Semiconductor storing device and semiconductor integrated circuit
A storage device and semiconductor technology, applied in semiconductor devices, semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, static memory, etc., can solve problems such as prolonging the time required for data readout, difficulty in identifying cell current or leakage current, and misreading data.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment
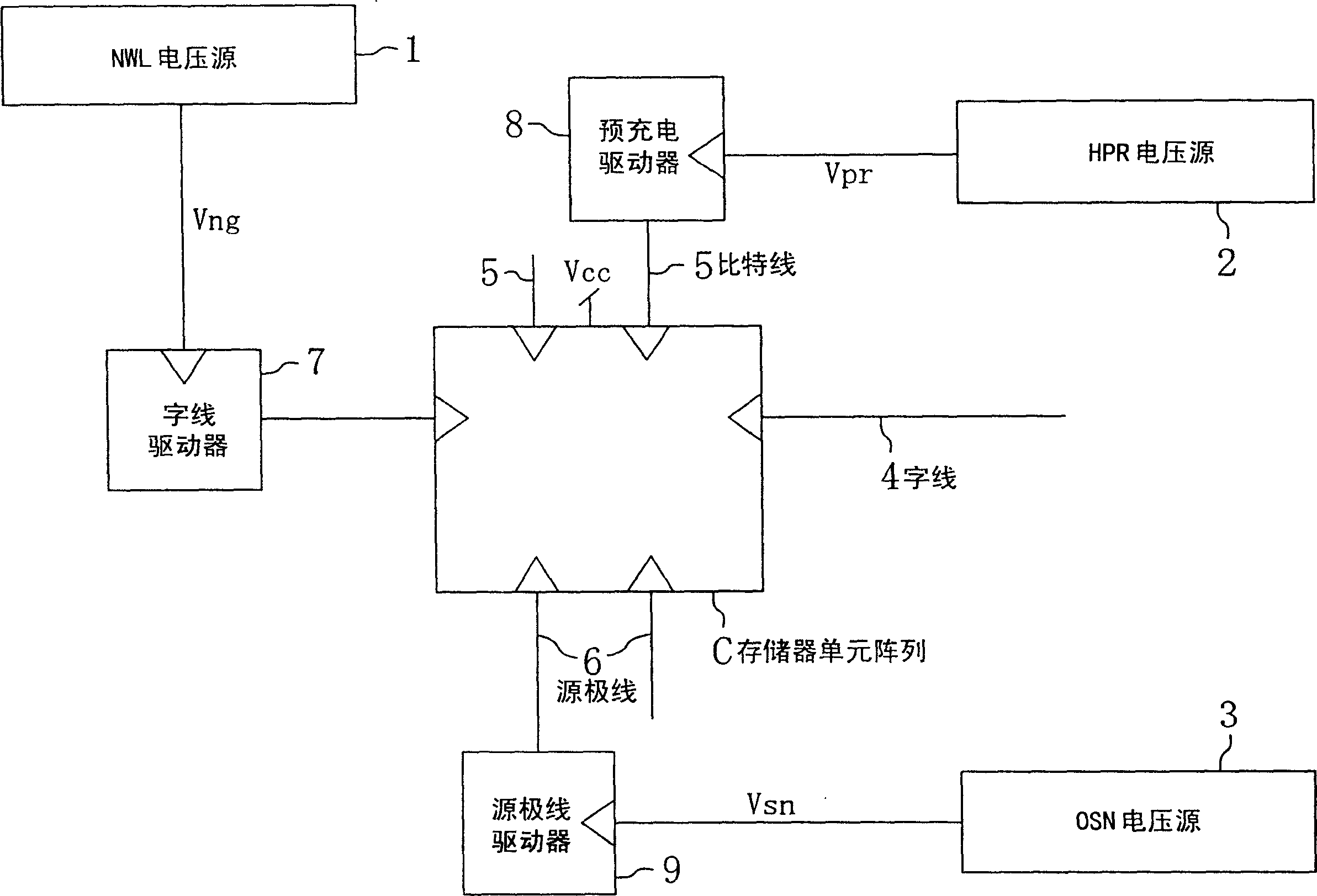
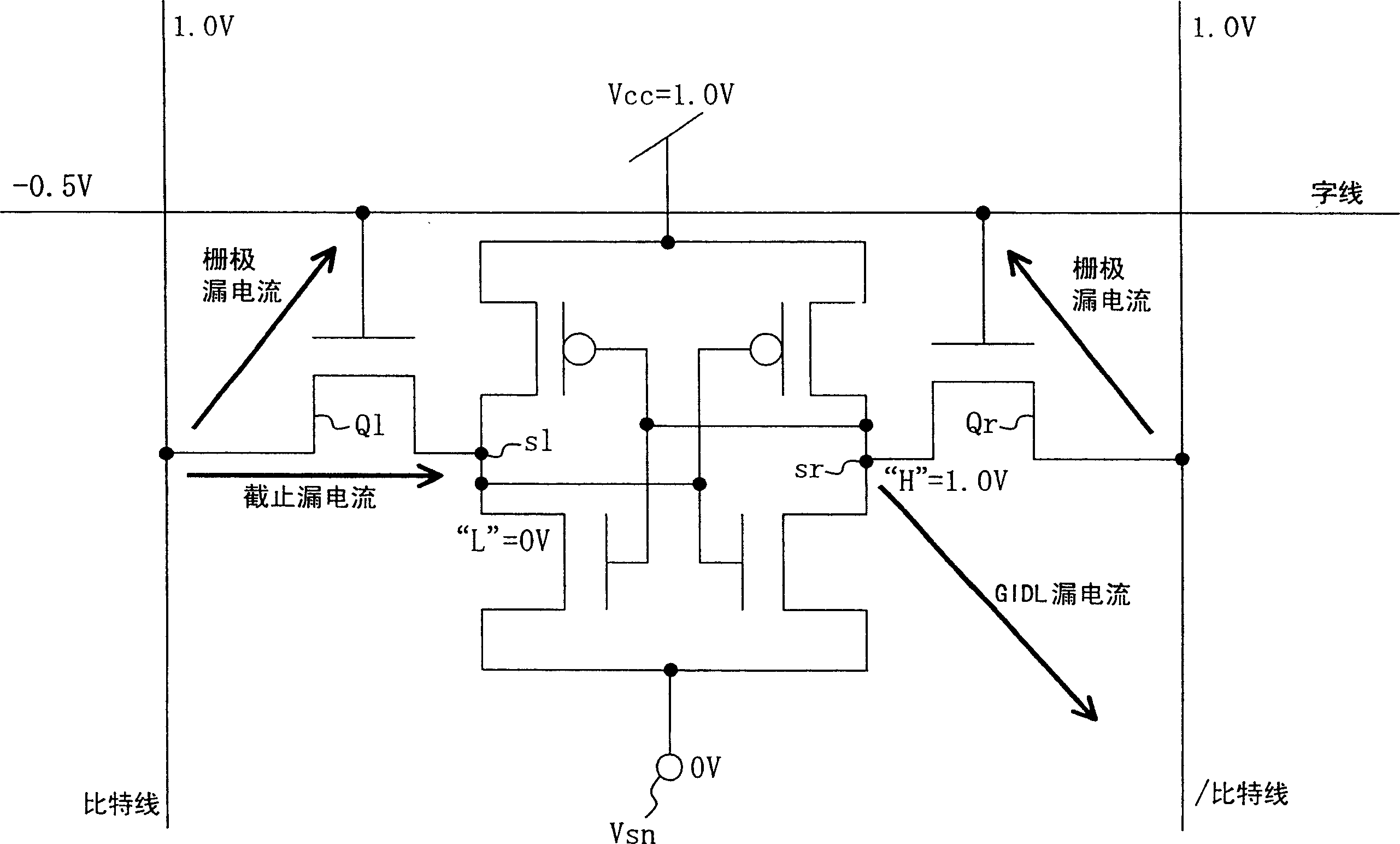
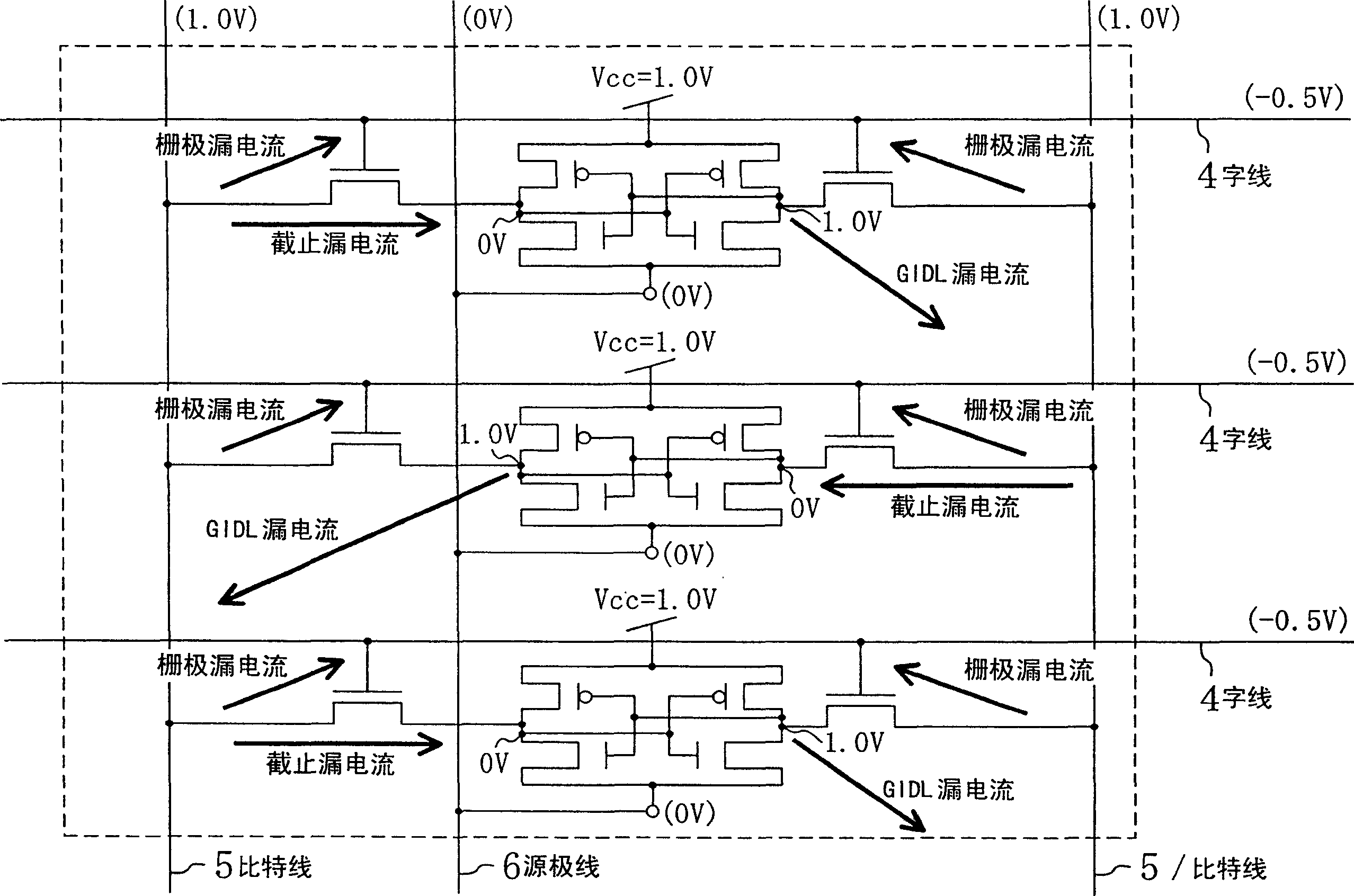
[0053] figure 1 A SRAM as a semiconductor memory device according to a first embodiment of the present invention is shown. In this figure, C represents the memory cell array, such as figure 2 As shown, two NMOS transistors and two PMOS transistors constituted by connecting two inverter circuits to form flip-flops, and two access transistors Ql and Qr arranged on the left and right are included as one memory cell. A plurality of memory cells are arranged in the column direction and the column direction. The two access transistors Ql and Qr constituting the memory cell have a large gate leakage current, and the difference between the off