Methods for vaccinating against malaria
A technology against malaria and vaccines, applied in botany equipment and methods, against vector-borne diseases, animal repellants, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
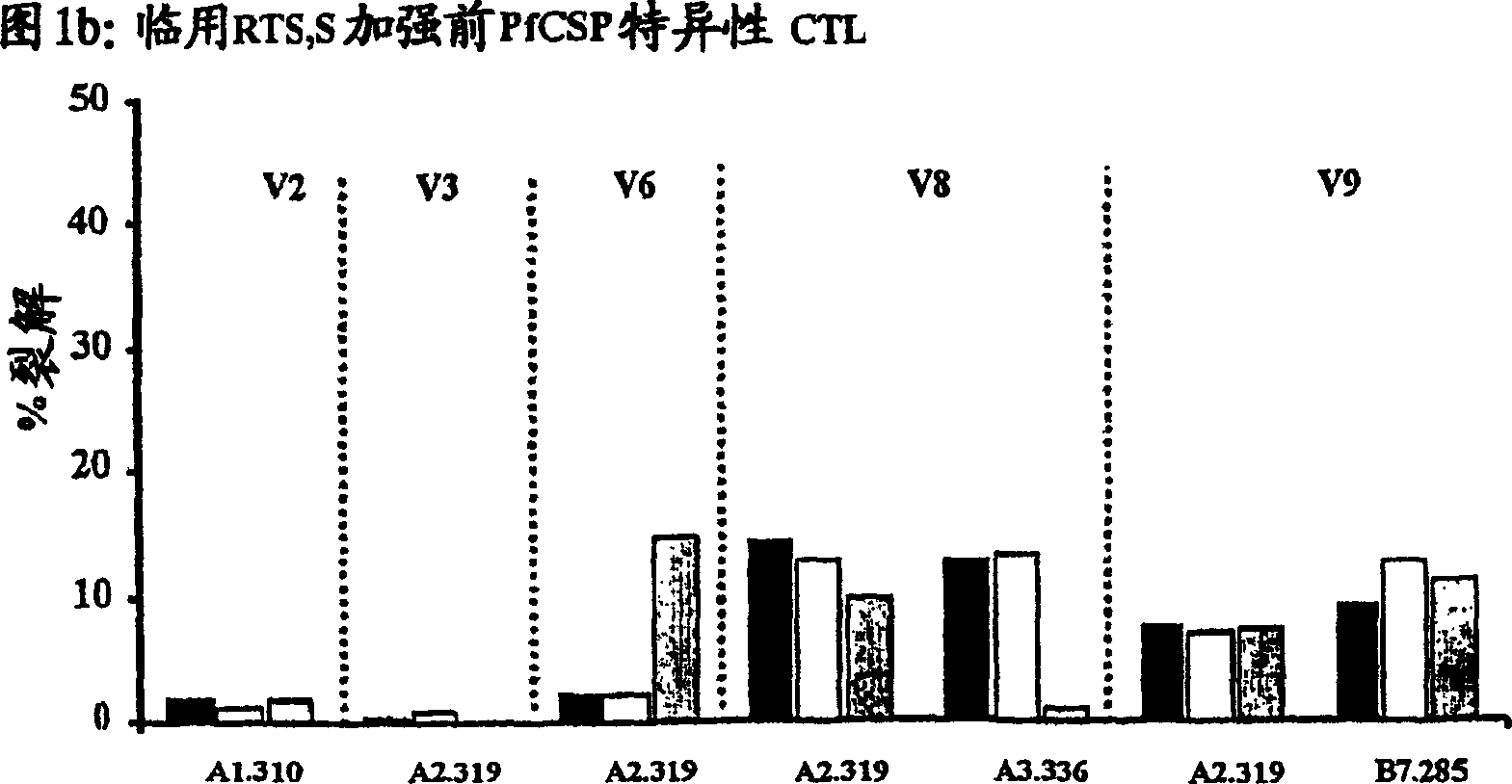
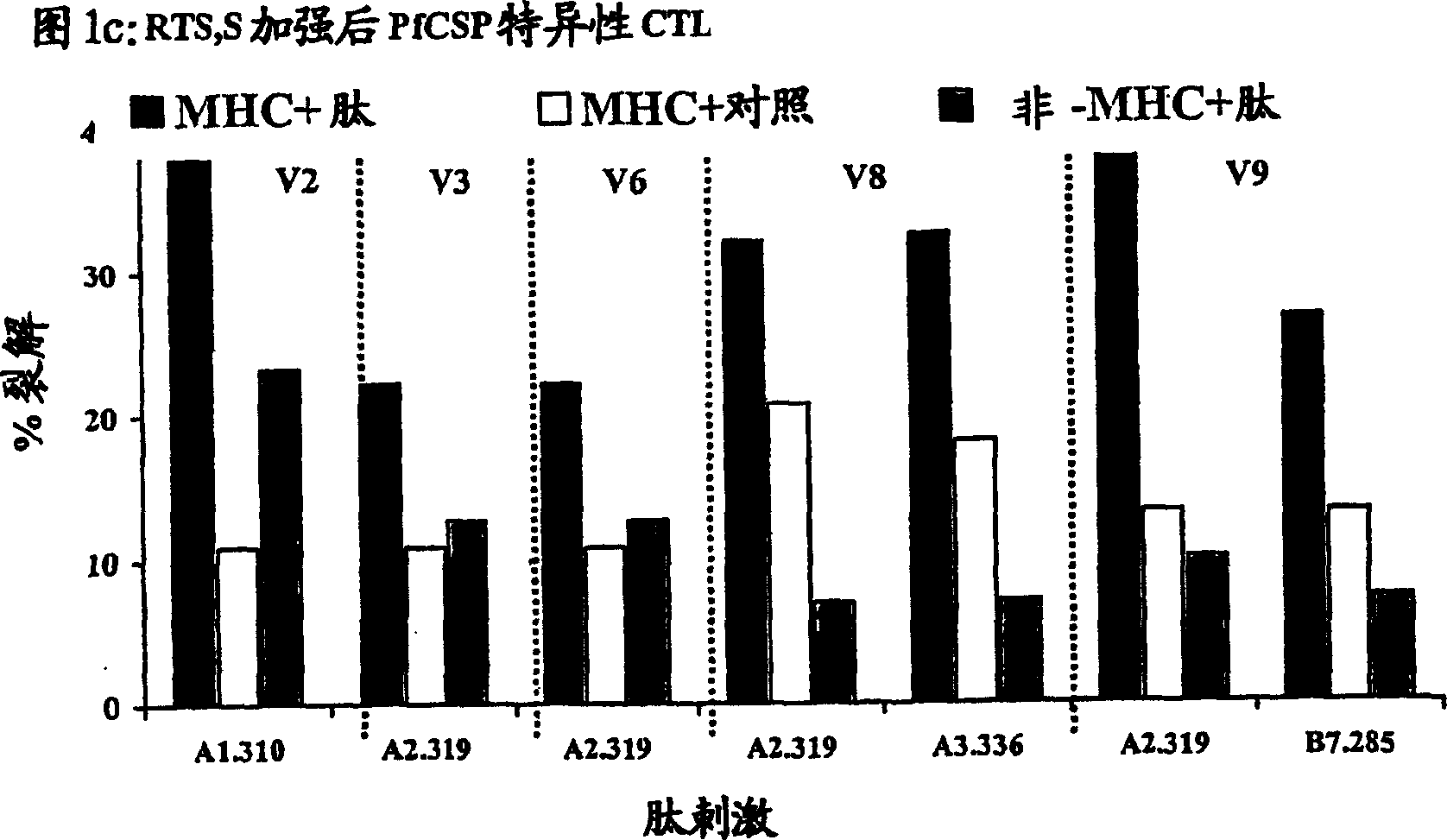
[0095] Boosting of primed anti-PfCSP responses with RTS,S vaccine
[0096] Twenty-four HLA-A*0201 positive volunteers were recruited for this study. To allow intergroup comparisons of genetically restricted T cell responses, volunteers' HLA diversity was restricted to the most common class I HLA subtype in the population. None of these volunteers had previous exposure to malaria. Among the 24 subjects, 10 participated in the above-mentioned second PfCSP vaccine clinical trial. During this trial, these volunteers had received a total of three doses of PfCSP DNA vaccine (VCL-2510, prepared by Vical, Inc (SanDiego, CA) as previously described (62)) at a dose of 2500 μg / dose with intervals between doses. 4 weeks (62). Therefore, in this trial, these 10 volunteers received their last dose of DNA vaccine 12-14 months before receiving the booster RTS,S vaccine. The remaining 14 volunteers had not previously received PfCSP DNA vaccine and thus served as unprimed controls. All 2...
