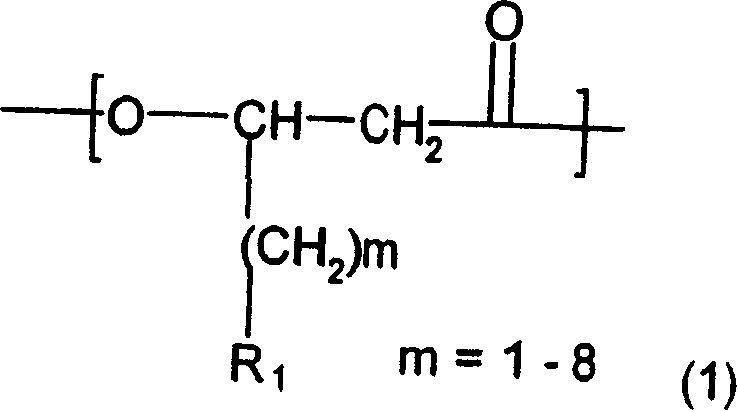
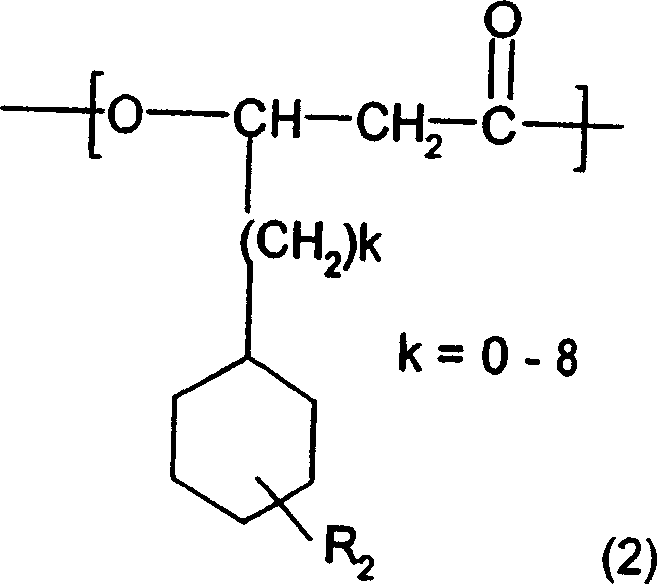
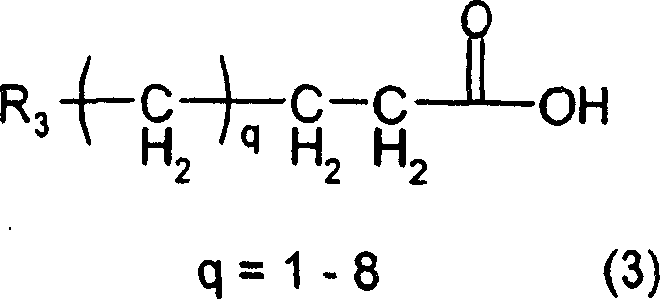Molecular weight control method of poly hydroxy alkane acid ester
A technology of polyhydroxyalkanoate and molecule, which is applied in the field of molecular weight control of polyhydroxyalkanoate, and can solve the problems that have not been developed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0124] [Example 1] Controlling the molecular weight of poly 3-hydroxyl-5-phenylvaleric acid (PHPV) with polyethylene glycol-1
[0125] Containing polypeptone (Wako Pure Chemical Industries) 0.5% (W / V), 5-phenylvaleric acid 0.1% (W / V) and molecular weight control agent polyethylene glycol 200 (PEG200: average molecular weight 190-210; Kishida Chemical 0%, 1%, 2%, 5% (V / V) M9 medium 200ml, add the culture of the Pseudomonascichorii YN2 bacterium that has been shaken at 30 ℃ for 8 hours with the M9 medium containing polyptone 0.5% in advance Incubate 1 mL of the solution in a 500-mL shaking flask at 30°C for 24 hours. After culturing, the cells were obtained by centrifugation, washed with methanol, and freeze-dried. After weighing the dried cells, chloroform was added, and the mixture was stirred at 50° C. for 24 hours to extract the polymer. The chloroform from which the polymer was extracted was filtered, concentrated by an evaporator, and the part solidified by precipitation...
Embodiment 2
[0132] [Example 2] Controlling the molecular weight of PHPV with polyethylene glycol-2
[0133] As a molecular weight control agent, except having used PEG600 (average molecular weight: 570-630) instead of PEG200, it experimented by the method similar to Example 1. use 1 The structure of the obtained polymer analyzed by H-NMR was the same as in Example 1, and it was roughly a PHPV homopolymer. Table 2 shows the weights of the obtained bacterial cells and polymers, the weight ratio of polymers to bacterial cells, the molecular weights and molecular weight distributions of the obtained polymers.
[0134] PEG600(%)
[0135] CDW: cell dry weight; PDW: polymer dry weight; P / C: PDW / CDW; Mn: number average molecular weight; Mw / Mn: molecular weight distribution
Embodiment 3
[0136] [Example 3] Controlling the molecular weight of PHPV with polyethylene glycol-3
[0137] As a molecular weight control agent, except having used PEG2000 (average molecular weight: 1800-2200) instead of PEG200, it experimented by the method similar to Example 1. use 1 The structure of the obtained polymer analyzed by H-NMR was the same as in Example 1, and it was roughly a PHPV homopolymer. Table 3 shows the weights of the obtained bacterial cells and polymers, the weight ratio of polymers to bacterial cells, the molecular weights and molecular weight distributions of the obtained polymers.
[0138] PEG2000(%)
[0139] CDW: cell dry weight; PDW: polymer dry weight; P / C: PDW / CDW; Mn: number average molecular weight; Mw / Mn: molecular weight distribution
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Resonant frequency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com