A non-hormonal approach to male contraception
A male and alkyl technology, applied in diseases, pharmaceutical formulations, organic active ingredients, etc., can solve problems such as poor metabolism and unacceptable testosterone preparations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0125] The effect of oral administration of embodiment 1-NB-DNJ on male mice
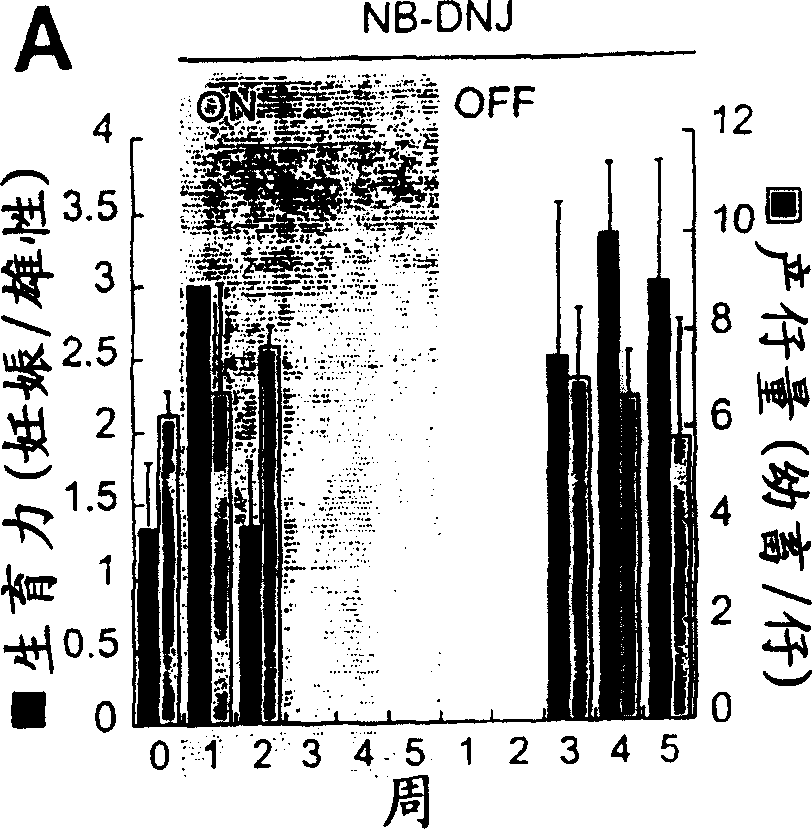
[0126] To determine the effect of NB-DNJ on the fertility of male mice, 6-week-old C57BL / 6 males were treated with 2400 mg / kg NB-DNJ / day for increasing durations with weekly increments (Fig. 1a), followed by mating trials, During this time they were housed with untreated female mice for 1 week. Figure 1A It was shown that males gave birth and were able to reproduce a normal number of pups at the start of the experiment, and this ability was maintained after 2 or 3 weeks after NB-DNJ treatment. Mice were sterile after at least 3 weeks of drug consumption ( Figure 1A ). When the male mice were withdrawn after 5 weeks, their fertility was restored in the fourth week, and a normal number of pups were produced ( Figure 1A ). 13-week-old males treated with the same dose for 5 weeks also became completely sterile (data not shown). Therefore, under NB-DNJ treatment, male mice became sterile and this ...
Embodiment 2
[0127] Example 2 - Dose Response
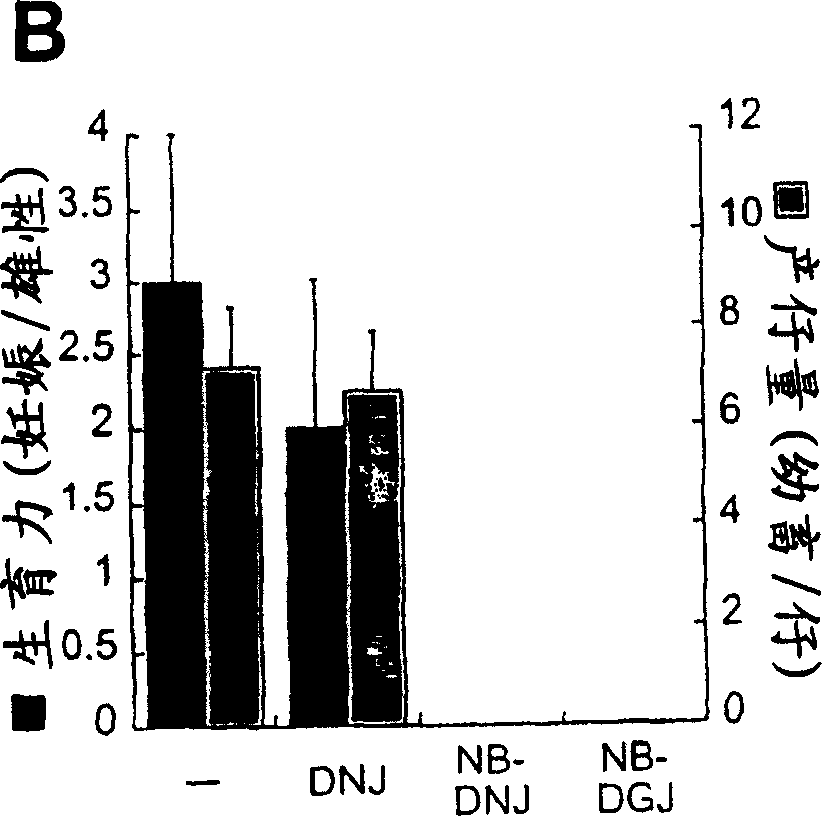
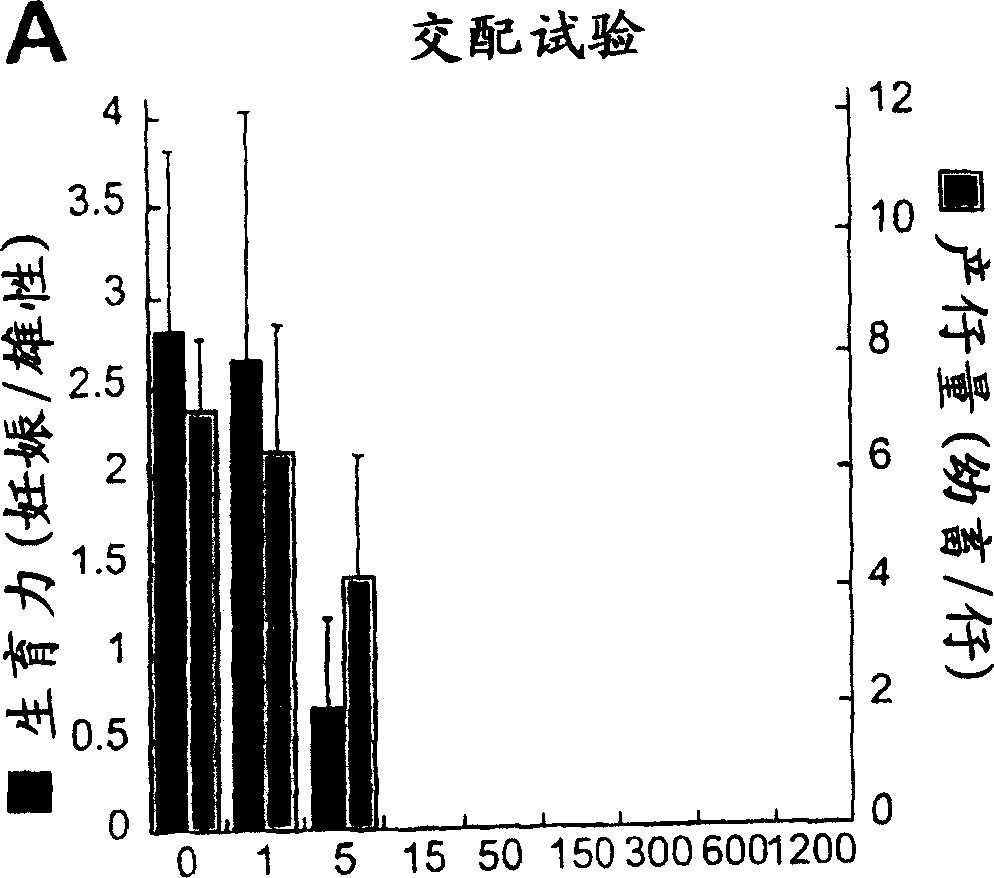
