Method for improving killing of German cockroaches by metarhizium anisopliae through interfering genes and application of method
A technology of Blattella germanica and Metarhizium anisopliae, applied in application, genetic engineering, plant gene improvement, etc., can solve the problems of slow insecticidal speed, low lethality, poor host selectivity, etc., and achieve increased sensitivity and improved poison killing effect of effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
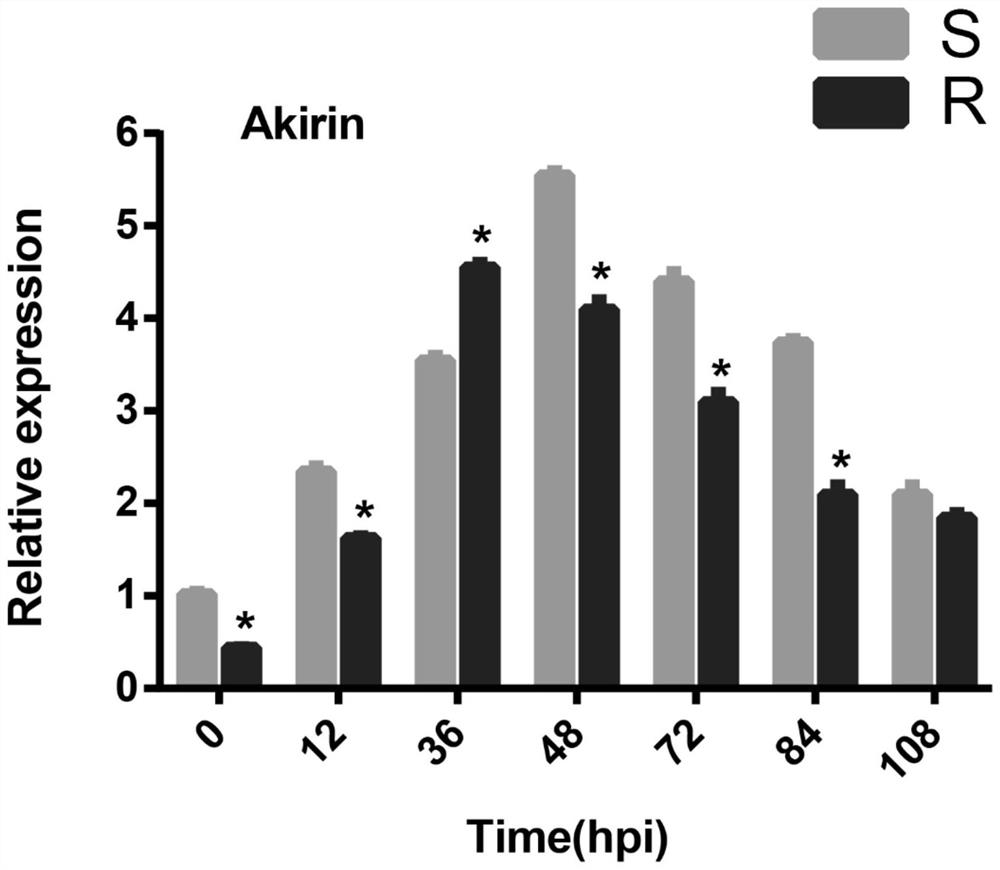
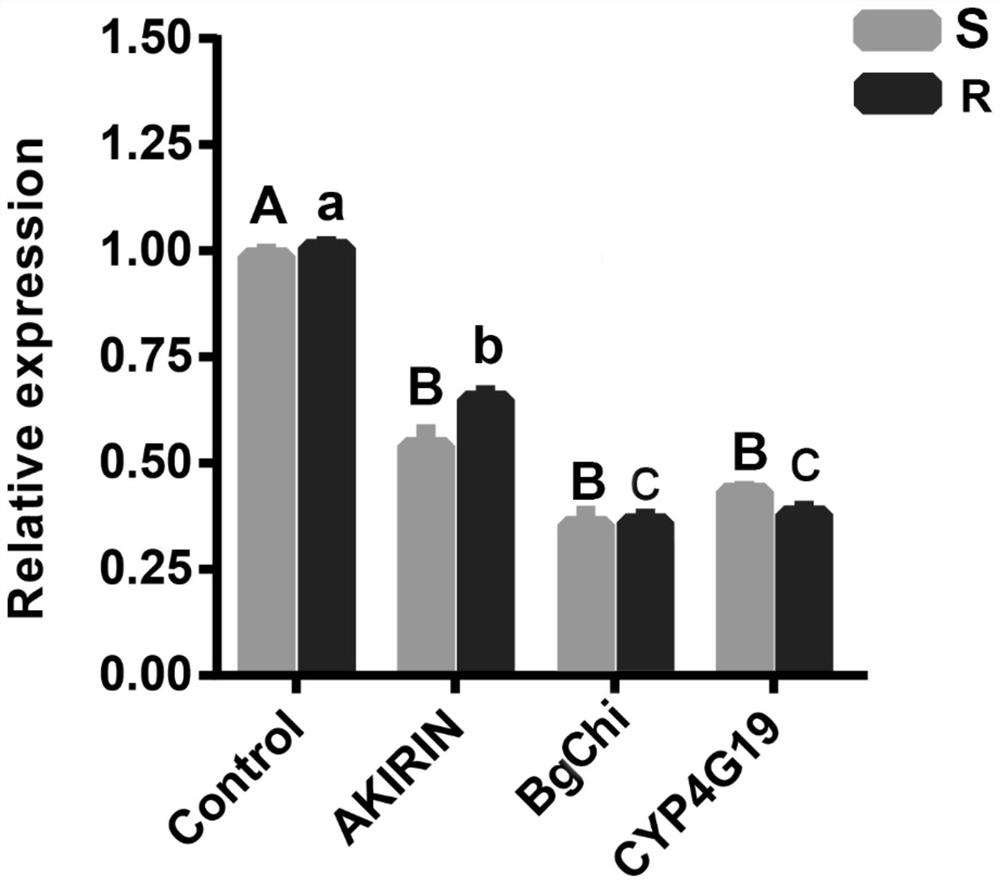
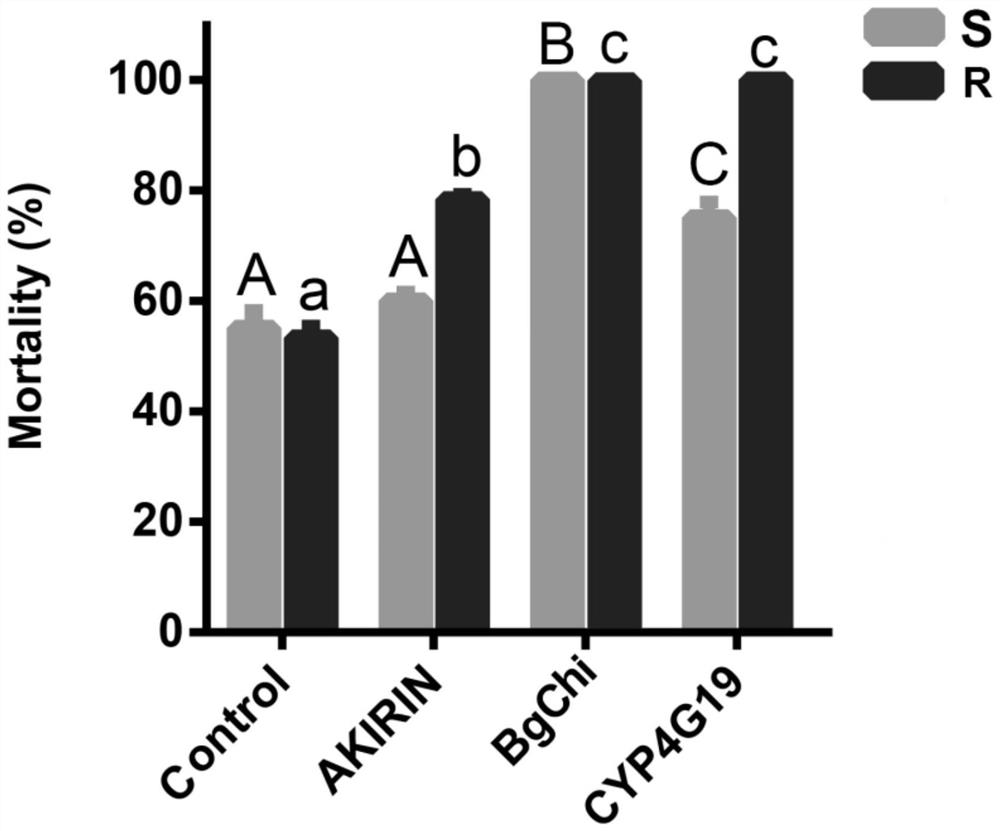
[0078] 1. Observe the changes of Akirin gene expression in different time periods after the German cockroach sensitive strain (S) and German cockroach resistant strain (R) are infected with Metarhizium anisopliae, and verify the immune function of the Akirin gene.
[0079] After Blattella germanica was infected with Metarhizium anisopliae, collect the whole worms of S and R strains of Blattella germanica at 12h, 36h, 48h, 72h, 84h, 108h after the infection of the control group and Metarhizium anisopliae, and treat Blattella germanica with 75% alcohol. Disinfect. The treated worms were cut off