Reluctance type random access memory circuit
A random access memory and magnetoresistive technology, applied in the field of storage arrays, can solve problems such as inability to achieve writing effects, programming errors, and poor reliability of MRAM modes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
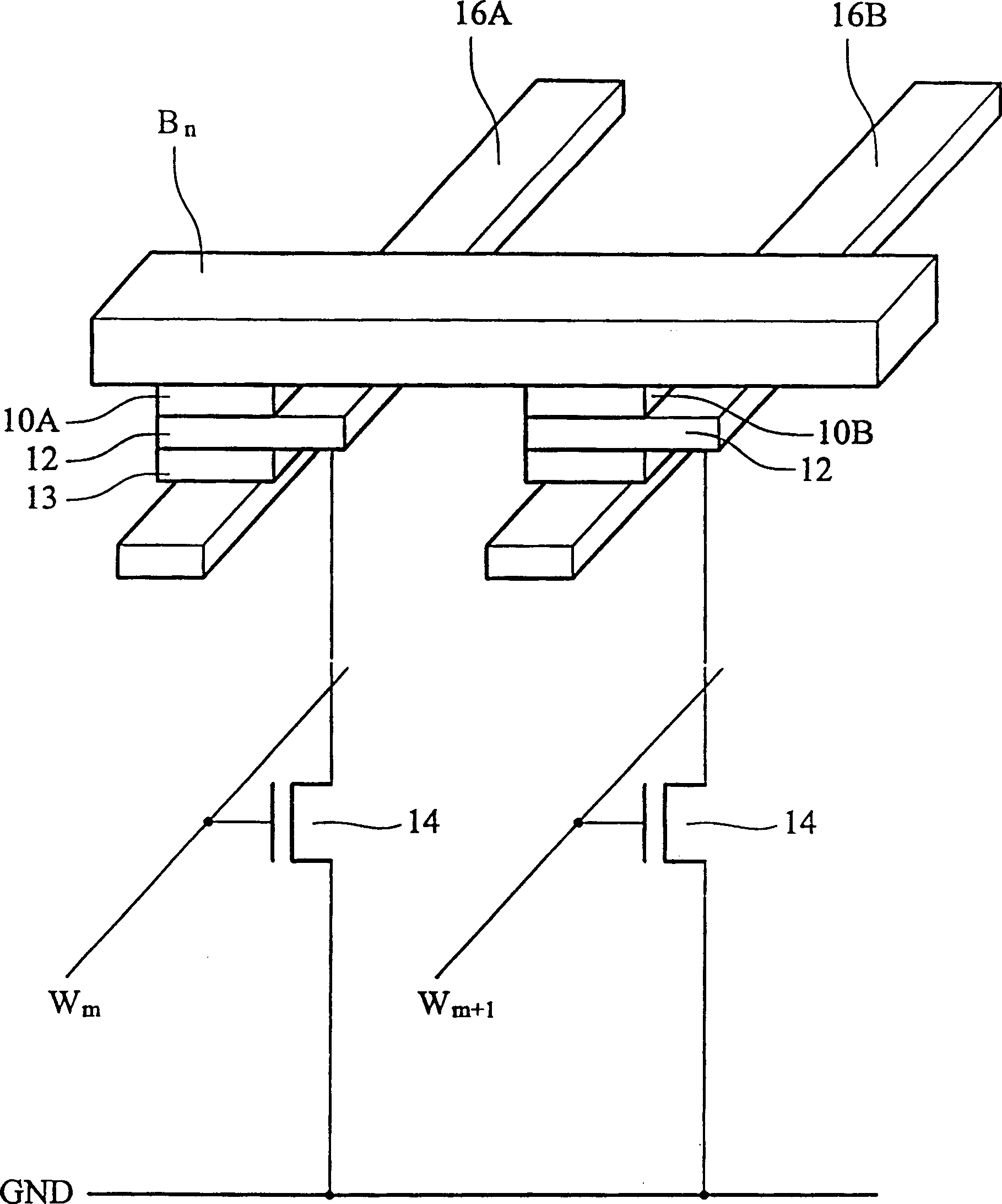
[0036] refer to Figure 4 , which is a schematic diagram showing a mode of a magnetoresistive random access memory cell (MRAM cell) according to an embodiment of the present invention.
