Ceramic heater
A ceramic heater and ceramic technology, applied in the field of conductive paste, can solve the problems that the temperature of the heater substrate cannot quickly keep up with the change of voltage or current, poor temperature control characteristics, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
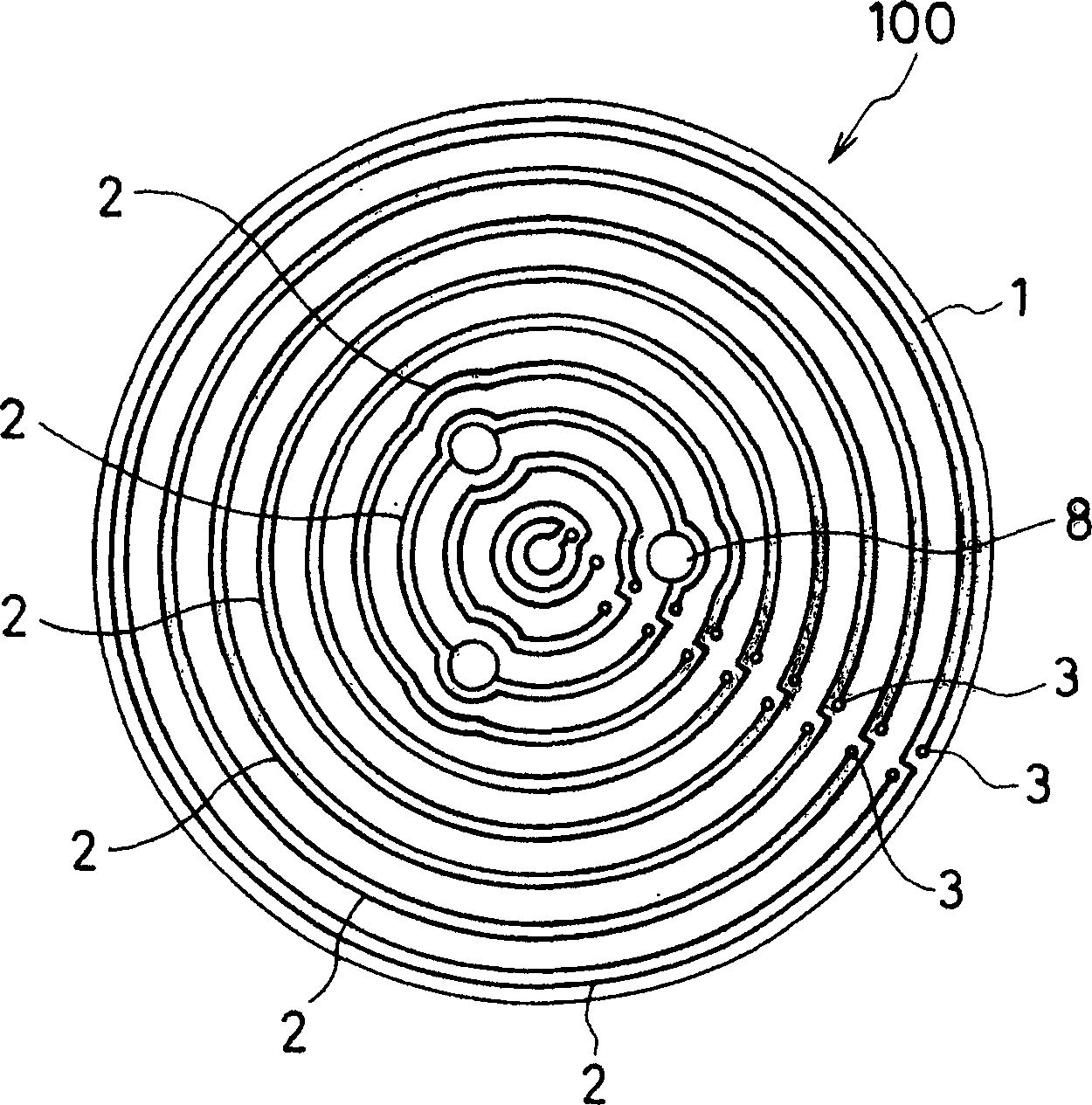
[0118] (Example 1) The heater is composed of an aluminum nitride ceramic substrate
[0119] (1) Using the spray drying method, a mixture of 100 parts by weight of aluminum nitride powder (average particle size of 1.1 microns), 4 parts of yttrium oxide (average particle size of 0.4 microns), 12 parts of acrylic binder and alcohol Made into granular powder.
