Isolation and characterization of fiber-specific actin promoter from cotton
A cotton fiber and actin technology, applied in the field of plant molecular science, can solve problems such as fiber property limitations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0017] The promoters of the invention are used to produce transgenic cotton with altered fiber properties. The use of the strong fiber-specific promoters of the present invention enables selective expression of transgenes in cotton fibers, allowing a wider range of types of transgenes to be used. Selective expression avoids the metabolic burden imposed on transgenic plants by systemic expression of the transgene, or the adverse effects of expression of the transgene in non-fibrous tissues. Desired genes expressed in cotton fibers but not in other parts of the cotton plant include, for example: (1) anthocyanin genes for dyeing cotton, (2) silk protein genes from silkworms or spiders, which increase the strength of cotton fibers , (3) Biosynthesis of polyhydroxybutyrate in cotton fiber to improve thermal conductivity and insulation properties [John et al., 1996]. There are many fiber-enhancing genes known in the art that can be conveniently linked to the promoters of the presen...
Embodiment 2
[0024] Northern blot analysis showed that the transcript of the CFACT1 gene exhibited the highest accumulation in newborn cotton fibers 8 days after anthesis, and then the accumulation of the gene product (mRNA) decreased significantly as the fibers further developed. Comparing gene expression in different developmental stages of cotton ovules also showed that gene transcripts accumulated more in ovules at 8 days after anthesis