Damage identification method of flexible material based on acoustic emission technology
An acoustic emission technology and flexible material technology, applied in the field of non-destructive testing, can solve the problems of complex manufacturing process of flexible substrates, poor interface between fibers and substrates, loss of material strength and stiffness, etc., to achieve reliable evaluation, high reduction accuracy, The effect of good time-frequency local characteristics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
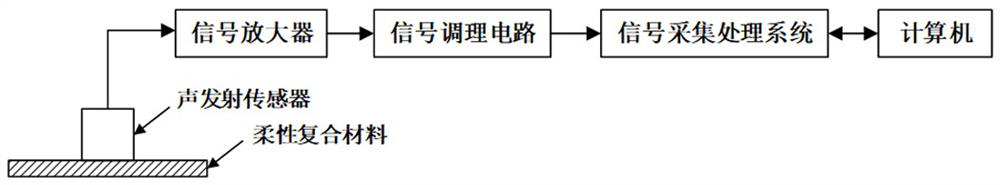
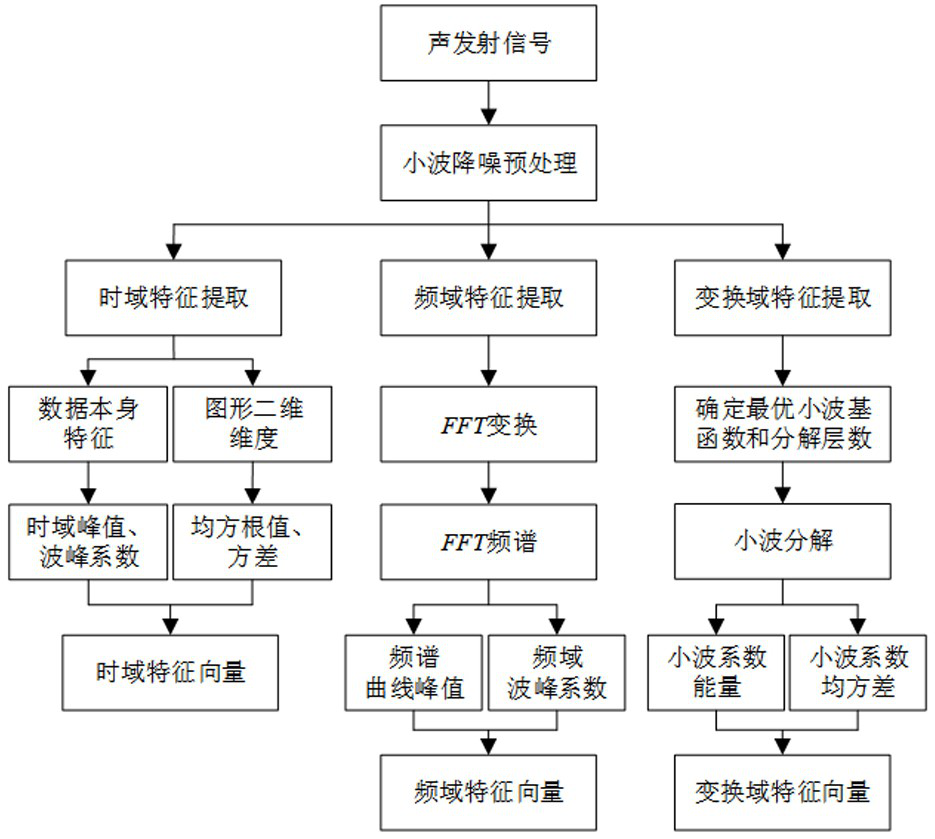
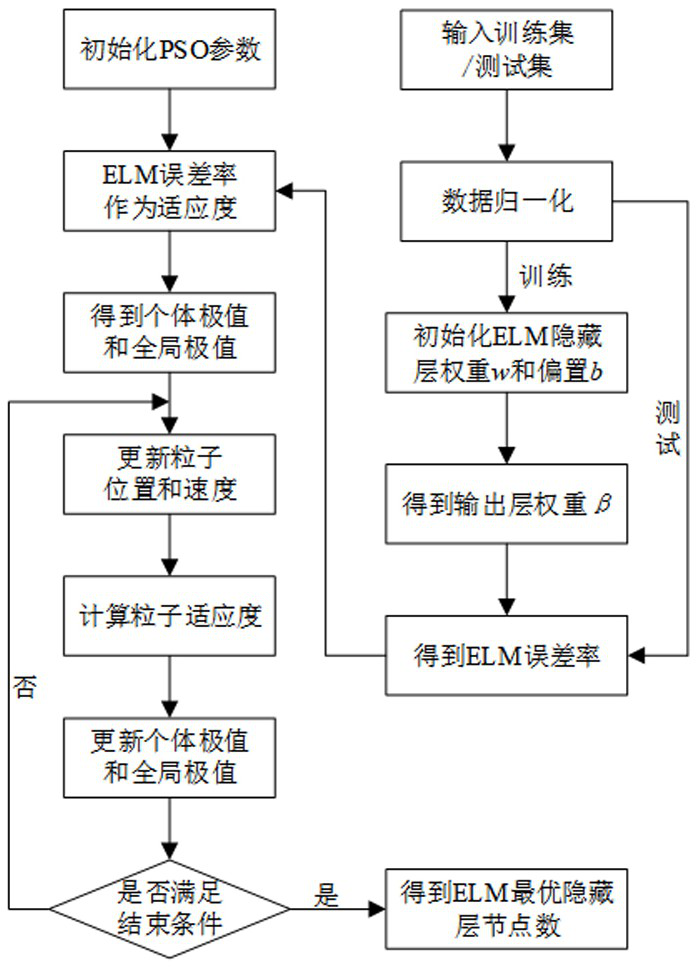
[0039] The damage identification method for flexible materials based on acoustic emission technology described in the present invention mainly uses the extreme learning machine algorithm of particle swarm optimization to identify different damages through acoustic emission detection, and then analyzes and discusses the classification results. The extreme learning machine is a neural network algorithm with simple parameter settings and is widely used. The algorithm randomly sets the weight between the input layer and the hidden layer and the threshold between the neurons in the hidden layer, and does not need to be adjusted during the training process. The only optimal solution can be obtained by setting the number of hidden layer nodes. However, the hidden layer parameters randomly generated by the extreme learning machine algorithm will cause poor generalization performance of the network. In order to improve the prediction accuracy, it is necessary to increase the number of h...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com