Embodiment 2
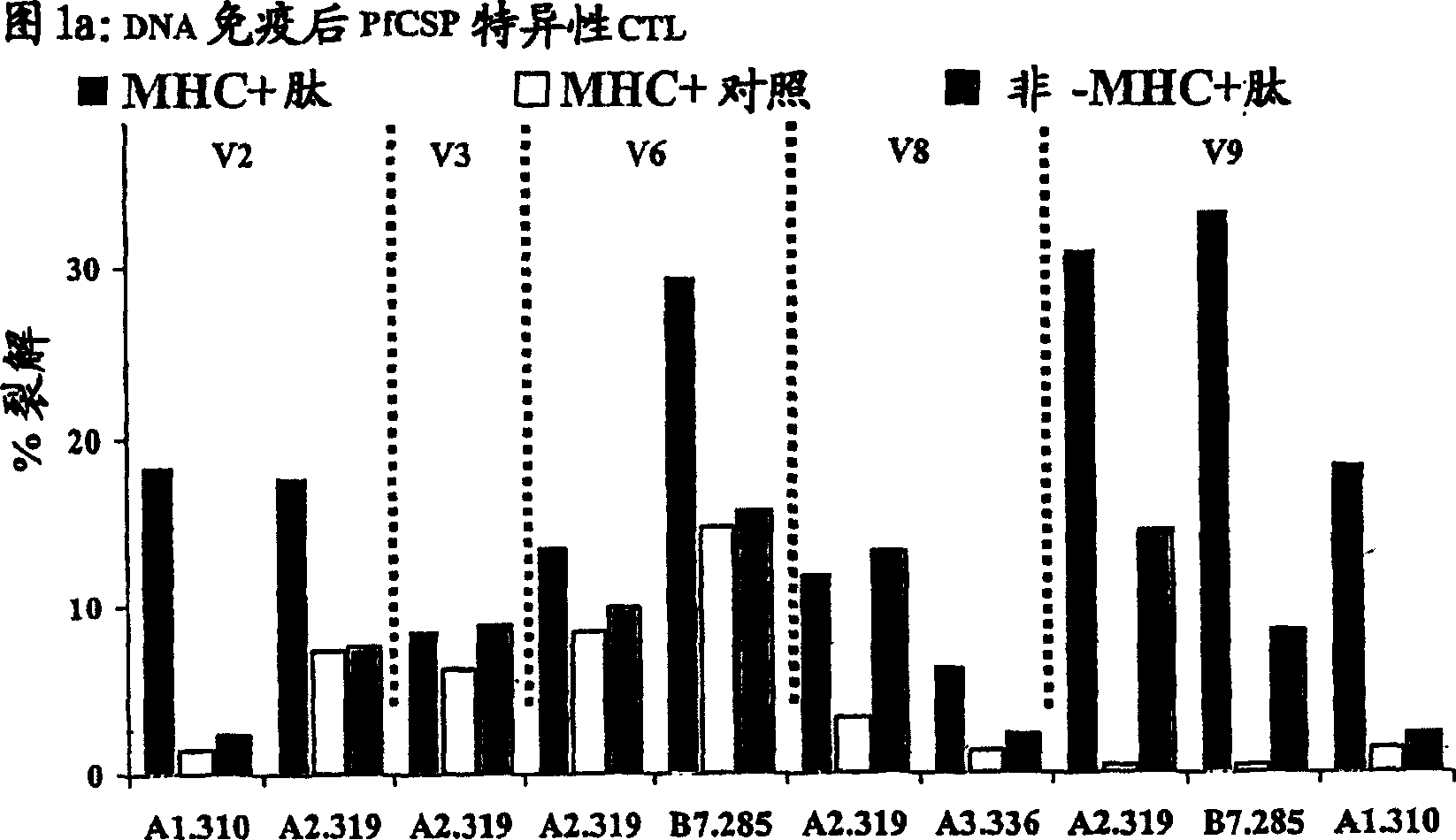
[0102] CTL response
[0103] As noted above, immunization with the RTS,S vaccine alone induced antibodies and CD4 + T cell-dependent IFN-γ responses, but have not been reported to elicit antigen-specific CTLs in humans (61). To determine whether DNA-induced memory CTLs could be recalled by boosting with the RTS,S vaccine and whether the boosted response was broader than the initial DNA-induced response, the cytotoxic activity of antigen-specific CTLs was tested in different volunteers. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were collected from the blood of DNA-primed or non-primed volunteers 1–2 weeks before immunization with RTS,S and 1 or 2 weeks after the first and / or second dose of RTS,S immunization. ). These PBMCs were then used in a chromium release assay to detect lysis of antigen-presenting target cells (105).
[0104] In vitro chromium release assays were performed as previously described (105). Specifically, to generate effector cells, 20% of the total PBM...
Embodiment 3
[0116] T cell IFN-γ response to PfCSp
[0117] IFN-γ responses were assessed using a standard ELISPOT assay as follows. The number of IFN-γ producing PfCSP-specific cells was determined by ELISPOT after 36 hours of in vitro stimulation in the presence of 10 μg / ml peptide as previously described (107). The number of spots corresponding to cytokine-producing cells (spot-forming cells; SFC) in the wells was counted using an automated spot counting system (Scanalytics, Fairfax, VA). The reaction is expressed as SFC / 10 6 The average number of PMBCs was considered significant if the following conditions were met: 1) the average number of cells in the wells containing the experimental peptide was significantly greater than that in the wells containing the control peptide (p<0.05, student's T test); 2) the net SFCs / Wells (average number of SFCs in test peptide wells minus mean number of SFCs in control peptide wells) ≥ 5 SFCs / well; and 3) stimulation index (average number of SFCs...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com