Optical variable image making method and its photocomposition system
A production method and imaging system technology, applied in 3D image processing, image data processing, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of difficult to form variable shape image coding effect, poor practical effect, low energy utilization rate of light source, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
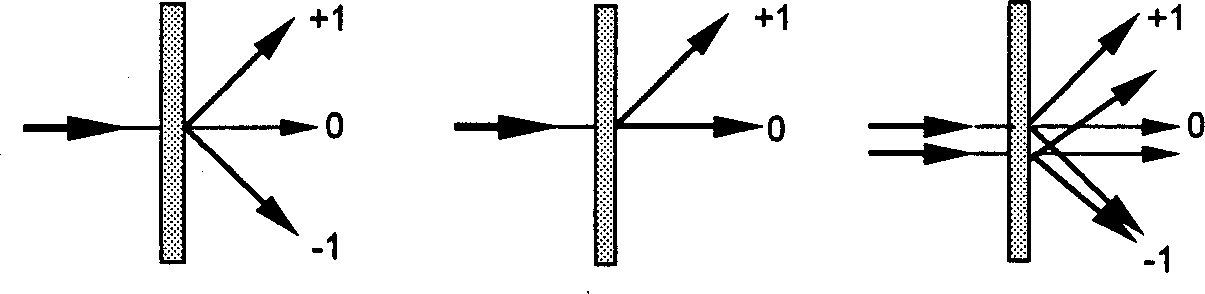
[0040] Embodiment one: see attached figure 2 As shown, a method for making an optically variable image is characterized in that: comprising the following steps, (1) imaging a shape diaphragm onto a holographic optical element 7 by a light source 1 through an optical imaging system to generate a pair of diffracted beams; (2) Converging the diffracted light beam on the recording material 13 to produce an interference fringe point; (3) moving the position of the recording material 13; (4) recording an interference fringe point; (5) repeating steps (3) and (4), until the production of the optically variable image is completed.
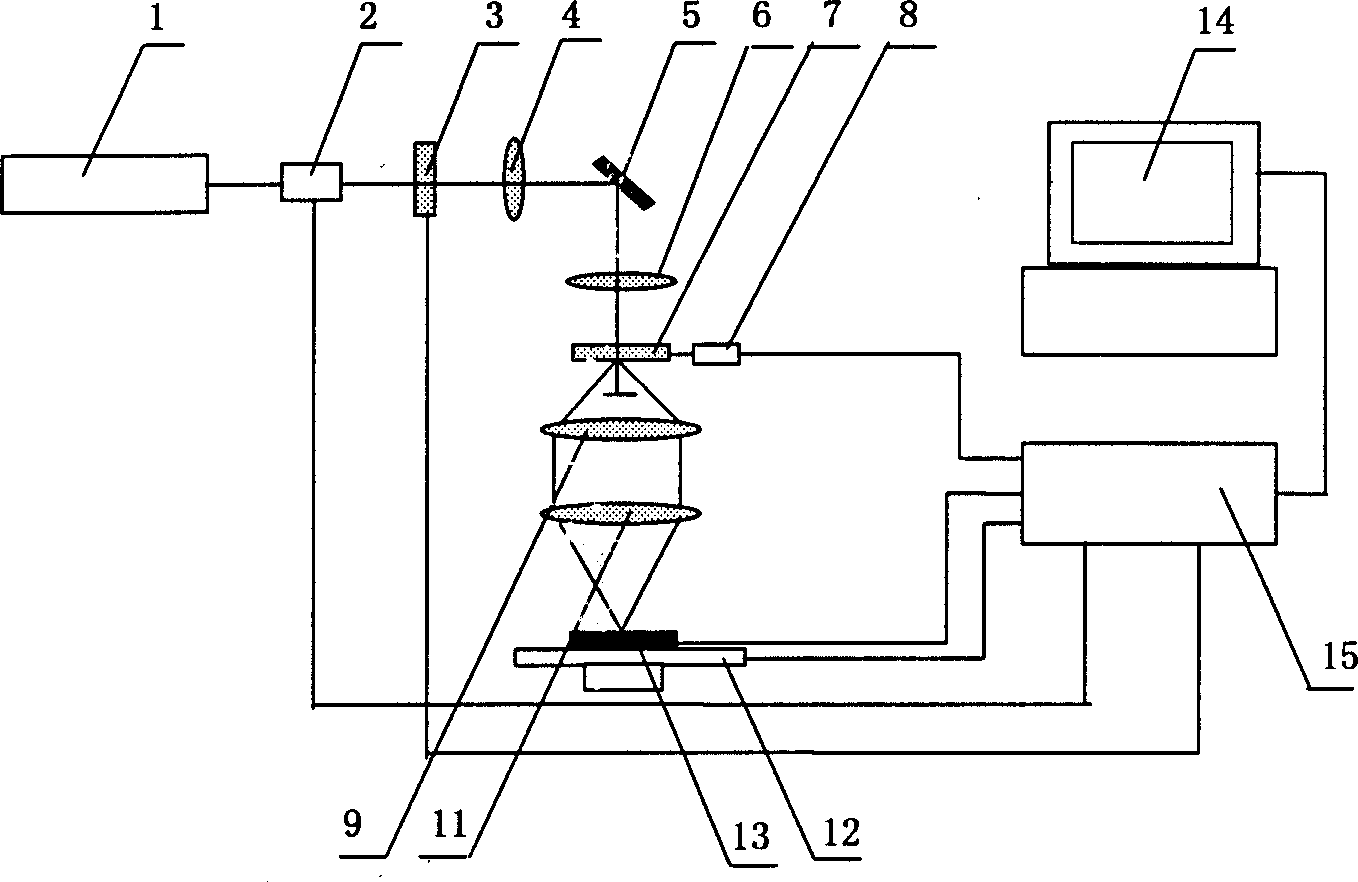
[0041] The optically variable image phototypesetting system of this embodiment includes an optical path system composed of a light source 1, a pre-diffraction imaging system, a holographic optical element 7, and a post-diffraction imaging system, a workbench 12 for placing recording materials 13, and a control system including a computer 14. part, the ho...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Embodiment two: see attached Figure 4 As shown, an optically variable image typesetting system includes an optical path composed of a light source 1, a photoelectric switch 2, a diaphragm 3, an imaging system before diffraction, a holographic optical element 7, an imaging system after diffraction, and a workbench for placing recording materials 13 12 and a control part 15 including a computer 14, the holographic optical element 7 is placed on the turntable 8, the diffraction front imaging system includes a mirror 5 and a lens 6, and the holographic optical element 7 converts the incident light into +1 order and 0th order light, the post-diffraction imaging system includes a lens group composed of a lens 9 and a lens 11, and an image input device 10 is arranged between the lens 9 and the lens 11.
[0044] In this embodiment, since the holographic optical element 7 with only +1 order and 0 order light is selected, the image input device 10 can be inserted into the post-d...
Embodiment 3
[0045] Embodiment three: see attached Figure 5 As shown, an optically variable image phototypesetting system has a structure similar to that of Embodiment 1, wherein, in the imaging system before diffraction, the mirror 5 adopts an x-y vibrating mirror combination, and the lens 6 adopts an F-θ mirror. In this way, when in use, the position of the recording beam can be moved through the movement of the galvanometer, reducing the range of movement of the X-Y coordinate stage.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com