Cathode structure for inversion type organic luminous assembly
A technology of light-emitting components and cathode structures, applied in the direction of light-emitting materials, electroluminescent light sources, light sources, etc., can solve the problems of easy diffusion, easy reaction and deterioration, and difficult use and processing of highly active metals
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0076] In order to illustrate that the use of the electron injection layer of the present invention can effectively improve the electron injection capability of an organic light-emitting device with an inverted structure using silver (Ag) as the cathode conductive metal, a dual-cathode electronic single-carrier device was fabricated for comparison.
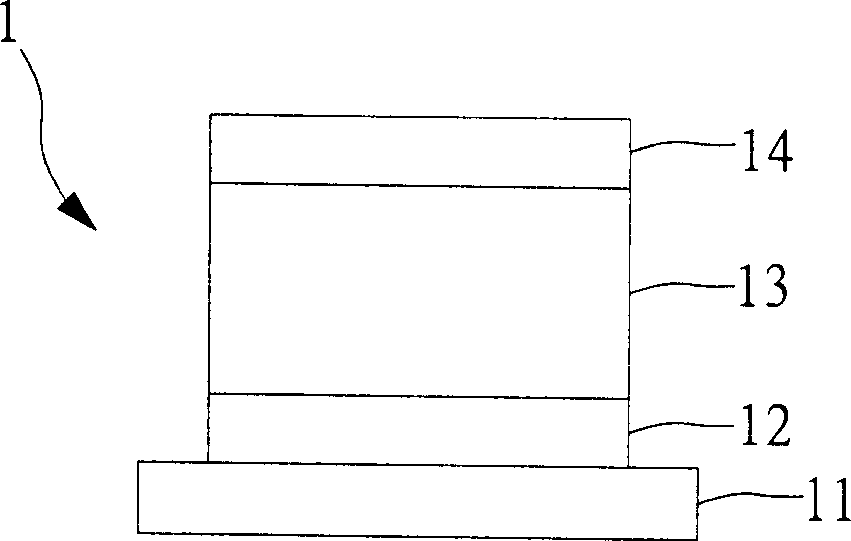
[0077] In this embodiment, please refer to the structure of component A Figure 4A , wherein the substrate 41 is a glass substrate, the lower electrode cathode layer 42 is 80 nanometers thick silver (Ag), and the organic electron transport layer 43 is 80 nanometers thick Alq 3 , the upper electrode cathode layer 44 is 0.5 nanometer thick lithium fluoride (LiF) / 100 nanometer thick aluminum (Al).
[0078] For the structure of component B, please refer to Figure 4B , wherein the substrate 51 is a glass substrate, the lower electrode cathode layer 52 is 80 nanometers thick silver (Ag), and the electron injection layer 53 is 0.2 nano...
Embodiment 2
[0082] In order to illustrate that the use of the electron injection layer of the present invention can effectively improve the electron injection capability of an organic light-emitting device with an inverted structure using aluminum (Al) as the cathode conductive metal, a dual-cathode electronic single-carrier device was fabricated for comparison.
[0083] In this embodiment, please refer to the structure of component C Figure 5A , wherein the substrate 61 is a glass substrate, the lower electrode cathode layer 62 is 80 nanometers thick silver (Ag), and the organic electron transport layer 63 is 80 nanometers thick Alq 3 , the upper electrode cathode layer 64 is 0.5 nanometer thick lithium fluoride (LiF) / 100 nanometer thick aluminum (Al).
[0084] Please refer to B of the figure for the structure of component D, wherein the substrate 71 is a glass substrate, the lower electrode cathode layer 72 is silver (Ag) with a thickness of 80 nanometers, and the electron injection la...
Embodiment 3
[0088] In this embodiment, in order to illustrate the influence of the electron injection layer of the present invention on the photoelectric characteristics of an organic light-emitting component with an inverted structure using silver (Ag) as the cathode of the lower electrode, the following components were fabricated for comparison:
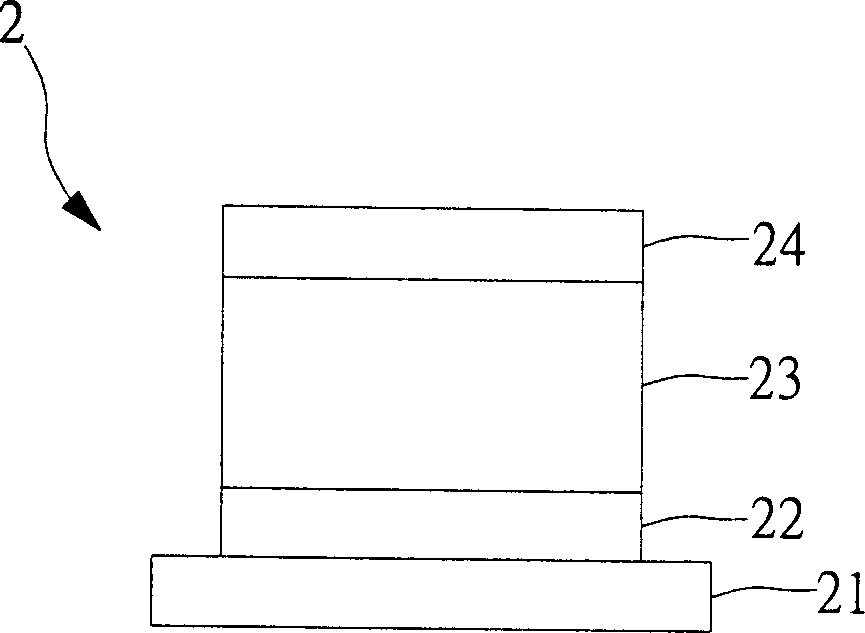
[0089] In this embodiment, the structure of component E can refer to Figure 2A , wherein the substrate 21 is a glass substrate, the cathode layer 22 is 80 nanometers thick silver (Ag), and the organic structure layer 23 is 50 nanometers thick Alq 3 / 40 nm thick α-NPD / 20 nm thick m-MTDATA and F 4 -TCNQ mixture, the anode layer 24 is 20 nanometers thick silver (Ag), and the outermost layer is provided with a 30 nanometers thick tellurium oxide (TeO 2 ) as a refractive index matching layer.
[0090] For the structure of component F, please refer to image 3 , wherein the substrate 31 is a glass substrate, the cathode layer 32 is 80 nanometers ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com