Advanced microbiome therapy engineered for serotonin production in vivo
A technology of microbes and drugs, applied in the field of advanced microbiome therapy engineered to produce serotonin in the body, can solve problems such as the spike in 5-HT levels
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0149] Example 1: Genetically Modified E. coli Cells Expressing Biosynthetic Pathways for 5-HT Production
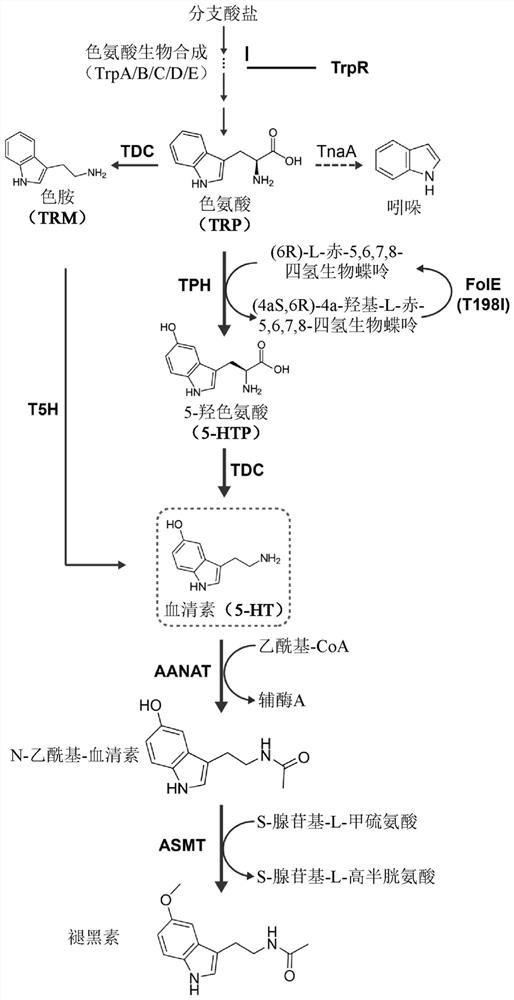
[0150] The 5-HT biosynthetic pathway was introduced into cells of E. coli Nissl to establish a synthetic serotonin pathway to catalyze the two sequential metabolic steps of conversion of TRP to 5-HTP and then 5-HTP to 5-HT ( figure 1 ). Identification of the optimal combined enzymes for catalyzing these two metabolic steps was determined by expressing and determining the 5-HT yields obtainable from the combination of TPH and TDC genes.
[0151] 1.1 Method
[0152] 1.1.1 The modified E. coli cells are engineered as follows, refer to Table 1:
[0153] The host strain Escherichia coli Nissl 1917 was purchased from Ardeypharm GmbH, Germany The gene for green fluorescent protein (GFP, GenBank: CAH64882.1) was placed under the control of a strong constitutive promoter (component BBa_J23101, Registry of Standard Biological Parts, www.parts.igem.org) and integrated into the...
example 2
[0161] Example 2: Enhancement of 5-HT and TRM production in genetically modified E. coli cells of the invention by increasing tryptophan pathway flux
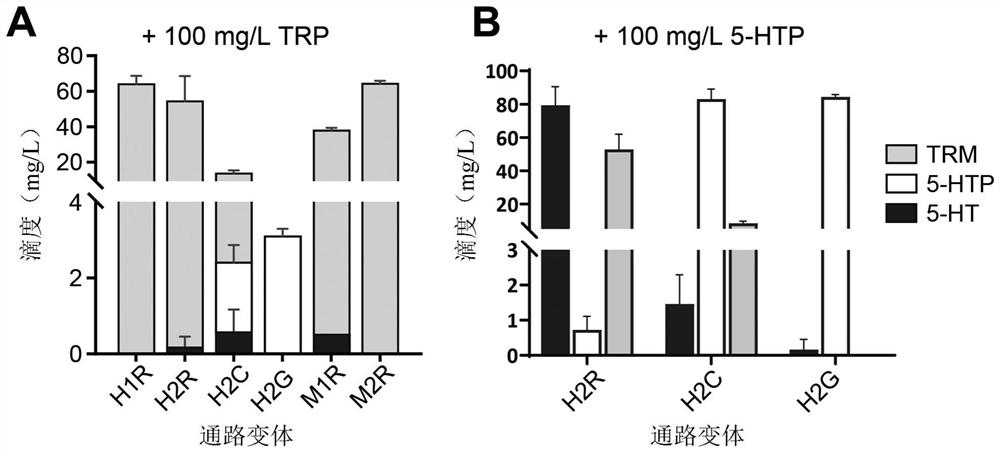
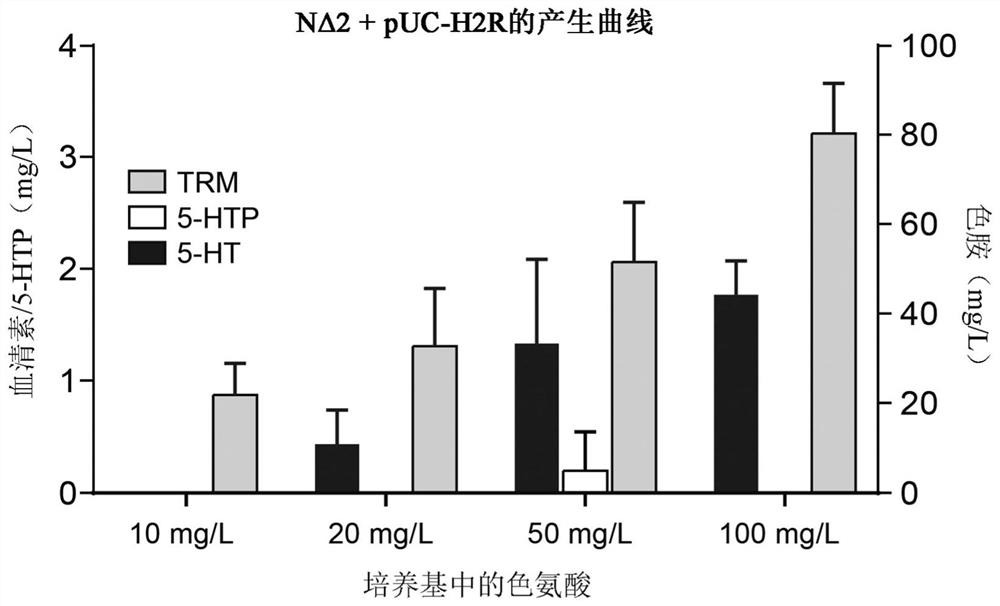
