly on both sides of the aluminum foil, dry, calender and vacuum dry, and use an ultrasonic welder to weld the aluminum lead wire to obtain the positive electrode , the thickness o...
Embodiment 2-19 and comparative example 1-3
[0147] Carry out according to the method for embodiment 1, difference is:
[0148] The types of positive active materials in the positive electrode of lithium-ion batteries are different;
[0149] The content of PVDF is different (when the content of PVDF in the positive electrode material increases, the amount of positive electrode active material is reduced in a corresponding proportion, and when the content of PVDF decreases, the amount of positive electrode active material is increased in a corresponding proportion);
[0150] The type and content of the compound represented by the formula (1) added to the electrolytic solution differ.
[0151] The details are shown in Table 2-4.
[0152] The results of Examples 1-19 and Comparative Examples 1-3 are shown in Table 2-4.
[0153] Table 2
[0154]
[0155] Note: % of compound content and PVDF content are all weight %; / means no corresponding substance added.
[0156] According to the comparison of the results of Exampl...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com