Method for controlling PWM pulse
A pulse control, vector technology, used in output power conversion devices, irreversible DC power input to AC power output, electrical components and other directions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
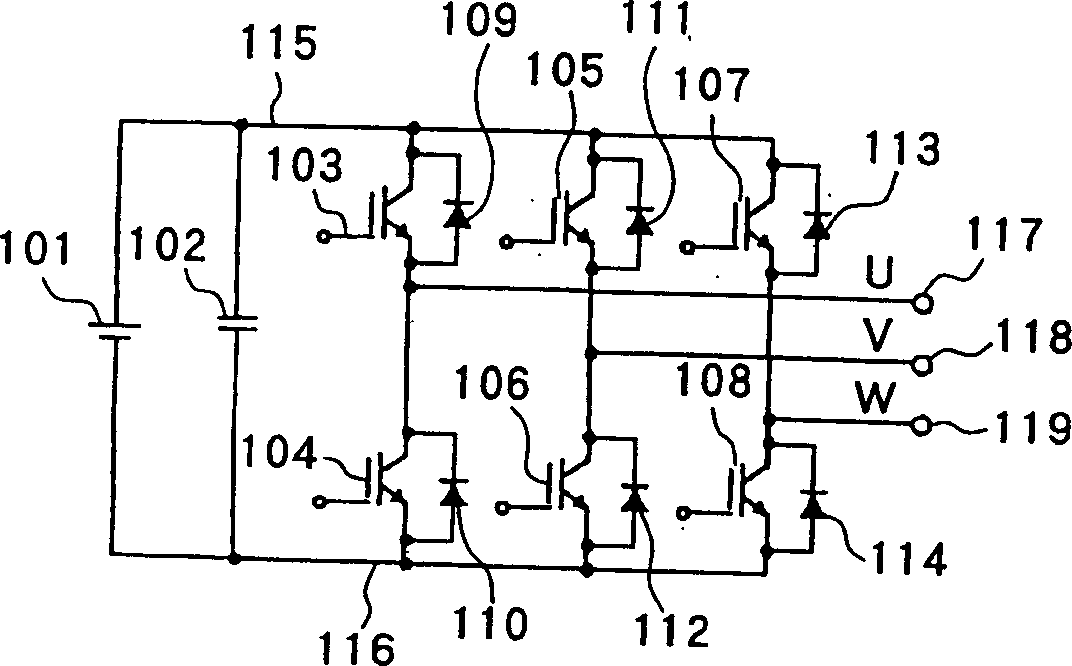
[0048] First refer to Figures 5 to 9 , to describe the PWM pulse control method of the first embodiment of the present invention in detail. The PWM pulse control method of this embodiment can be applied to such as figure 1 The three-phase two-bit PWM inverter shown. In this three-phase two-bit PWM inverter, three-phase modulation is used when the output frequency and modulation percentage are low.
