Polypeptide inhibitors of neutrophil elastase activity and uses thereof
A technology of inhibitor and activator, which is applied to the polypeptide inhibitor of neutrophil elastase activity and its application field, and can solve the problems of unsuitability for transplantation and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment I
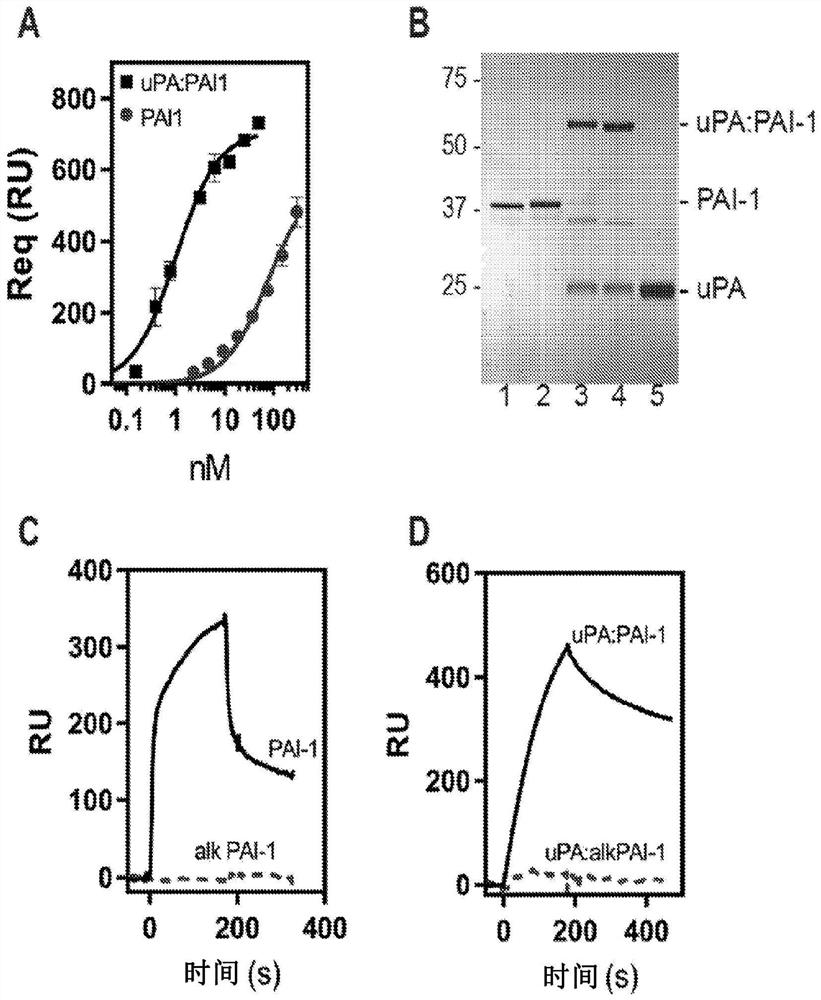
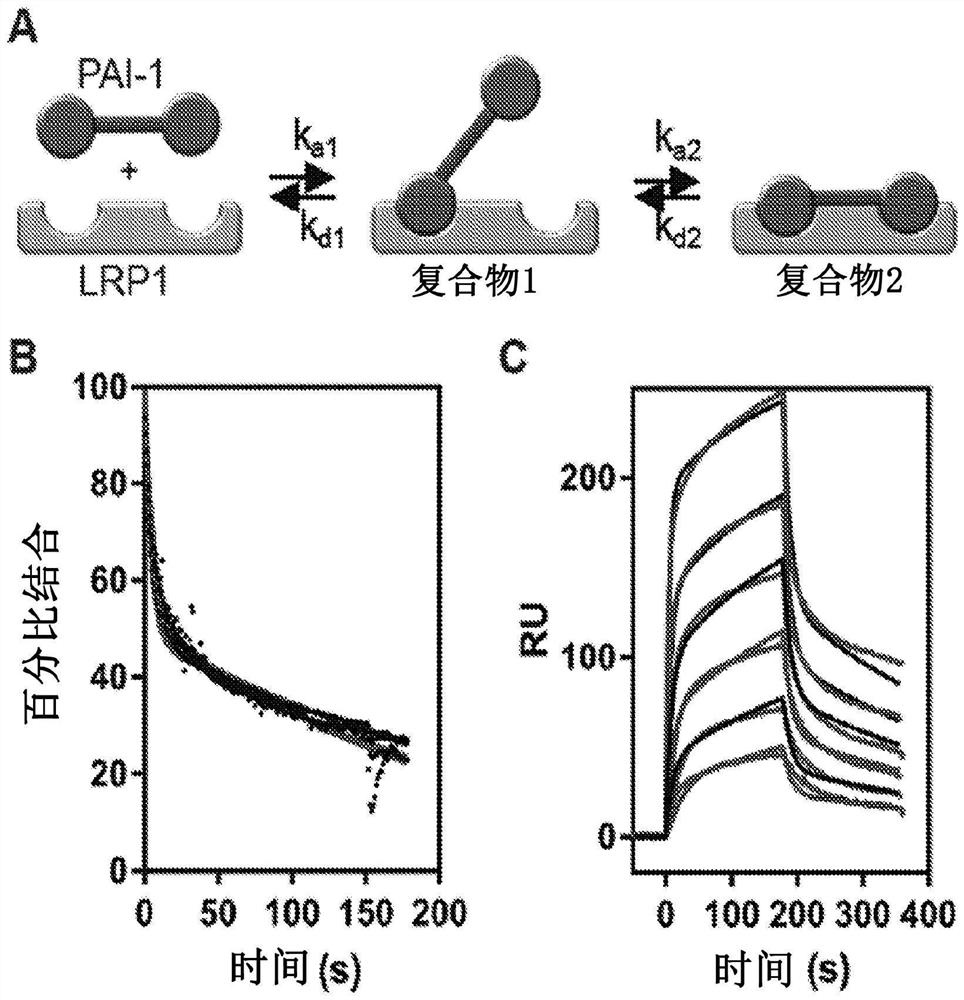
[0164] This example shows that the LMWuPA:PAI-1 complex binds to LRP1 with higher affinity than PAI-1 alone.
