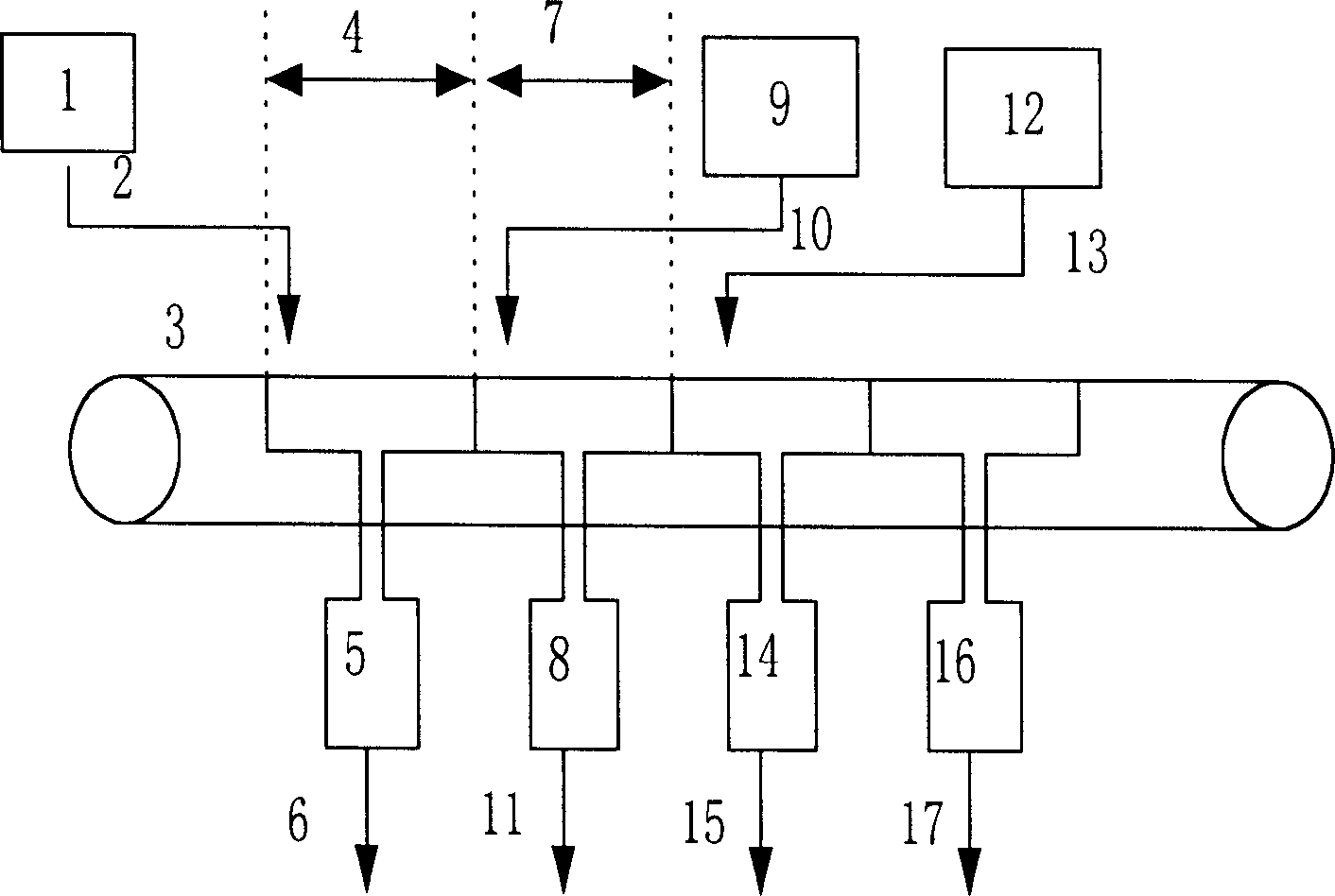
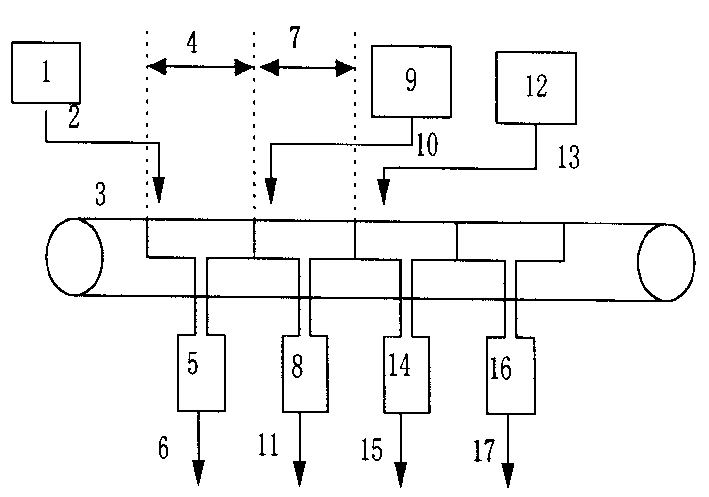
Molecular sieve RE ion exchange method
A rare earth ion and ion exchange technology, applied in the field of rare earth ion exchange of molecular sieves, can solve problems such as inability to exchange, and achieve the effects of low water consumption and high efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0044] The cross-baking ultra-stable Y molecular sieve described in Comparative Example 1, deionized water and the filtrate A1 described in Comparative Example 1 are mixed and beaten to make a molecular sieve content of 120 grams per liter containing molecular sieve, wherein salt (i.e. the filtrate used The amount of rare earth chloride and sodium chloride contained in A1 is 1.1% by weight of the molecular sieve. The obtained molecular sieve slurry was heated to 90° C., poured into a Buchner funnel, and at the same time, the filter bottle was evacuated to 0.07 MPa to form a filter cake with a thickness of 10 mm on the filter cloth. When there is no liquid on the surface of the filter cake, immediately add a rare earth chloride solution (wherein La 2 o 3 The content is 16.6 g / L, CeO 2 The content of the rare earth oxide is 29.6 grams per liter, and the other rare earth oxide content is 3.8 grams per liter), the addition speed ensures that the surface of the filter cake does n...
example 2
[0046] The cross-calcined hydrogen Y molecular sieve described in comparative example 2, deionized water and the filtrate A2 described in comparative example 2 are mixed and beaten to make a slurry with a molecular sieve content of 200 grams per liter, wherein the salt (i.e. the used filtrate A2) Containing rare earth chloride