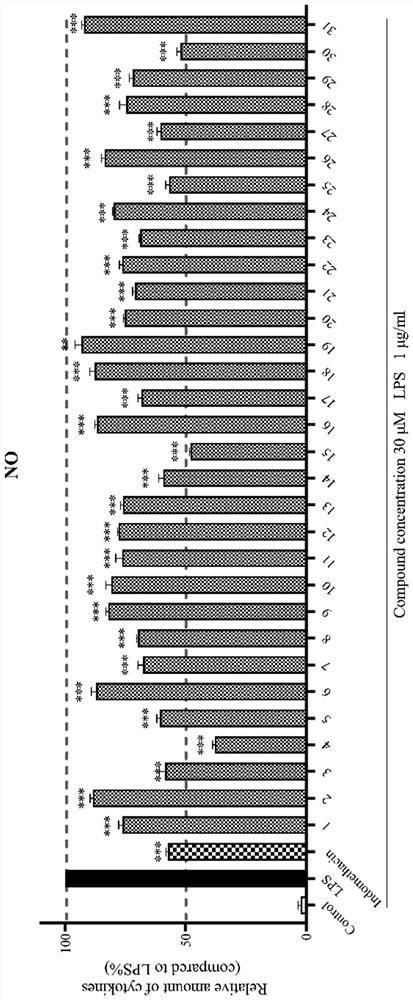
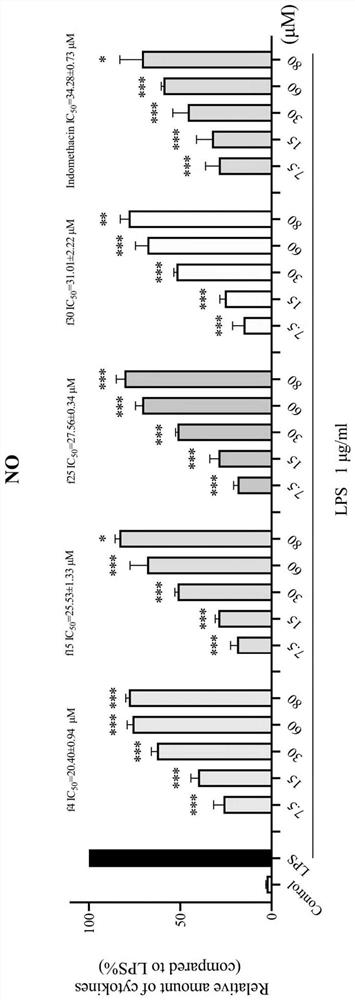
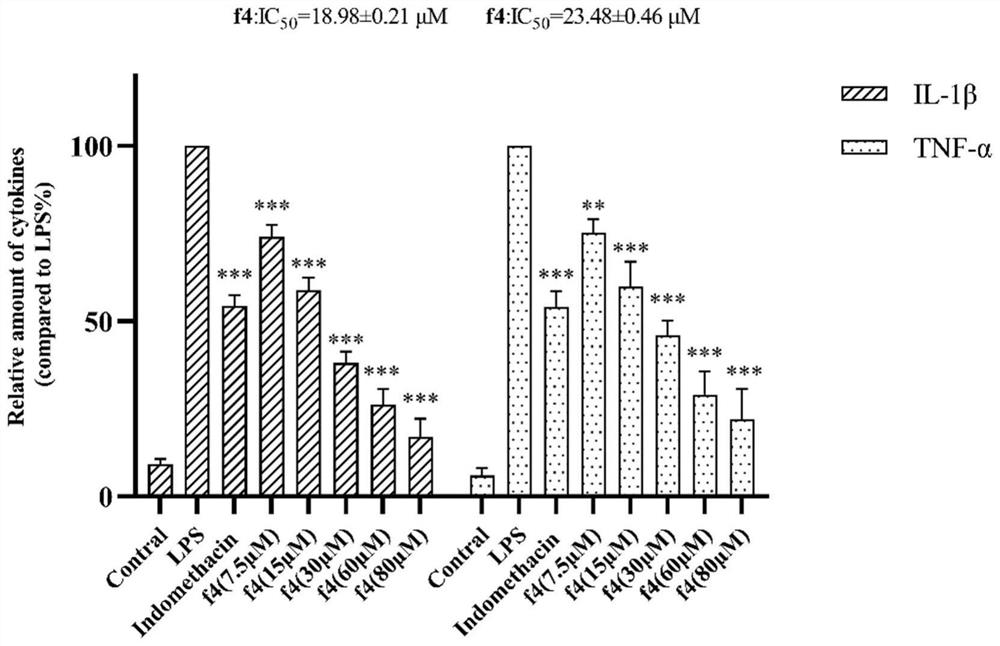
8-quinoline sulfonamide compound and application thereof
A quinoline sulfonamide and compound technology, applied in the field of medicinal chemistry, can solve problems such as incomplete remission
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Synthesis of compound f1:
[0040]
[0041] Compound d (299 mg, 1 mM) was dissolved in 2 mL of pyridine, and then benzenesulfonyl chloride (substituent R was hydrogen) (176 mg, 1 mM) was added to react at room temperature for 8-12 h. The progress of the reaction was checked by TLC. After the reaction was completed, the reaction solvent was removed. Compound f1 was obtained by ethyl acetate:petroleum ether (1:4) column chromatography to obtain compound f1, which was a white solid with a yield of 68%.
