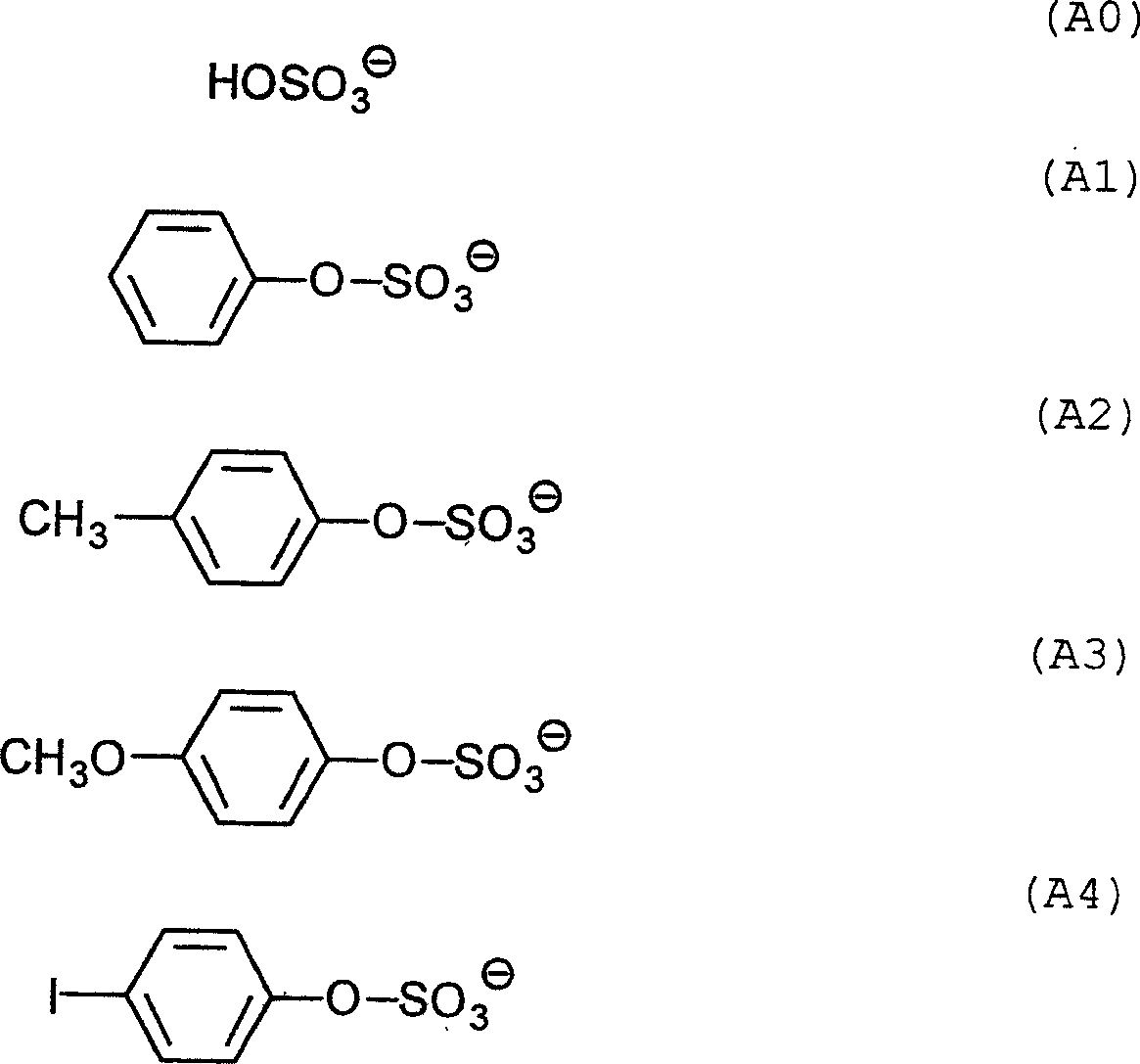
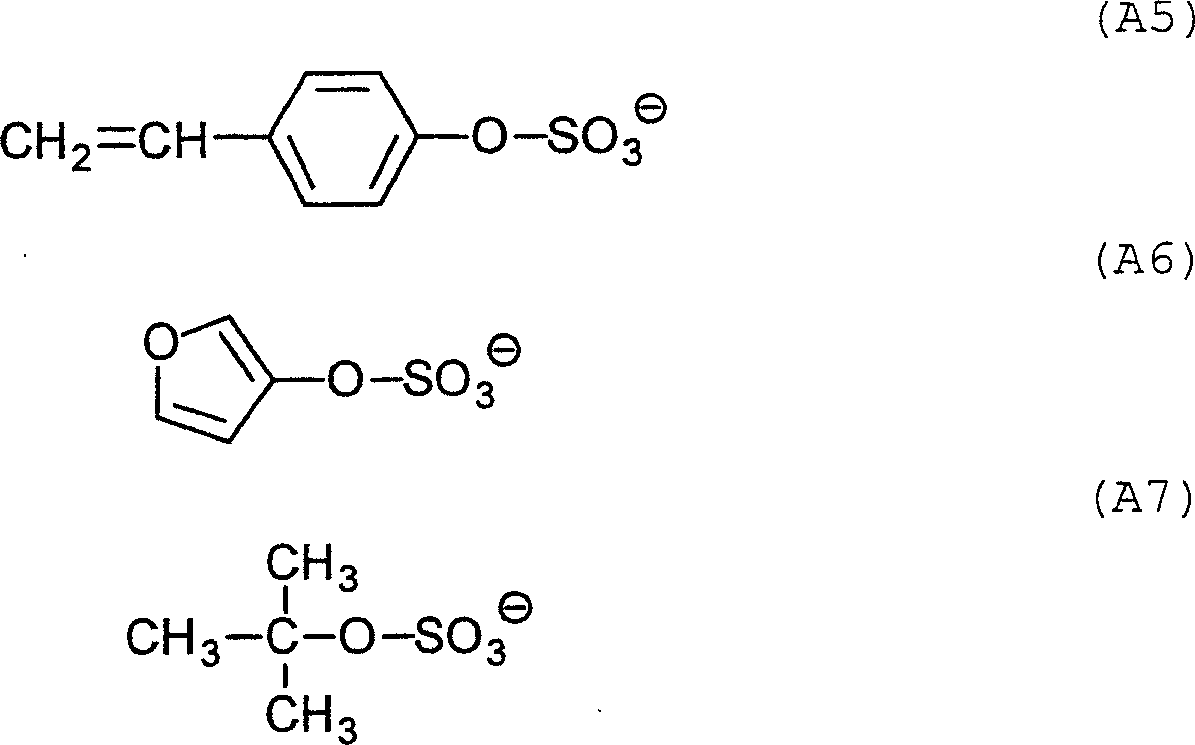
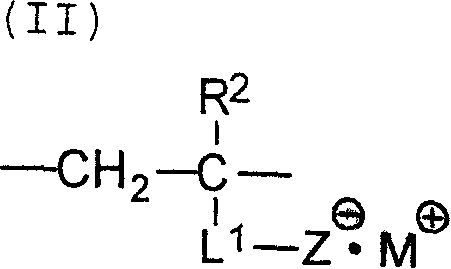Lithographic process involving on press development
A technology of lithographic printing and lithographic printing plates, which is applied in the field of lithographic printing and can solve problems such as poor wear resistance of printing plates
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0167] (Synthesis of sulfonium ion C10))
[0168] In 800ml of benzene, 50.9g of diphenylsulfoxide was dissolved. To the solution, 200 g of ammonium chloride was added. The mixture was refluxed for 24 hours. The reaction mixture was ice-cooled, and gradually poured into 2 liters of water. To the mixture was added 400 ml of concentrated hydrochloric acid. The reaction mixture was heated at 70°C for 10 minutes. The resulting aqueous solution was washed with ethyl acetate and filtered. A solution of 200 g ammonium iodide in 400 ml water was added to the filtrate.
[0169] The precipitated powder was filtered, washed with water, washed with ethyl acetate, and dried to obtain 70 g of triphenylsulfonium iodide.
[0170] (synthesis of salt (1))
[0171] In 100 ml of methanol, 7.8 g of triphenylsulfonium iodide was dissolved. To the solution, 4.87 g of silver oxide was added. The mixture was stirred at room temperature for 4 hours. Filter the solution. To the filtrate was ad...
Embodiment 2
[0174] (synthesis of salt (3))
[0175] In 100 ml of methanol, 7.8 g of triphenylsulfonium iodide prepared in Synthesis Example 1 was dissolved. 4.87 g of silver oxide were added to the solution. The mixture was stirred at room temperature for 4 hours. Filter the solution. 2.20 g of concentrated sulfuric acid was added to the filtrate to start the reaction. The reaction mixture was concentrated. The concentrate was washed with ethyl acetate and hexanes and dried in vacuo to give a solid.