and sodium chloride) in an amount of 1.7% by weight of molecular sieves. The obtained molecular sieve slurry was heated to 90° C., poured into a Buchner funnel, and at the same time, the filter bottle was evacuated to 0.05 MPa. A filter cake with a thickness of 12 mm was formed on the filter cloth. When there is no liquid on the surface of the filter cake, it is 40 grams per liter to add the rare earth oxide content immediately, and the temperature is a rare earth chloride solution (the ratio of each rare earth oxide is the same as example 1) at 90°C, and the addition speed ensures that the surface of the filter cake does not form turtle Crack, the cons...
example 3
[0048] Take by weighing one calcined rare earth Y molecular sieve described in comparative example 3, deionized water and the filtrate A3 described in comparative example 3 and mix and make a slurry, make the molecular sieve content and be the slurry containing molecular sieve of 150 g / liter, wherein salt (i.e. used The amount of rare earth chloride and sodium chloride contained in the filtrate A3 is 2.5% by weight of the molecular sieve. The obtained molecular sieve slurry was heated to 70° C., poured into a Buchner funnel, and at the same time, the filter flask was evacuated to 0.05 MPa. A filter cake with a thickness of 8 mm was formed on the filter cloth. When there is no liquid on the surface of the filter cake, immediately add a rare earth chloride solution (where La 2 o 3 The content is 41.7 g / L, CeO 2 The content of the rare earth oxide is 3.7 grams per liter, and the content of other rare earth oxides is 4.6 grams per liter), the addition speed ensures that the sur...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com