Method for obtaining flat-topped light beam utilizing secondary stimulated Brillouin scattering light amplitude limiting
A stimulated Brillouin and flat-top beam technology, applied in the field of nonlinear optics, can solve the problems of low damage threshold, flexible adjustment of transmittance function, inability to apply strong laser system safety protection, etc. The method is simple and flexible. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
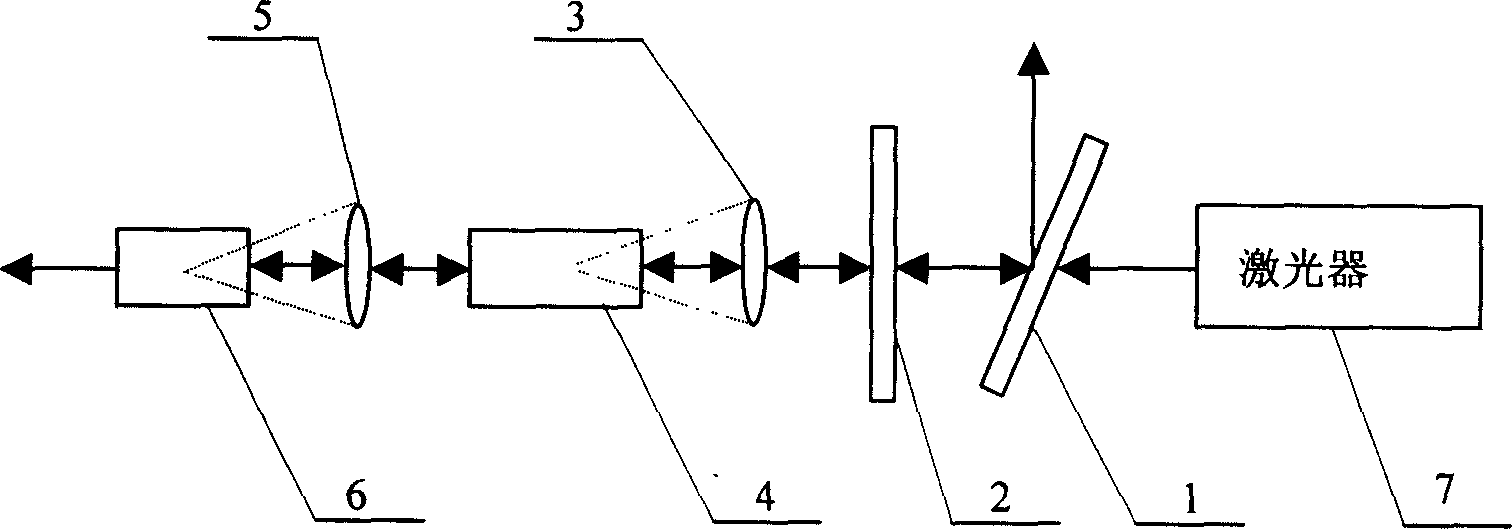
[0010] Specific implementation mode one: combine figure 1 Describe this specific embodiment, the twice stimulated Brillouin scattering system of this specific embodiment consists of a polarizer 1, a 1 / 4 wave plate 2, a first convex lens 3, a first oscillation pool 4, a second convex lens 5, a second The oscillating pool 6 and the laser 7 are composed, and the method for realizing light limiting to obtain a flat-top beam in this specific embodiment is: the p-polarized light output by the laser 7 is input to the input end of the polarizer 1, then transmitted through the polarizer 1 and transmitted from the polarizer 1 The output end of the 1 / 4 wave plate 2 is output to the input end of the 1 / 4 wave plate 2, after the transmission transformation of the 1 / 4 wave plate 2, the circularly polarized light is obtained at the output end of the 1 / 4 wave plate 2 and input to the input end of the first convex lens 3 Among them, the circularly polarized light transmitted by the first conve...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0011] Specific implementation mode two: combination figure 1 Describe this specific embodiment, in specific embodiment one, the medium in the described first oscillating pool 4 and the medium in the described second oscillating pool 6 are selected to have an absorption coefficient less than 0.005 cm -1 (per centimeter) of the Brillouin medium. The smaller the absorption coefficient is, the higher the energy of the SBS optical limiting output is. Therefore, in order to increase the energy of the optical limiting output of the present invention, a Brillouin medium with a small absorption coefficient is selected.