[0165] To address the contradictions that exist in the literature regarding the relative affinities of PAI-1 and the protease:PAI-1 complex for LRP1, our initial experiments compared the binding of free PAI-1 and PAI-1 complexed with LMWuPA to LRP1. Notably, LMWuPA itself does not bind to LRP1. Because wild-type PAI-1 is relatively unstable and rapidly converts to a latent form, experiments in this study and all subsequent studies (unless otherwise stated) used the I91L mutant of PAI-1, which converts PAI- The stability of 1 extends from a half-life of 2.0 h to a half-life of 18.4 h (see, Berkenpas, M.B., Lawrence, D.A., and Ginsburg, D. (1995) EMBO J. 14, 2969-77). Experiments to form a complex of I91L PAI-1 with LMWuPA were performed and compared to the binding of free PAI-1 to LRP1 using equilibrium SPR measurements. data( figure 1 A) shows that the LMWuPA:PAI-1...
Embodiment II
[0167] This example shows that lysine residues on PAI-1 are critical for the binding of both PAI-1 and the LMWuPA:PAI-1 complex to LRP1.
[0168] To determine the contribution of lysine residues to the interaction of PAI-1 with LRP1, these residues were analyzed with sulfo-NHS-acetate that forms a stable covalent amide bond with the primary amine of the lysine residue chemical modification. This modification does not prevent PAI-1 from forming a stable complex with LMWuPA ( figure 1 B). Notably, however, this modification prevented free PAI-1 ( figure 1 C) and binding of both LMWuPA and modified AI-1 complexes to LRP1 ( figure 1 D). These results suggest that lysine residues on PAI-1 contribute to the binding of both PAI-1 and the LMWuPA:PA1-1 complex to LRP1.
Embodiment III
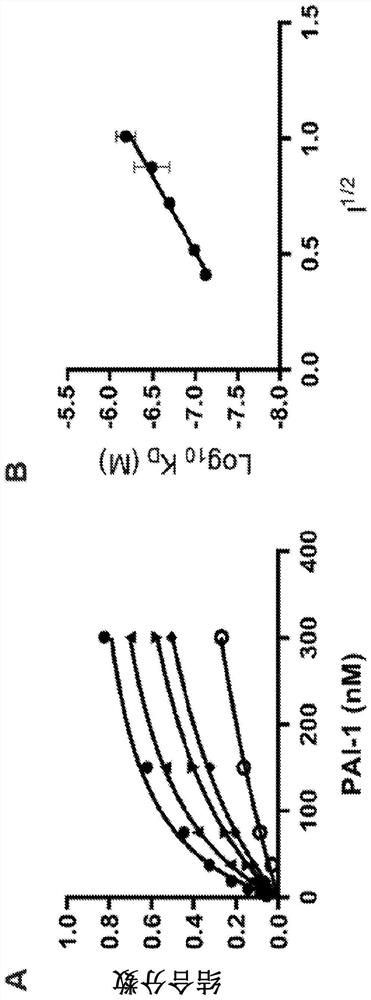
[0170] This example demonstrates that two charged residues are involved in the binding of PAI-1 to LRP1.
[0171] Experiments to examine the effect of ionic strength on the binding of PAI-1 to LRP1 were next performed. The results of these experiments suggest that the binding of PAI-1 to LRP1 depends on the ionic strength ( figure 2 A). figure 2 B shows the data plotted as a Debye-Hückel plot, where log 10 K D Plotted against ionic strength. These results suggest that 2 ionic interactions are involved in the binding of PAI-1 to LRP1, as indicated by the slope (slope=1.5±0.1). This is consistent with the standard model of ligand binding to members of the LDL receptor family, in which two (or more) ε-amino groups of specific lysine residues located on the ligand are associated with aspartame within the LDLa repeat Carboxylates of amino acid residues form salt bridges (see, Fisher, C., et al., (2006) Mol. Cell. 22, 277-283).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com