Method for segmenting anatomical structures from 3d image data by using topological information
A three-dimensional image, anatomical structure technology, applied in image data processing, image data processing, image analysis and other directions, can solve problems such as inability to reach blood vessels
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
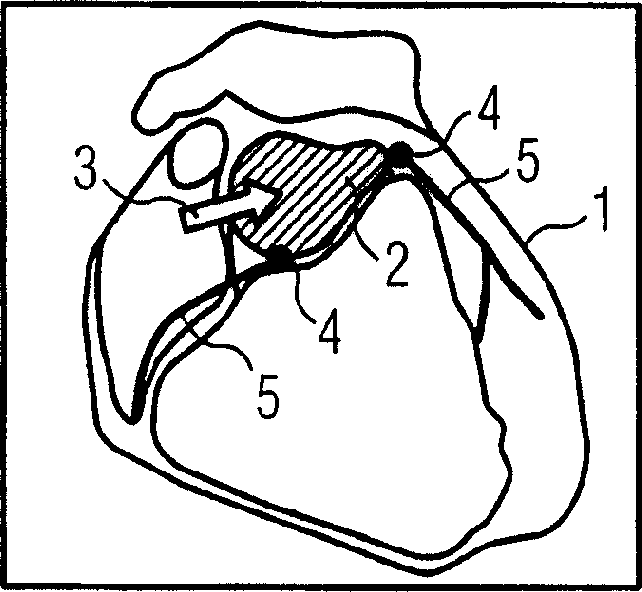
[0020] In this example, the individual steps for segmenting a coronary vessel tree from three-dimensional image data recorded with CTA techniques are described. The figures here show different views of the heart with the atria and blood vessels contained therein, which are only shown schematically due to the lack of visualization of the image itself. here figure 1 A view of the entire heart 1 is shown, a section through the aorta 2 being visible at the top. In a first step, a starting point is set, eg interactively with the mouse cursor 3 , by clicking on the aorta 2 on the screen where the image is displayed. Starting from this starting point, two bifurcation points 4 are automatically detected at which the aorta 2 diverges into coronary vessel structures 5 . Mark the bifurcation point 4.
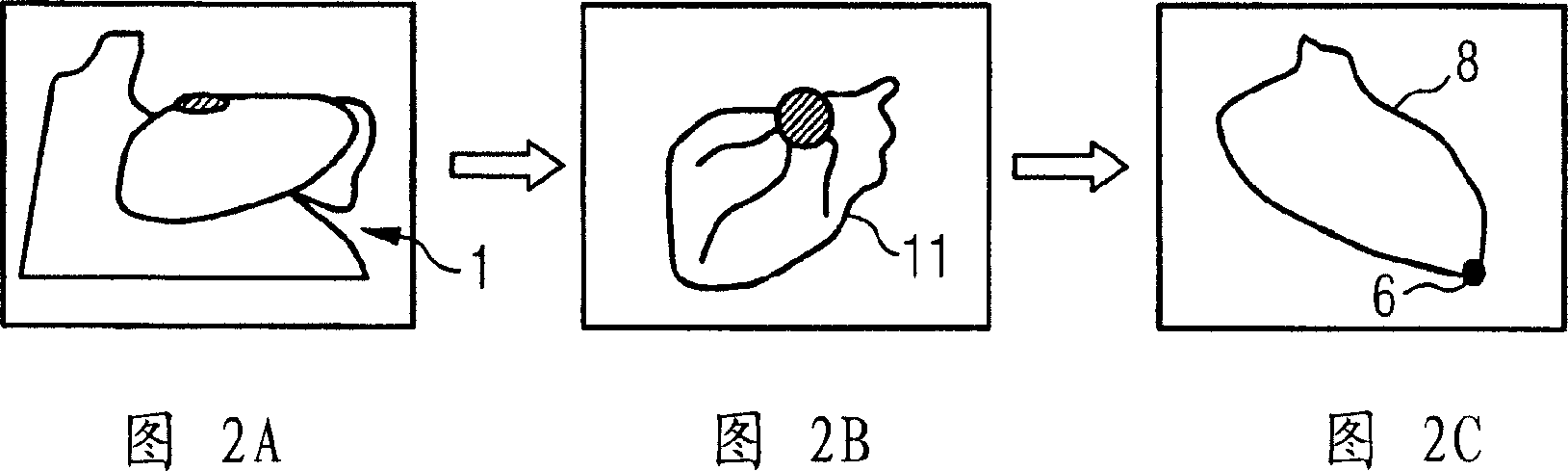
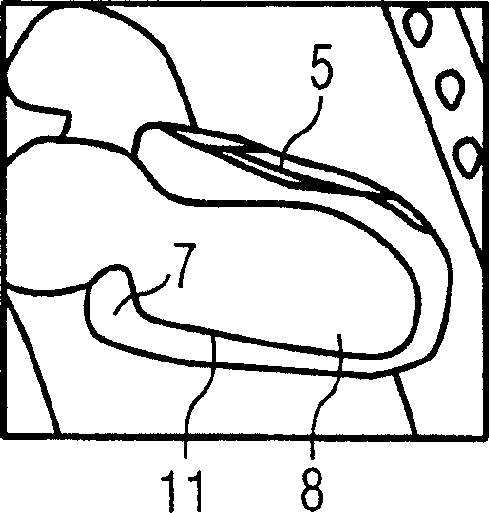
[0021] In the next step, seen with the help of parts of FIGS. 2A, 2B, 2C, the atrium 11, that is, the left and right atrium and the ventricle, is segmented and anatomical landmarks, in ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com