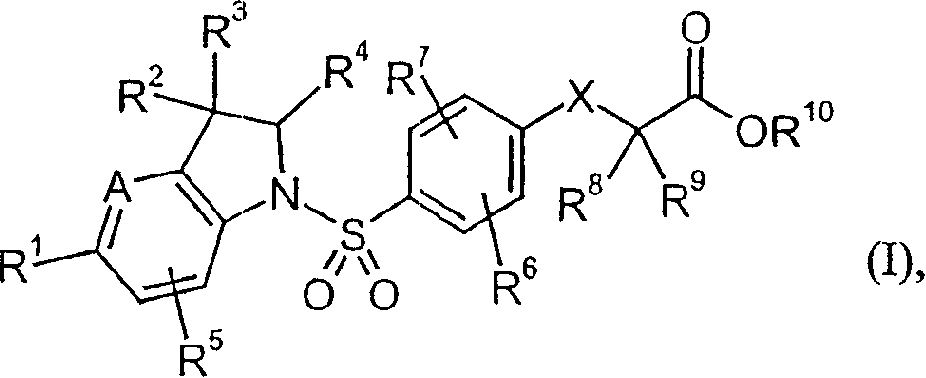
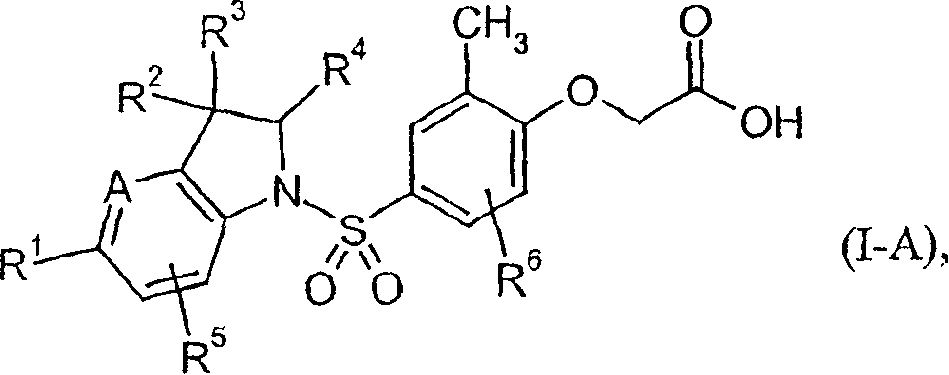
Indolin phenylsulfonamide derivatives
An alkyl and methyl technology, applied in the field of indoline phenylsulfonamide derivatives, can solve problems such as weak interactions, large side effects, and high daily doses
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0262] [4-({3-isopropyl-7-methyl-5-[4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-1-yl}-sulfonyl )-2-Methylphenoxy]acetic acid
[0263]
[0264] Step a):
[0265] 1-(4-Bromo-2-methylphenyl)hydrazine
[0266]
[0267] 50 g (267.7 mmol) of 4-bromo-2-methylaniline were heated in 190 ml of concentrated hydrochloric acid at 80° C. for 30 min. After cooling to 5° C., 18.5 g (267.7 mmol) of sodium nitrite in 95 ml of water were added dropwise thereto within 30 minutes. After it was stirred at 5° C. for 30 minutes, the reaction mixture was added dropwise to a solution of 384 g (2 mol) of stannous chloride in 190 ml of concentrated hydrochloric acid within 45 min. After it was stirred at RT for a further 45 min, the mixture was made basic with 50% concentrated aqueous sodium hydroxide. The precipitate was filtered off and extracted repeatedly with dichloromethane and ethyl acetate. The combined organic phases were dried over magnesium sulfate and concentrated. This gave 4...
Embodiment 2
[0313] [2-Methyl-4-({2,3,7-trimethyl-5-[4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-1-yl }sulfonyl)phenoxy]acetic acid
[0314]
[0315] Step a):
[0316] 5-Bromo-2,3,7-trimethyl-1H-indole
[0317]
[0318] 8 g (39.8 mmol) of 1-(4-bromo-2-methylphenyl)hydrazine (example 1 / step a) were suspended in 14 ml of ethanol, and 3.7 g (52 mmol) of methyl ethyl ketone were added thereto. After it was stirred at RT for 30 minutes, the solvent was removed under reduced pressure and the intermediate was melted without further purification at 170° C. together with 5.9 g (43 mmol) of anhydrous zinc chloride. After 30-45 min, the melt was cooled to RT, taken up with dichloromethane and extracted with dilute hydrochloric acid and water. The organic phase was dried over magnesium sulfate and the solvent was removed under reduced pressure. The crude product was dissolved in ethyl acetate and purified on silica gel (mobile phase: cyclohexane-ethyl acetate 9:1). This gives 3.8 g of pro...
Embodiment 3
[0344] [4-({3,7-Dimethyl-5-[4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-1-yl}sulfonyl)-2- Methylphenoxy]acetic acid
[0345]
[0346] Step a):
[0347] 5-bromo-3,7-dimethyl-1H-indole
[0348]
[0349] 5 g (24.8 mmol) of 1-(4-bromo-2-methylphenyl)hydrazine (example 1 / step a) were suspended in 14 ml of ethanol, and 1.8 g (32 mmol) of propionaldehyde were added thereto. The mixture was stirred at RT for 30 min, then the solvent was removed under reduced pressure and the intermediate was melted at 170° C. without further purification together with 3.7 g (27 mmol) of anhydrous zinc chloride. After 30-45 min, the melt was cooled to RT, taken up with dichloromethane and extracted with dilute hydrochloric acid and water. The organic phase was dried over magnesium sulfate and the solvent was removed under reduced pressure. The crude product was dissolved in ethyl acetate and purified on silica gel (mobile phase: cyclohexane-ethyl acetate 9:1). This gives 1.5 g of product (2...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com