with sterilized scissors and tweezers to remove the wings and antennae, and rinsed three times in PBS to remove impurities. The obtained tissues were used for the extraction of total RNA. Reverse transcription and cDNA synthesis were performed on the RNA samples extracted above, and the RNA concentration was adjusted to be consistent before inversion, and the samples of the two strains w...
Embodiment 2
[0122] 1. Detect the changes of Bgchi gene expression at different time periods after the German cockroach sensitive strain (S) and German cockroach resistant strain (R) are infected with Metarhizium anisopliae, and verify the immune effect of the Bgchi gene (GenBank accession number: KJ789158).
[0123] (1) Primer design
[0124] In this example, the Bgchi gene, an immune gene related to the German cockroach's resistance to pathogenic fungi, was selected, and Primer5.0 was used to design primers to obtain the following primer sequences:
[0125]
[0126] (2) RNA extraction
[0127] After Blattella germanica was infected with Metarhizium anisopliae, the whole worms of S and R strains of Blattella germanica were collected from the control group and 12h, 36h, 48h, 72h, 84h, and 108h after infection with Metarhizium anisopliae. The german cockroaches were disinfected with 75% alcohol. The treated worms were cut off with sterilized scissors and tweezers for wings and antennae...
Embodiment 3
[0169] 1. Changes of CYP4G19 gene expression after Blattella germanica infection with Metarhizium anisopliae
[0170] (1) Primer design
[0171] The CYP4G19 gene (GenBank accession number: AY176056.1) selected in this embodiment is an immune gene related to the defense against pathogenic fungi by Blattella germanica. Primers were designed with Primer5.0 to obtain the following primer sequences:
[0172]
[0173] (2) RNA extraction
[0174] After Blattella germanica was infected with Metarhizium anisopliae, the whole worms of S and R strains of Blattella germanica were collected from the control group and 12h, 36h, 48h, 72h, 84h, and 108h after infection with Metarhizium anisopliae. The german cockroaches were disinfected with 75% alcohol. The treated worms were cut off with sterilized scissors and tweezers for wings and antennae, and rinsed three times in PBS to remove impurities. The obtained tissues were used for the extraction of total RNA.
[0175] RNA extraction ki...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com