[0176] The resulting solid was washed with ethyl acetate and hexane, and dried again in vacuo to yield 6.48 g of salt (3).
[0177] Other salts can also be prepared by appropriately changing the starting materials and adjusting the reaction conditions in a similar manner to the Synthetic Examples.
[0178] The synthesis of sulfonium salts is described in J. Amer. Chem. Soc.; 91; 1969; 145-150.
[0179] It is preferable that the maximum absorption wavelength of the salt of a sulfonium ...
Embodiment 3
[0230] (Synthesis of ethyl 4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethylbenzoylformate)
[0231] With 350ml of nitrobenzene, mix with 133g of aluminum chloride at room temperature. The mixture was maintained at 0 to 10°C. To the mixture, 136.5 g of ethyl chloroformate was added dropwise at 0 to 10°C for 15 minutes. The mixture was stirred for 15 minutes.
[0232] In 150ml of nitrobenzene, dissolve 2,6-dimethylphenol. The solution was kept at 0 to 10°C, and it was added dropwise to the mixture prepared above for 30 minutes. The mixture was stirred at 0 to 10°C for 2 hours and at room temperature for 1 hour.
[0233] With 2 liters of ice-cold water, mix 60 ml of concentrated hydrochloric acid. The reaction mixture prepared above was poured quietly into diluted hydrochloric acid. The mixture was extracted with 500 ml of ethyl acetate. Dry over sodium sulfate and concentrate the organic phase. The nitrobenzene was removed under reduced pressure to give a solid. The resulting solid was reslurrie...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com