[0162] Increased availability of the tryptophan pathway substrate tryptophan was shown to increase 5-HT production in the 5-HT producing strains of the invention ( image 3 ). Based on this observed increase, the endogenous pool of TRP available in the genetically engineered cells of the invention is increased by inactivation of the endogenous genes encoding the tryptophan repressor trpR and the tryptophanase tnaA , such as enhancing tryptophan pathway flux.
[0163] 2.1 Method:
[0164] Knockdown of trpR and tnaA from the host E. coli Nissl genome was performed using CRISPR / Cas9 as described in (Mehrer et al., 2018). Briefly, a two-plasmid system consisting of an inducible cas9 / λ-Red expression plasmid and a guide RNA (gRNA) plasmid was used to introduce double-strand breaks at desired gene loci in the host genome. The gRN...
example 3
[0168] Example 3: Genetically Modified E. coli Strains of the Invention Exhibit Stable 5-HT Production
[0169] When the 5-HT operon encoding the 5-HT biosynthetic pathway is cloned into a multi-copy plasmid in the host cells of the present invention, 5-HT production depends on the stability of the plasmid. Stability is preferably not dependent on plasmid genes conferring antibiotic resistance. Two solutions for conferring plasmid stability were compared; the pUC-based plasmid backbone (as in Examples 1 and 2) and the two native plasmids of E. coli Nissl pMUT1 (Blum-Oehler et al., 2003).
[0170] 3.1 Method:
[0171] A high copy number 5-HT producing plasmid (pUC-H2R) was modified by introducing a synthetic copy of the essential bacterial gene infA downstream of the H2R pathway operon. The corresponding infA gene in the host genome was knocked out using the protocol described in Example 2.1 in order to generate E. coli Nissler strain NΔ3 (ΔtrpR, ΔtnaA, ΔinfA).
[0172] The ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com