Multi-scale link prediction method and system based on hierarchical link mode
A link mode and prediction method technology, applied in the field of network topology, can solve problems such as large memory overhead and computational complexity, inability to capture hierarchical structure, lack of data adaptability, etc., to improve link prediction performance, solve network too sparse, The effect of improving prediction performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
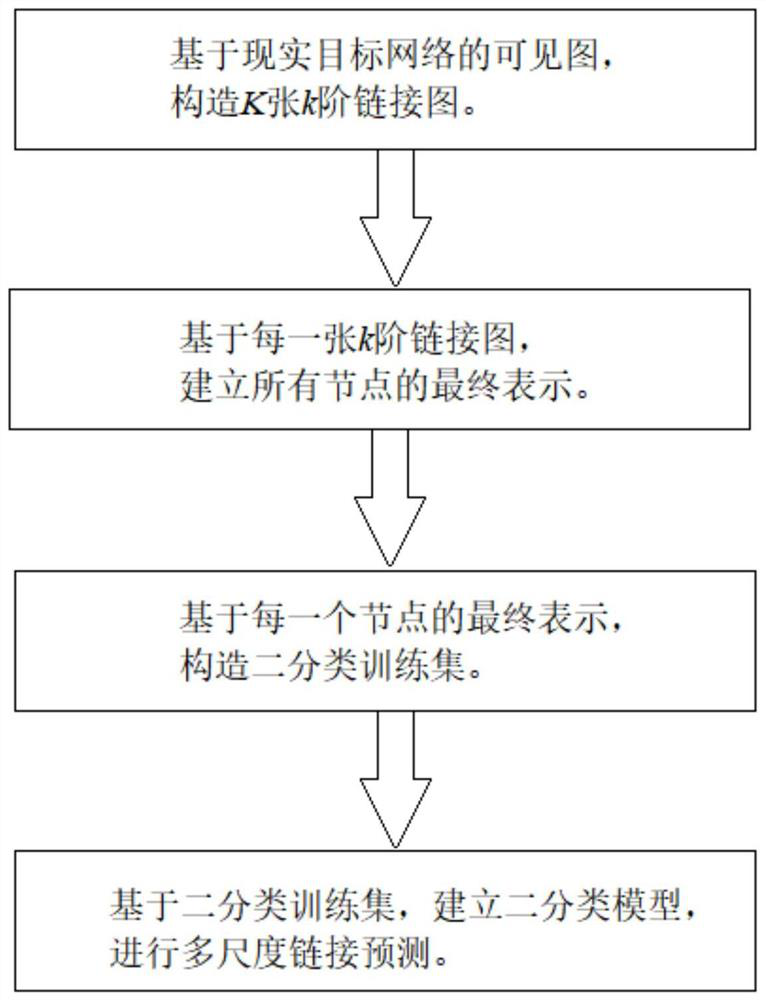
[0051] In this embodiment of the present application, drawing on the idea of hierarchical structure modeling and graph sampling, a set of reachability graphs composed of links of different orders between nodes is constructed, and random walks are used to sample the link graphs of different levels. The node sequence is contextually embedded to learn the hierarchical pattern of links and improve the performance of link prediction.
[0052] like figure 1 As shown, it is a schematic flowchart of the multi-scale link prediction method based on the hierarchical link mode according to the first embodiment of the present application.
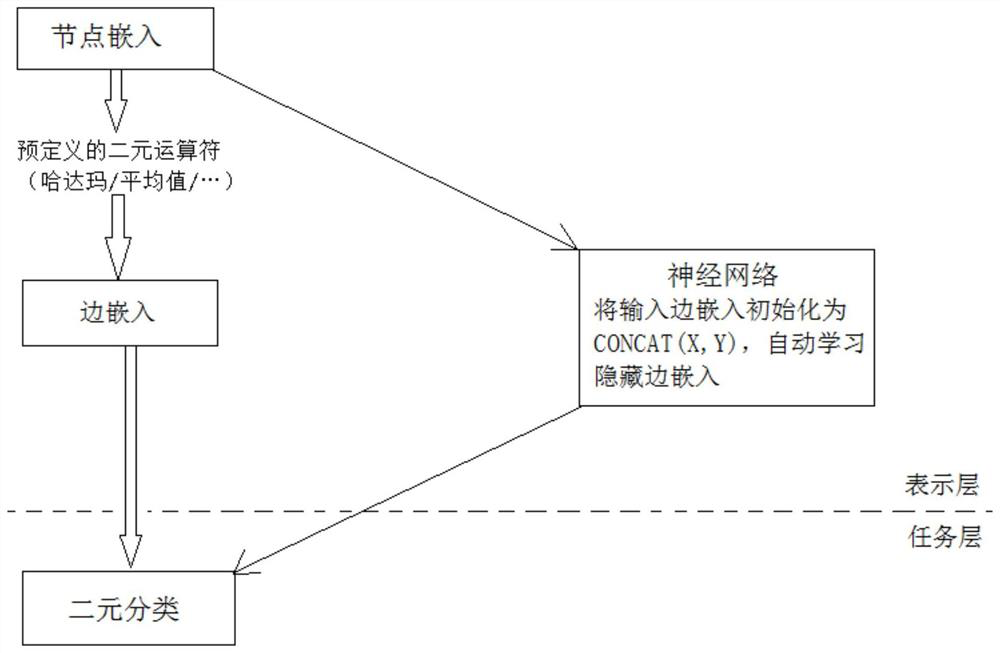
[0053] First, we extract the k-order link graph between nodes by a hierarchical approach. Secondly, the node sequence is collected by random walk, and the word vector embedding model Word2Vec based on negative sampling is used to process the context information of the node in the walk sequence, so as to obtain the vector representation of the node on...