than at ovules at 4 and 14 days after anthesis, as the fibers progressed from 8 days after anthesis to By 28 days of development, the accumulation of gene products gradually and significantly decreased to undetectable levels. This suggests that the genes are tightly regulated and specifically expressed at the transcriptional level during cotton fiber and ovule development, like other cotton fiber-specific genes [Whittaker and Triplett, 1999; Shin and Brown, 1999; Kawai et al., 1998; John, 1996a; Song and Allen, 1997; Ma et al., 1997; Rinehart et al., 19...
Embodiment 3
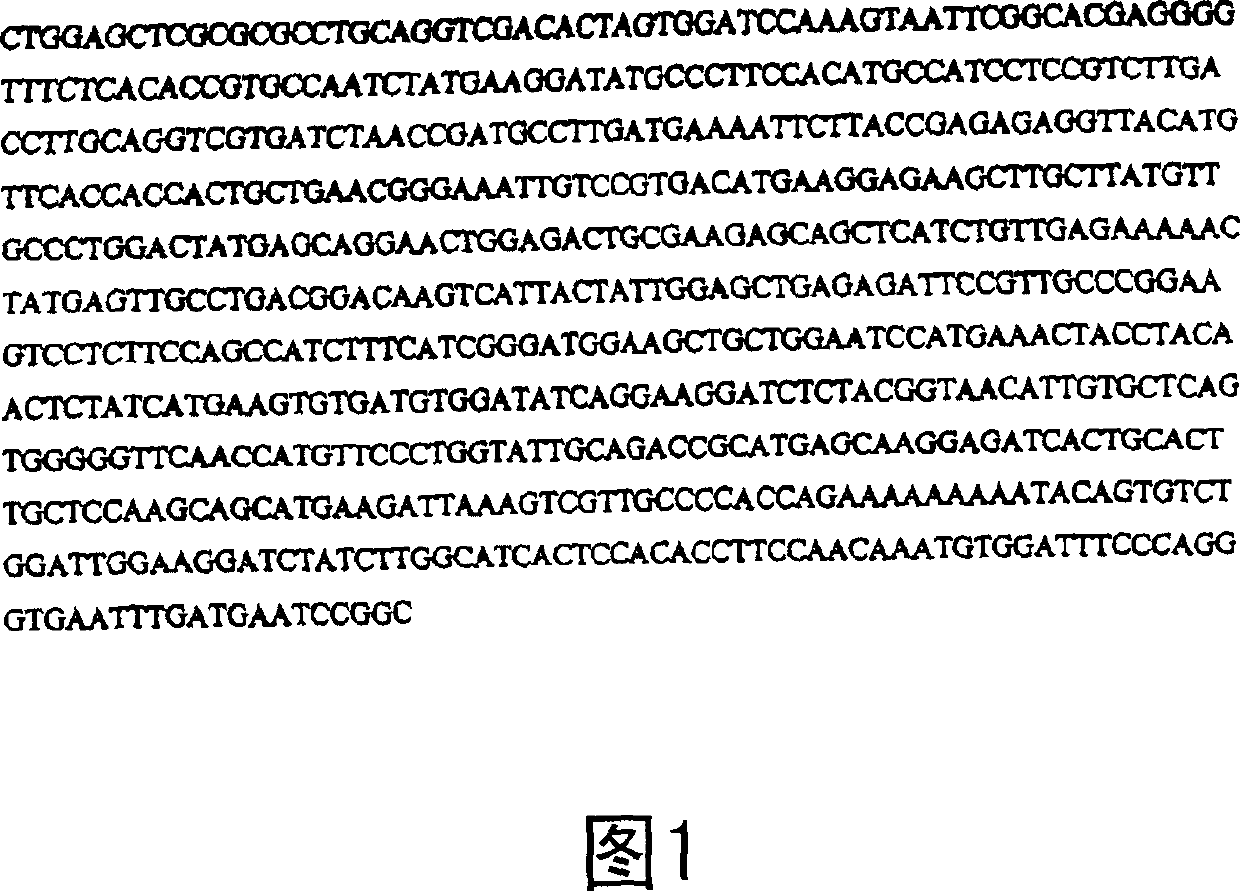
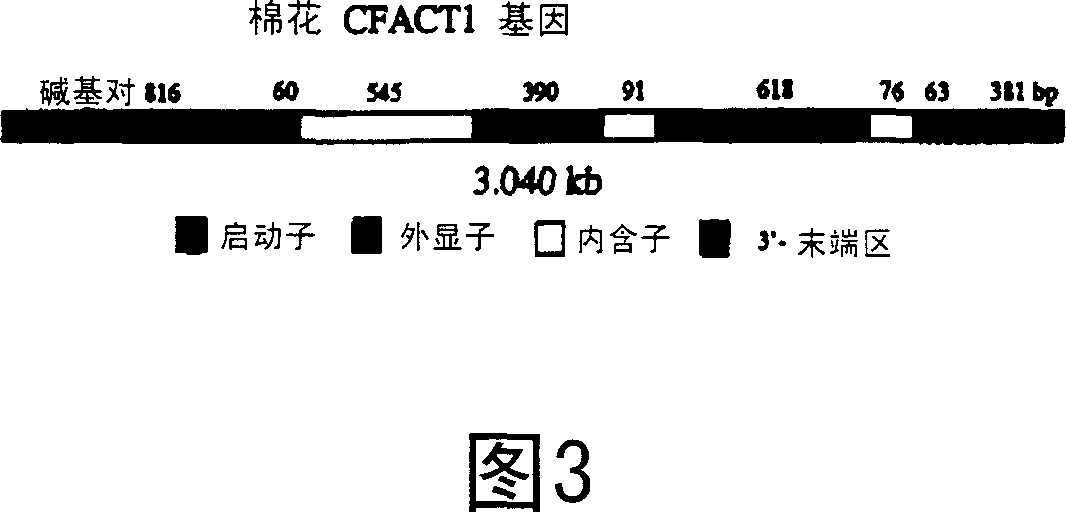
[0028] Two overlapping fragments covering the full-length CFACT1 gene were isolated by a genome walking approach and fully sequenced. The complete CFACT1 gene is 3040bp in length, including a 0.8kb promoter (Fig. 2). Comparing the nucleotide sequence and deduced polypeptide sequence of the cotton CFACT1 gene with the sequence shown in the database, it was found that this gene was highly homologous to the known actin gene at the amino acid level and nucleotide level. The actin gene is derived from plants such as Malva pusilla (AF112538), soybean (U60499), Brassica napus (AF11812), and the like. The CFACT1 gene and the known cotton actin gene (AF059484) only show 71%-93% homology at the amino acid level, and 80-82% homology at the nucleotide level. In addition, its promoter is different from that of known cotton and non-cotton actin genes, so it is a novel actin gene isolated from cotton. Sequence analysis of the CFACT1 gene showed that its open reading frame contained 4 exons...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com