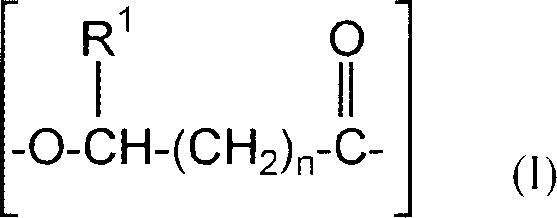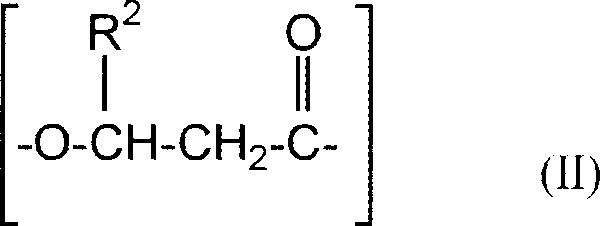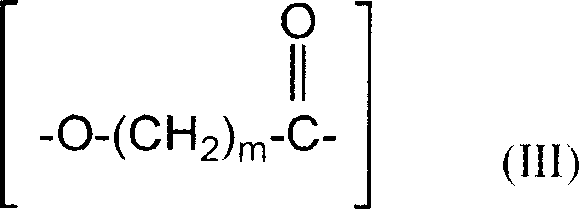Polyhydroxyalkanoate copolymer and polylactic acid polymer compsns. for laminates and films
A polyhydroxyalkanoate, composition technology, applied in the field of laminated materials, polyhydroxyalkanoate copolymer/polylactic acid polymer or copolymer blends, can solve the problem of hindering product collection and limiting polymerization speed of product production, sticking together or sticking to processing equipment, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0091] This example shows the processing of a binary blend comprising a preferred polyhydroxyalkanoate copolymer and a PLA polymer. Specifically, a polyhydroxyalkanoate copolymer comprising 3-hydroxybutyrate and about 12 mole percent of 3-hydroxyhexanoate (hereinafter referred to as PHBH copolymer) and crystallized Blends of polylactic acid (PLA) polymers are melt processed into films. The PHBH content ranges from 10% to 70% based on the total weight of PHBH and PLA. At levels below about 35% PHBH, no observable residual stickiness occurs. Compared with pure PLA films, these PHBH / PLA films showed a significant softness improvement with the addition of low to moderate amounts of PHBH to PLA. Some residual stickiness occurs at about 40% to 65% PHBH content. Significant sticky residue occurs at PHBH levels above about 70%.
Embodiment 2
[0093] This example shows the processing of a ternary blend comprising a preferred polyhydroxyalkanoate copolymer, a PLA polymer and a preferred moisture sensitive polymer. Specifically, the blend of PHBH copolymer and PLA polymer and polyethylene oxide (PEO) polymer of Example 1 was first prepared by the melt blending step in Example 1, wherein the content of PHA by weight The PLA content is 20%, the PLA content is 64%, and the PEO content is 16%. The blended PHBH / PLA / PEO blend was melt-processed into film by web extrusion. Compared to the 20 / 80 and 40 / 60 PHBH / PLA blends of Example 1, these PHBH / PLA / PEO films showed significant softness with the addition of small amounts of PEO to the PHBH / PLA blends improvement, wherein the PHA content in the first PHBH / PLA blend was the same as that in the PHBH / PLA / PEO blend, and the PLA content in the second PHBH / PLA blend was the same as that in the PHBH / PLA / PEO blend. The content is similar.
Embodiment 3
[0095] This example shows the processing of a bilayer laminate film using the PHA copolymer of Example 1 in the first layer. PLA resin L5000 from Biomer was used in the second layer, the ratio of the first layer to the second layer was 20 / 80, 40 / 60, 60 / 40 and 80 / 20. A co-extrusion process is used to produce this bilayer laminated film.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com