Application of tobacco mosaic virus in stimulation of polarization of macrophages into M1 type macrophages
A technology of tobacco mosaic virus and macrophages, which is applied in the field of immunotherapy, can solve the problems of replication infection and injury, and achieve the effect of avoiding the risk of infection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
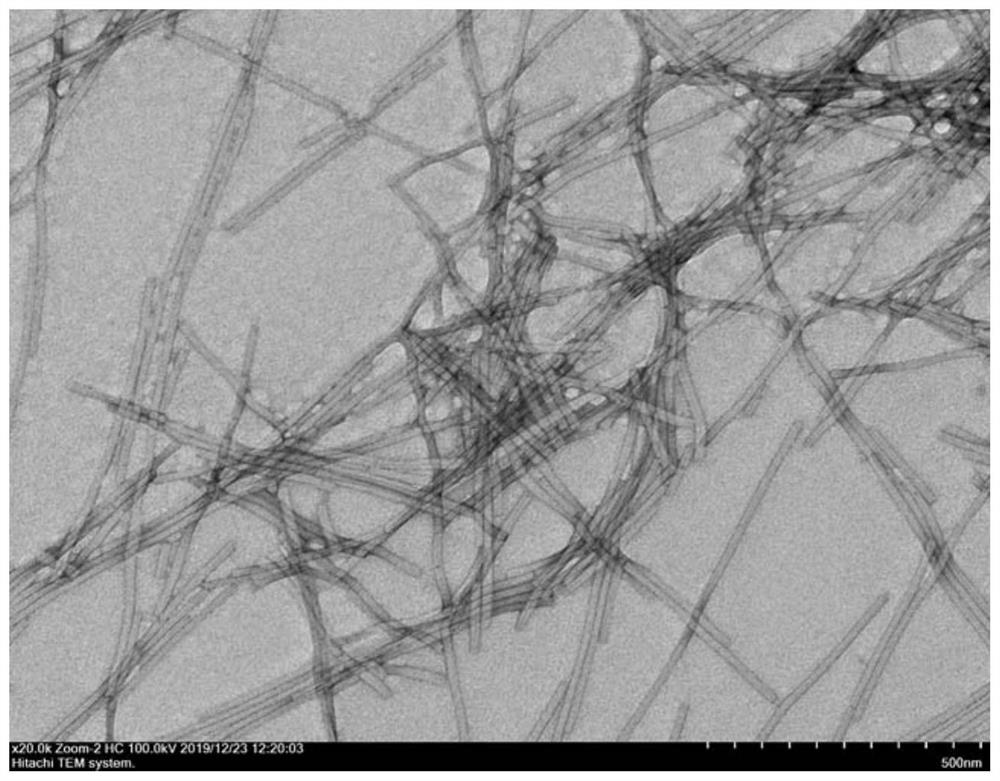
[0039] The acquisition of embodiment 1 tobacco mosaic virus
[0040]Obtain tobacco mosaic virus (G.Xie, S.Gao, J.Ou, M.Zhu, M.Wu, X.Ju, Z.Li, Y.Tian, Z.Niu, Conjugating peptides by the method of prior art onto 1D rodlike bionanoparticles forenhanced activity against gram-negative bacteria. Nano Lett. 21, 1722-1728 (2021)). The method is as follows:
[0041] (1) Place the leaves of Nicotiana benthamiana infected with tobacco mosaic virus in a juice extractor, add PBS (pH 7.4) and β-mercaptoethanol (0.2-0.3%) with a concentration of 10 mM, and fully pulverize them into homogenate.
[0042] (2) Collect the homogenate and filter it with cotton cloth to collect the filtrate. The filtrate was centrifuged at 8000 rpm at 4°C for 40 minutes to remove unfiltered fine leaf foam.
[0043] (3) Collect the supernatant. Under ice-water bath conditions, a mixture of chloroform and n-butanol (1:1) equal to the volume of the filtrate was slowly added to the filtrate, and the stirring was...
Embodiment 2
[0049] A certain amount of tobacco mosaic virus was added to the mouse macrophage cell line RAW 264.7, so that the final concentrations were 5, 25 and 100 μg / mL, respectively, under normal cell culture conditions (37 ° C, 5% CO 2 , saturated humidity) for 24 hours. In this experiment, unstimulated mouse macrophage RAW 264.7 was used as negative control, RAW264.7 stimulated by bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and IFN-γ was used as positive control, and all other experimental steps were the same. After incubation, the cells were blown down and collected, and labeled with a fluorescently labeled anti-CD86 antibody. Finally, CD86 was detected using flow cytometry + RAW 264.7 ratio. The results showed that, compared with unstimulated RAW 264.7 cells, the percentage of CD86 positive cells in RAW 264.7 cells gradually increased with the increase of the concentration of tobacco mosaic virus (attached figure 2 ).
Embodiment 3
[0051] A certain amount of tobacco mosaic virus was added to the mouse macrophage cell line RAW 264.7 so that the final concentration was 100 μg / mL, under normal cell culture conditions (37°C, 5% CO 2 , saturated humidity) for 24 hours. The stimulated macrophages were immunofluorescently stained to mark CD86 protein, and the expression of CD86 protein on the surface was observed by laser confocal microscope (attached image 3 ). The results showed that compared with unstimulated RAW 264.7 cells, the surface of RAW 264.7 cells stimulated with TMV expressed more M1 macrophage marker CD86 protein.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com