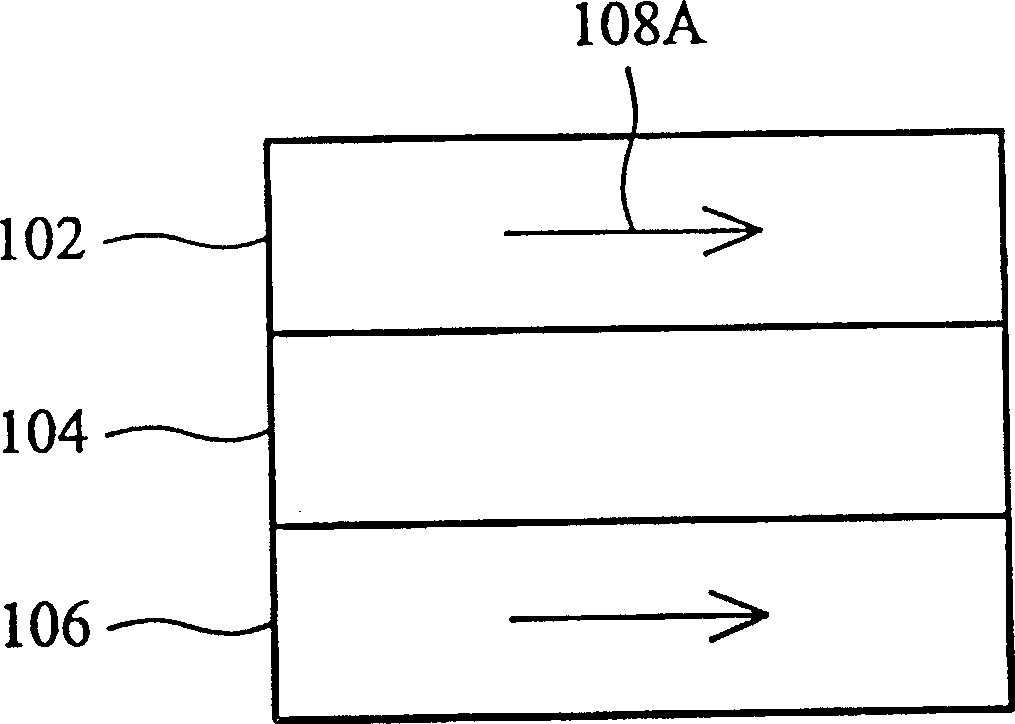
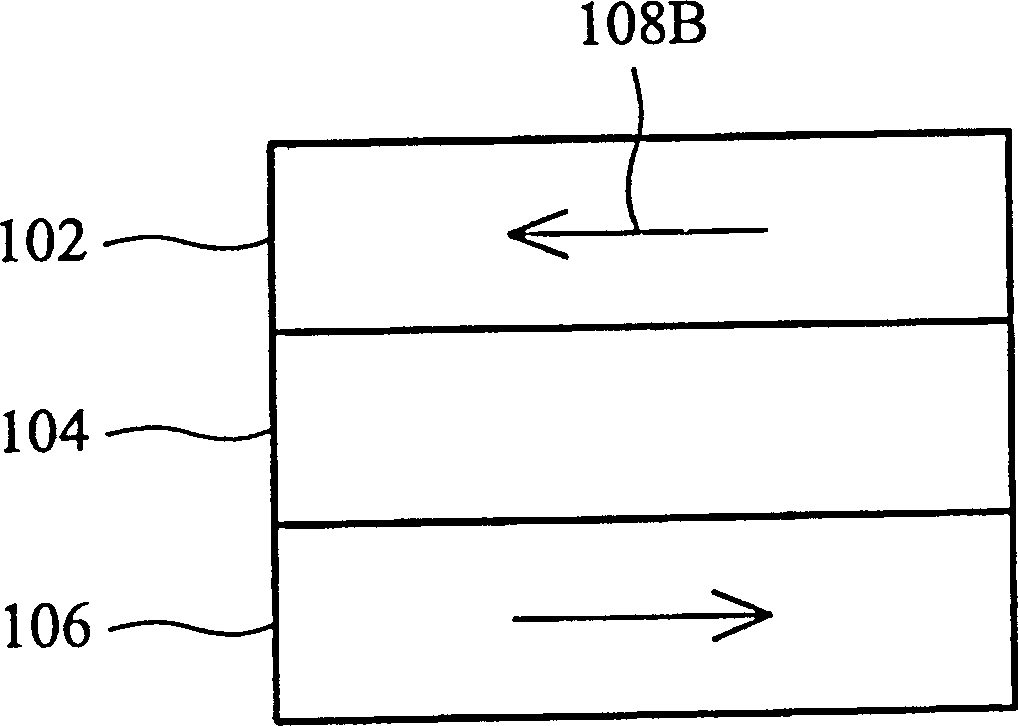
[0037] The internal structures of the magnetoresistive memory cells 40A and 40B (or called magnetic channel junction cells) are as follows: Figure 2A As shown, there is a fixed magnetic axis layer 106, a free magnetic axis layer 102, and an insulating layer (magnetic tunneling junction) 104 disposed between the fixed magnetic axis layer 106 and the free magnetic axis layer 102, and the magnetoresistive memory cell 40A The magnetoresistance of 40B and 40B is determined by the directions of the magnetic axes of the fixed magnetic axis layer 106 and the free magnetic axis layer 102 . When the magnetic axis directions of the free magnetic axis layer 102 and the fixed magnetic axis layer 106 are in the same direction, the MRAM unit will have low resistance, and when the free magnetic axis layer 1...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com