[0120] (2) The granulated powder is put into a mold and formed into a flat plate to obtain a green sheet shape. This green sheet is drilled with a drill to form through-holes 8 for inserting support pins of the semiconductor wafer and recesses (not shown) for embedding thermocouples.
[0121] (3) at 200kg / cm 2 Under the pressure of 1800° C., the green sheet was hot-pressed to obtain an aluminum nitride plate with a thickness of 3 mm. It was cut into discs with a diameter of 210 mm to form a ceramic plate body (ceramic substrate) 1 .
[0122] (4) Conductive paste is screen-printed on the ceramic substrate 1 obtained in (...
example 3
[0130] Regarding the heaters of Examples 1 and 2, the temperature responsiveness and tensile strength of the heating surface of the ceramic substrate were measured when the power supply or current of the heating body 2 was changed, that is, when a voltage was applied to each heater, the heating of Example 1 was observed. The temperature change of the heater within 0.5 seconds, and the temperature change of the heater in observation example 2 within 2 seconds. On the other hand, the tensile strengths of the heating body 2 are respectively: 3.1 kg / mm in the heater of Example 1 2 , Example 2 heater 3kg / mm 2 .
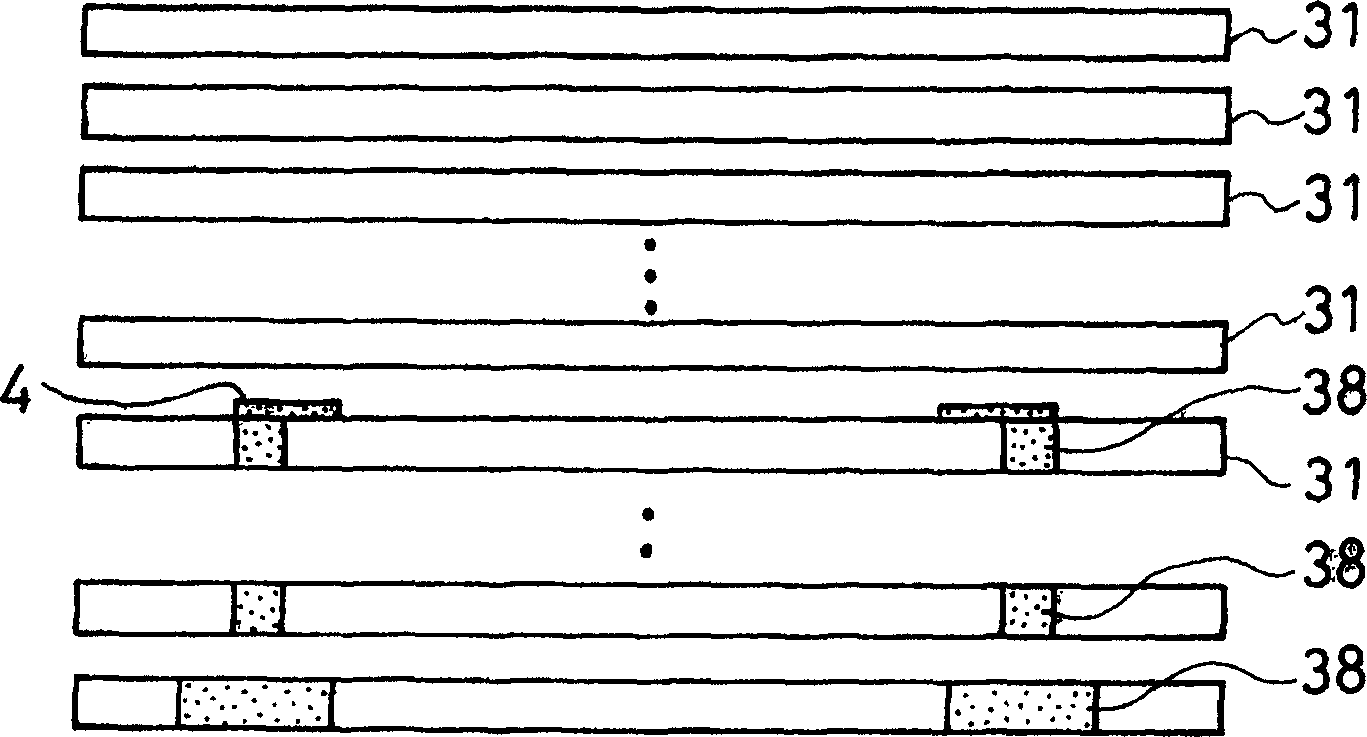
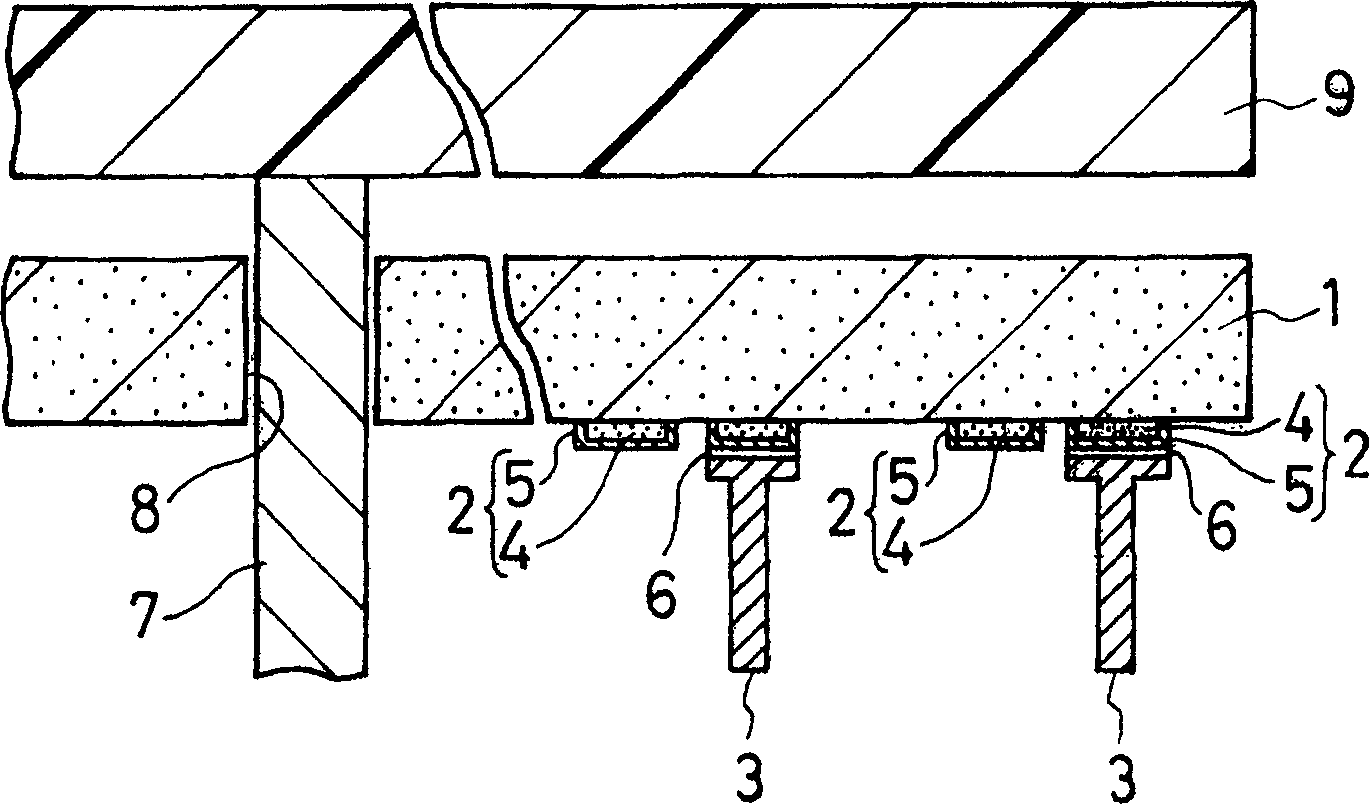
[0131] (Example 4) A heater with a heating body installed inside it ( image 3 , 5)
[0132] (1) Using a doctor blade, 100 parts by weight of aluminum nitride powder (manufactured by Tokuyama Corporation, with an average particle size of 1.1 μm), 4 parts of yttrium oxide (with an average particle size of 0.4 μm), 11.5 parts of an acrylic binder, A mixture of 0.5 part...
example 5
[0149] The same procedure as in Example 4 was basically repeated except that the heating body was not flat but had a cross-section of 20 microns thick by 20 microns wide square (aspect ratio of 1).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com