[0128] Earlier work has demonstrated that the in vivo reduction in GSL levels caused by NB-DNJ is dose-dependent; for example, doses of 600-2400 mg / kg / day resulted in a 10-70% reduction in the levels of ganglioside GM1 on the surface of mouse splenocytes, respectively. % (Platt et al. (1997) J Biol Chem 272, 19365-72). It has been established that male mice become sterile when treated with 2400 mg / kg / day of NB-DNJ ( Figure 1A with 1B ), they were exposed to gradually decreasing doses of the compound to determine the lowest dose causing sterility. The result is as Figure 2A with 2B shown. Although 1mg / kg / day did not affect males, 5mg / kg / day weakened their fertility ( Figure 2A ) and litter size ( Figure 2B ), and 15 mg / kg / day they were completely sterile. Therefore, the mouse male reproductive system is exceptionally sensitive to NB-DNJ. Drug-induced fertility loss was not due to changes in mating behavior, such as the frequency ...
Embodiment 3
[0129] Example 3 - Fertility of female mice
[0130] Treatment of NB-DNJ at 1200 mg / kg / day did not cause sterility in female mice as compared to male mice. After a mating period of 4 days with untreated males, 100% of treated (n=5) as well as untreated females (n=4) were fertile; these mice had 6.2±2.7 and 7.8±1.0 pups per litter, respectively.
[0131] NB-DNJ was administered to 15-week-old female mice of strain 129 at 2400 mg / kg per day for 12 weeks. Thereafter, the drug was withdrawn and the females were housed with untreated males of the 129 line. All females conceived rapidly and had an average litter size of 6 pups. Mice in this experiment were heterozygous for disruption of the gene encoding ceramide galactosyltransferase. These mice are phenotypically indistinguishable from wild-type 129 mice and reproduce normally (Coetzee et al., (1996), Cell, 86:209-219).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com