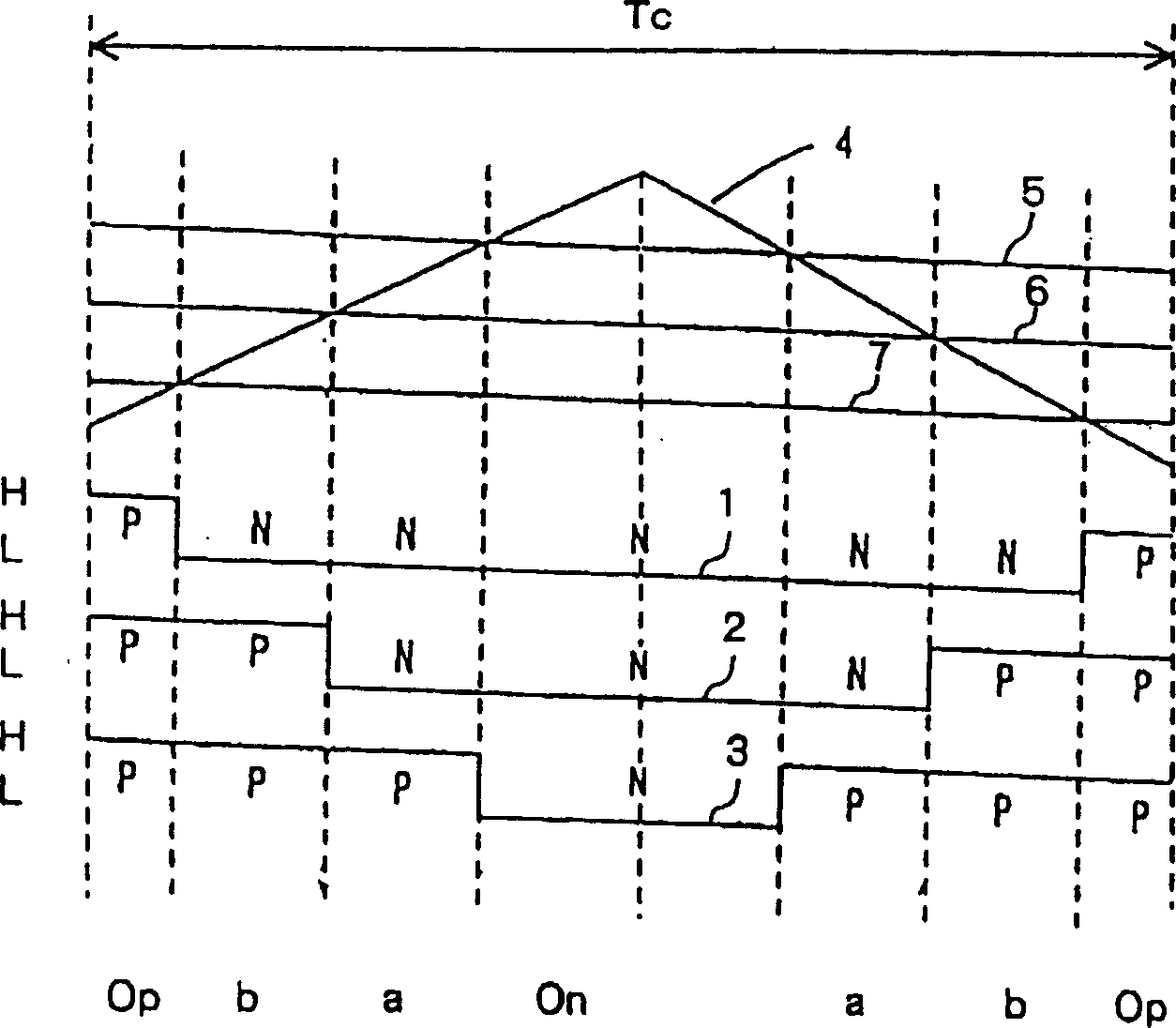
[0049] Figure 5 The timing chart shown represents the basic method in the PWM pulse control method described in this embodiment. Such as Figure 5 Shown in (a), in the PWM pulse control method of the present invention, just like the PWM pulse control method described in the prior art, when generating PWM pulse 1-3, observe the output sequence of each vector and output time. (Op-vector, b-vector) and (On-vector, a-vector) are divided into the next group, dividing the interior of one period Tc of the triangular waveform period 4 into time intervals, and in these time interval...