Embodiment 2
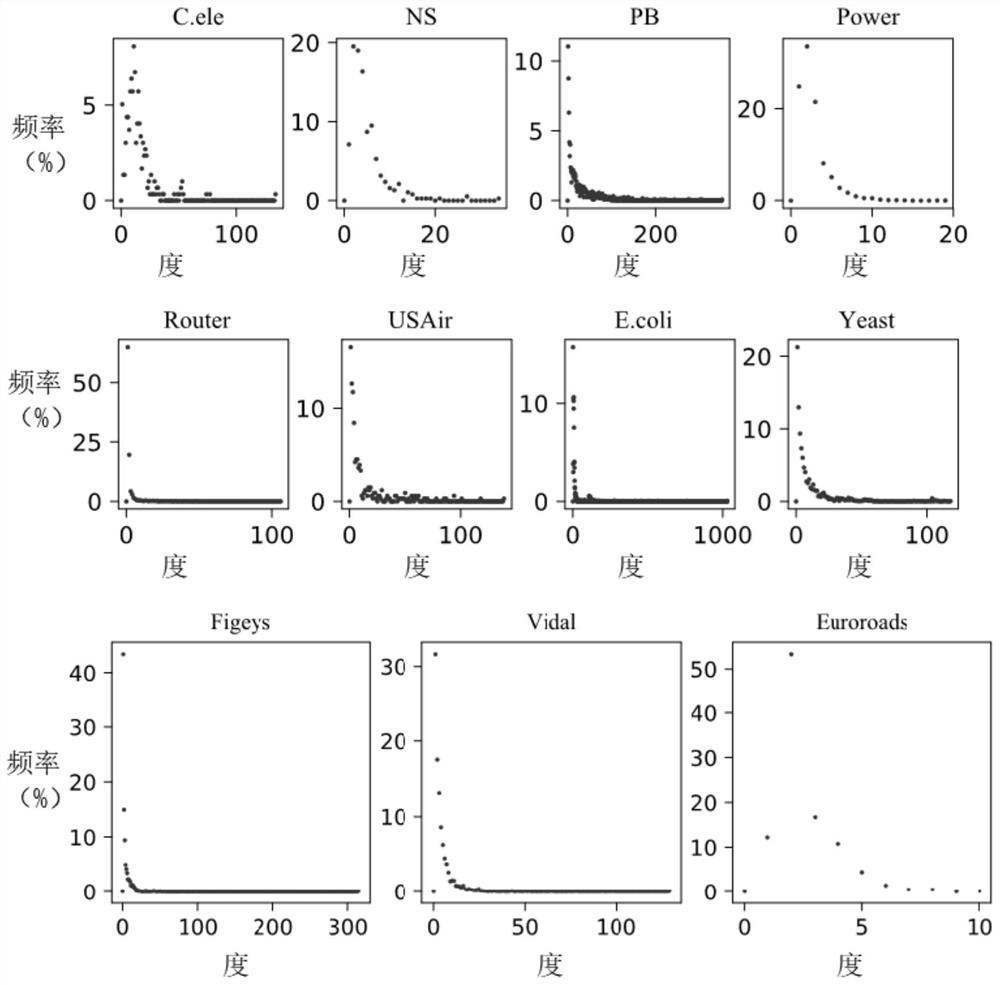
[0076] Based on the prediction model constructed in this application, the second embodiment conducts experiments on eight classical networks and three sparse networks.
[0077] Eight classic network datasets: USAir is an American airline network with 332 nodes and 2126 edges. NS is a scientific research collaboration network for researchers in the field of network science, with 1589 nodes and 2742 edges. PB is an American political blog network with 1222 nodes and 16714 edges. Yeast is a yeast protein interaction network with 2375 nodes and 11693 edges. C.ele is a C. elegans neural network with 297 nodes and 2148 edges. Power is a transmission network in the western United States with 4,941 nodes and 6,594 edges. Router is a router network with 5022 nodes and 6258 edges. E.coli is an interaction network between metabolites of Escherichia coli, with 1805 nodes and 14660 edges.
[0078] Three sparse network datasets: Figeys is a human (Homo sapiens) protein interaction netw...
Embodiment 3
[0107] In the third embodiment, the technical solution of the present application is applied to aviation route planning.
[0108] In this embodiment, taking an air route network composed of existing air routes between several cities in a region as an example, taking cities as nodes, the shortest paths between cities are obtained through breadth-first search, and air routes links with different distance scales are generated based on this. Reachability graph to describe the hierarchical link pattern in the airline network between cities. Then, the node sequence (city sequence) is sampled by random walk, and the context embedding learning of city nodes is performed according to the word embedding method in the language model, and the vector representation of each city under different distance scale link modes is generated. Then, the vector representations of these inter-city routes are merged to obtain the route feature representation for each city. Using cities with existing ai...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com