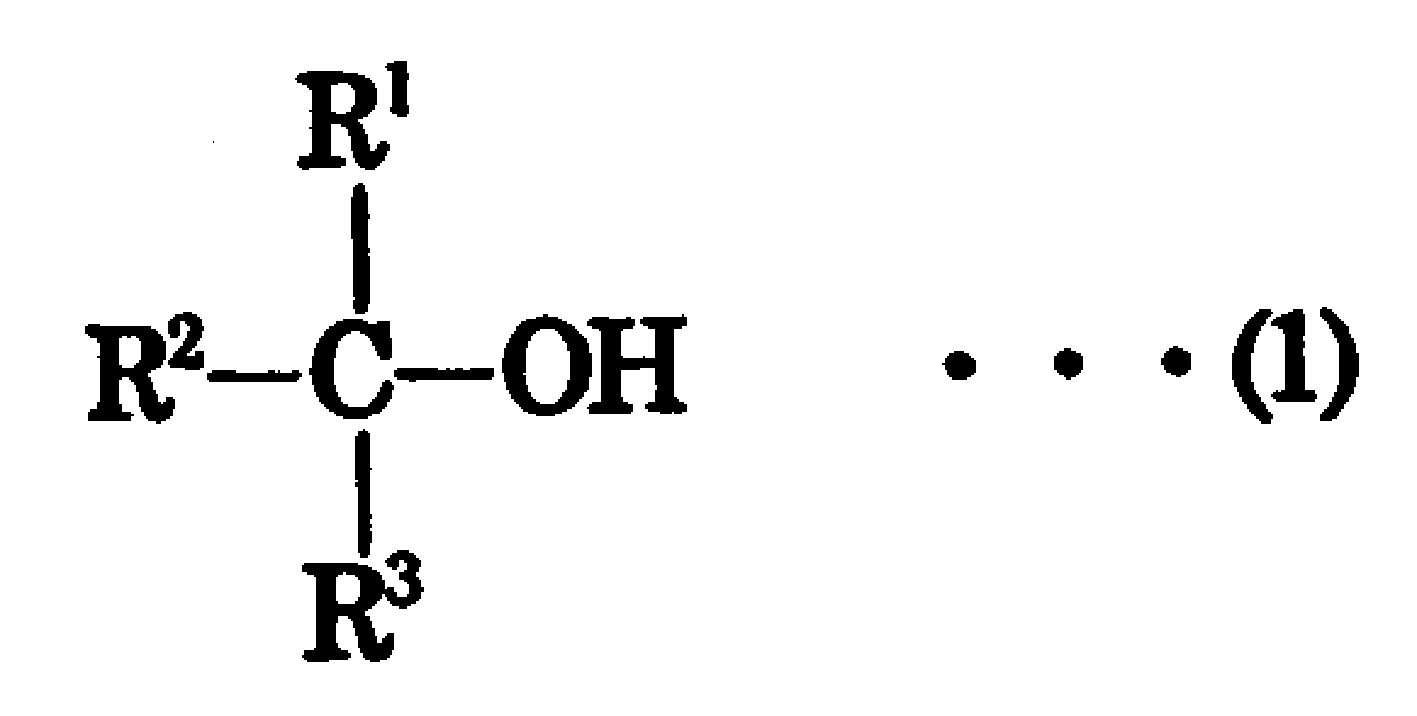
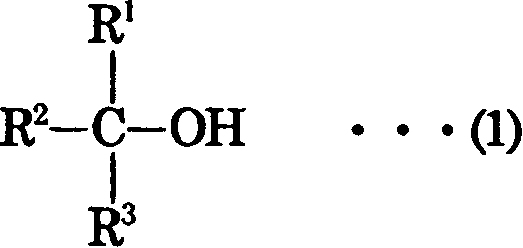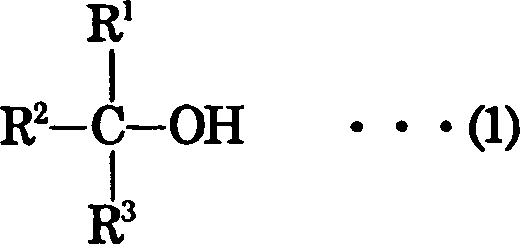Composition for optical material, optical material, process for producing the same, and lens
A technology of optical materials and compositions, applied in optics, optical components, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as the decrease in transparency of optical materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1-8
[0086] After mixing the monomer components, ultraviolet absorber, pigment and surfactant shown in Table 1, impurities in the mixture were removed with a nylon filter (5 μm) to prepare an optical material composition. In addition, pigments and surfactants are mixed in advance to prepare a concentrated pigment solution by the following method. The stability of the prepared composition for optical materials was measured from the rate of change of the pigment concentration before and after filtering through the filter, and expressed in terms of visible light transmission (460 nm). The compositions prepared in Examples 1-8 are stable, and there is no change in pigment concentration after being placed at 40° C. for 30 days.
[0087] Next, after adding 0.6 g of IPP or 0.7 g of NPP as a polymerization initiator to 20 g of each of the prepared compositions, the mixture was poured into a mold consisting of two glass discs with a diameter of 7 cm and a glass disk with a thickness of 1.5 ...
Embodiment 9-17
[0101] Use the thick pigment solution that is prepared as pigment by the mixed system of 0.9g PB-100 (produced by Daiichi Chemical Industry Co., Ltd., particle size 0.3-2 μm) and 0.1g ルビクロン red 500RS (Tonn-Co., Ltd.), except press Except for the compositions shown in Table 2, compositions for optical materials were prepared in the same manner as in Examples 1-8, resin plates, test pieces, etc. were prepared from the compositions, and their physical properties were measured. The results are shown in Table 2.
[0102] In addition, the compositions for optical materials prepared in Examples 9-17 were stable, and there was no change in pigment concentration when left at 40° C. for 30 days. Moreover, the resin board has not been yellowed after being placed for 2 years.
[0103] Example
Embodiment 18-22
[0105] Except for the composition shown in Table 3, compositions for optical materials were prepared in the same manner as in Examples 9-17, resin plates, test pieces, etc. were prepared from the compositions, and their physical properties were measured. The results are shown in Table 3.
[0106] In addition, the compositions for optical materials prepared in Examples 18-22 were stable, and there was no change in pigment concentration when left at 40° C. for 30 days. Moreover, the resin board has not been yellowed after being placed for 2 years.
[0107] Example
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com