leakage current and the gate leakage current per unit gate width at normal temperature is within 2 digits. It is effective to apply the present invention when transistors Q1 and Qr having this characteristic are used.
[0054] In addition, in figure 1 as well as figure 2 Among them, 5 and 5 denote two paired bit lines connected to the sto...
no. 2 Embodiment
[0073] Then, refer to Figure 10 A semiconductor integrated circuit according to a second embodiment of the present invention will be described. This embodiment relates to the internal structure of the word line driver in the SRAM described in the first embodiment.
[0074] exist Figure 10 Among them, 15 represents SRAM, and inside it, although not shown in the figure, it has the above-mentioned figure 2 A plurality of memory cells and bit lines that have been described in , and a plurality of word lines 4 (only one is shown in this figure). Further, in the SARM 15, a decoder (decoding circuit) 16 for selecting any one of the plurality of word lines and a word line driver (word line driver circuit) for driving the selected word line 4 after receiving the output of the decoder 16 are included. 17. The above-mentioned SARM 15 may also be constituted by the SRAM described in the above-mentioned first embodiment.
[0075] In this figure, 20 denotes a first logic circuit, 21...
no. 3 Embodiment
[0092] Finally, a third embodiment of the present invention will be described. In this embodiment, a ROM is used as a semiconductor memory device.
[0093] In a ROM, since the number of memory cells connected to one bit line is relatively large, the influence of gate leakage current of a cell transistor between a non-selected word line and a bit line becomes relatively large. As already explained, if the negative potential of the non-selected word line is made relatively deep (the maximum value is a large value), although the off-leakage current is limited, when the bit line is selectively precharged with the power supply voltage, the bit line- The potential difference between the word lines exceeds the power supply voltage, increasing the gate leakage current. As a result, the potential of the precharged bit line is pulled to the negative potential of a plurality of non-selected word lines instead of the original source line, and greatly drops, causing a malfunction in readi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com