no. 2 example
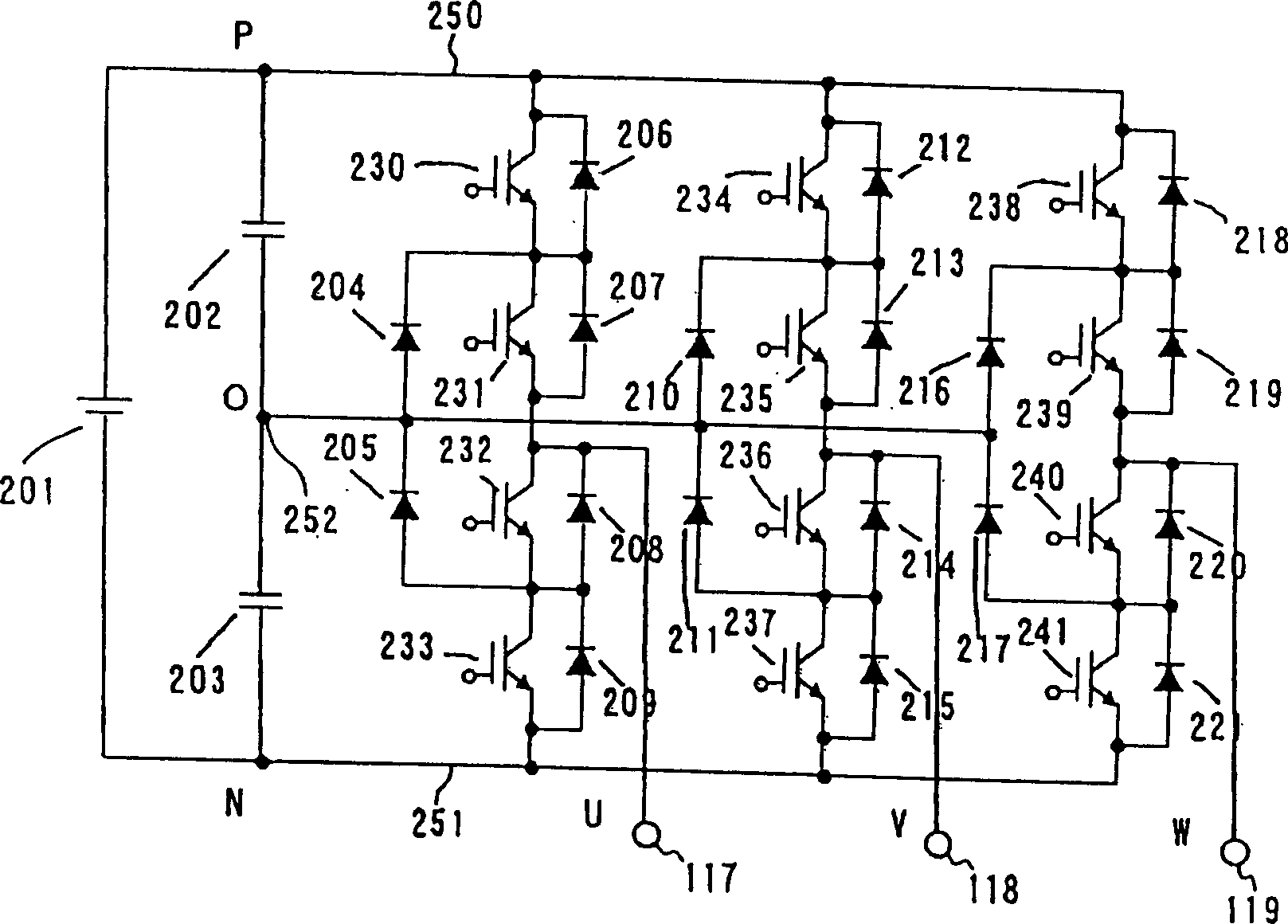
[0078] Refer below Figures 10 to 12 , to describe in detail the PWM pulse control method of the second embodiment of the present invention. The PWM pulse control method of this embodiment can be applied to image 3 The three-phase three-bit PWM inverter shown is the neutral point clamped inverter. With this three-phase three-bit PWM inverter, bipolar modulation is used when the output frequency and modulation percentage of the inverter are both low.
[0079] First refer to Figure 10, the timing diagram shown in this figure represents the basic method in the PWM pulse control method described in this embodiment. In the PWM pulse control method of the present embodiment, just like the PWM pulse control method described in the prior art, when generating PWM pulses 1-3, at first generate each vector in one period of the triangular waveform voltage 4 output sequence and output time.
[0080] In the prior art PWM pulse control method, the output time of each vector is as Fi...
no. 3 example
[0093] Refer below Figure 13 and 14 illustrate the PWM pulse control method according to the third embodiment of the present invention. Figure 7 and Figure 8 The control circuit and working process of the induction motor 305 using the PWM pulse control method described in the first embodiment are shown. However, in this control circuit, when the first set value m and the second set value n are the initial values M1 and N1 respectively, the ON delay correction amount output from the ON delay correction amount operation unit 310 is ΔU", ΔV " and ΔW" are the ON delay correction amount.
[0094] As described above, the ON delay correction amount can be determined by generating the product of the ON delay time required to switch the semiconductor switching element once and the number of times of switching at a certain point of time, and since the number of times of switching is detected based on the number of divisions per vector, the When the initial values M1 and N1 are...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com