[0042] 1 H NMR (500MHz, DMSO-d 6 )δ10.09(d,J=28.9Hz,2H),9.11(dd,J=4.3,1.8Hz,1H),8.50(d,J=8.4Hz,1H),8.28(dd,J=15.5,7.1 Hz, 2H), 7.79(d, J=7.0Hz, 1H), 7.60(t, J=7.7Hz, 1H), 7.54(t, J=7.4Hz, 2H), 7.50(d, J=7.1Hz, 2H), 7.40(t, J=7.8Hz, 2H), 7.06(s, 1H), 6.89(t, J=8.1Hz, 1H), 6.69(d, J=8.1Hz, 1H), 6.54(d, J=8.0Hz, 1H); 13 C NMR (126MHz, DMSO) δ 151.38, 142.61, 139.27, 138.10, 136.84, 134.97, 134.14, 132.69, 132.10, 129.23, 128.93, 127.67, 126.37, 125.51, 122.54, 115.9...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Synthesis of compound f2:
[0045]
[0046] The method is the same as in Example 1, except that the substituent R in the benzenesulfonyl chloride is 4-methyl, and a white solid, namely compound f2, is obtained in a yield of 70%.
[0047] 1 H NMR (500MHz, DMSO-d 6 )δ10.31(s, 2H), 9.33(dd, J=4.2, 1.9Hz, 1H), 8.72(d, J=8.2Hz, 1H), 8.51(dd, J=23.6, 7.9Hz, 2H), 7.98–7.86(m, 2H), 7.61(d, J=8.3Hz, 2H), 7.40(d, J=7.9Hz, 2H), 7.28(s, 1H), 7.10(t, J=8.1Hz, 1H) ), 6.89(d, J=8.1Hz, 1H), 6.74(d, J=8.0Hz, 1H), 2.50(s, 3H); 13 C NMR (126MHz, DMSO) δ 151.46, 143.07, 142.67, 138.50, 138.31, 136.90, 136.44, 135.00, 134.21, 132.23, 129.44, 128.38, 126.53, 125.57, 122.61, 20.617, 110.61, 115.61.
Embodiment 3
[0049] Synthesis of compound f3:
[0050]
[0051] The method is the same as in Example 1, except that the substituent R in the benzenesulfonyl chloride is 4-isopropyl, and a white solid, namely compound f3, is obtained in a yield of 76%.
[0052] 1 H NMR (500MHz, DMSO-d 6 )δ10.15(s, 2H), 9.12(dd, J=4.2, 1.8Hz, 1H), 8.52(dd, J=8.4, 1.8Hz, 1H), 8.33(dd, J=7.3, 1.5Hz, 1H) ),8.28(dd,J=8.3,1.4Hz,1H),7.75–7.66(m,2H),7.46(d,J=8.5Hz,2H),7.27(d,J=8.5Hz,2H),7.10 (t, J=2.1Hz, 1H), 6.88 (t, J=8.1Hz, 1H), 6.67 (dd, J=8.1, 1.2Hz, 1H), 6.53 (dd, J=8.1, 1.2Hz, 1H) ,2.89(p,J=6.9Hz,1H),1.14(d,J=6.9Hz,7H); 13 C NMR (126MHz, DMSO) δ 153.51, 151.48, 142.71, 138.56, 138.37, 136.95, 135.06, 134.24, 132.25, 129.35, 128.41, 126.98, 126.66, 125.60, 122.63, 3.3.2.9,2,17
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com