specific Embodiment approach 3
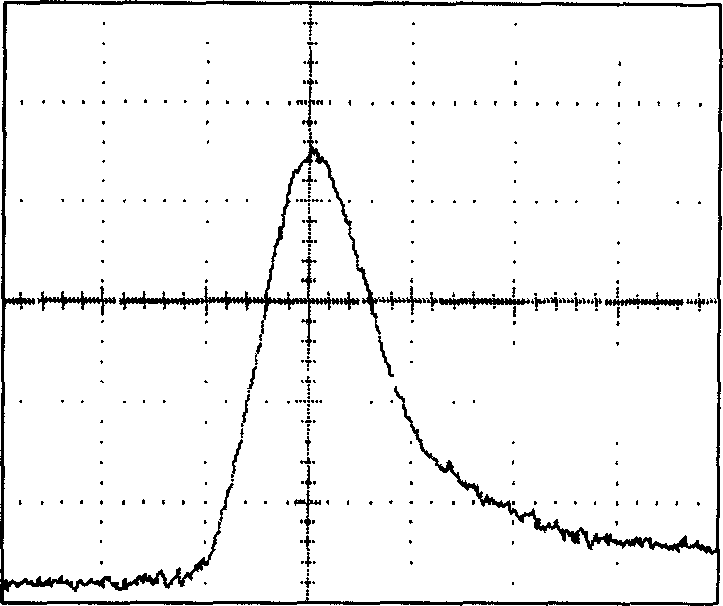
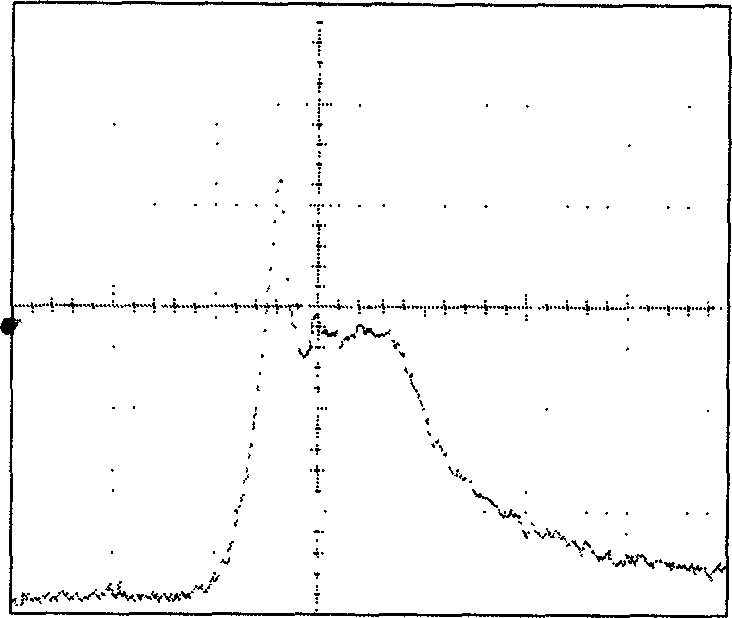
[0012] Specific implementation mode three: combination figure 1 To describe this specific embodiment, in the first specific embodiment, the gain coefficient of the medium in the first oscillating cell 4 is determined by the energy of the required top-hat beam. Since the SBS optical limiting output energy is determined by the system index gain coefficient (G=gIL formula, G is the system index gain coefficient, g is the medium gain coefficient, L is the effective length of action, and I is the light intensity), the smaller the gain coefficient is , the trailing edge platform generated after the first SBS action is high, and the energy of the required flat-top beam is high; the larger the gain coefficient is, the trailing edge platform generated after the first SBS action is lower, and the required flat-top beam energy is Energy is low.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Absorption coefficient | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Gain factor | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Gain factor | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com