Process for producing 4-hydroxydiphenyl ether
A technology of hydroxydiphenyl ether and acyl diphenyl ether, which is applied in the field of preparation of 4-hydroxydiphenyl ether, can solve the problems of low reactivity, high temperature and long process procedures, etc., and achieve the effect of high-efficiency preparation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
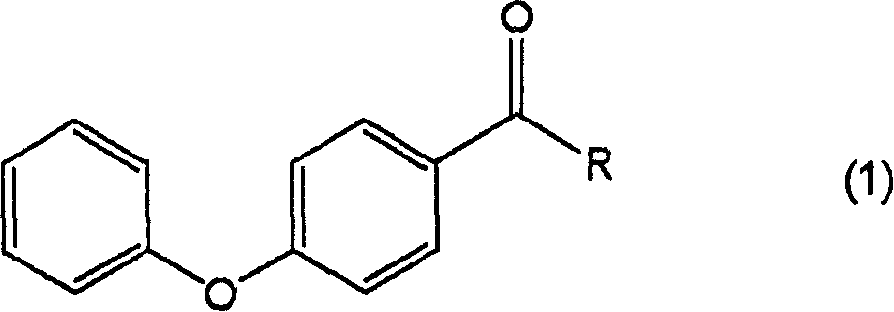
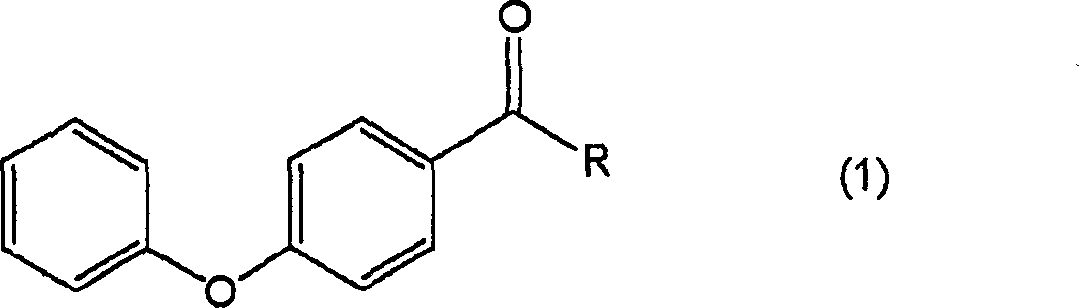
[0051] 1) Put 0.17g (1.0mmol) of diphenyl ether, 0.5mL of o-dichlorobenzene and 0.16g (1.2mmol) of aluminum chloride into a nitrogen-substituted 50mL eggplant flask, and add 0.09g of it while stirring at 50°C (1.1 mmol) Acetyl chloride. After stirring at the same temperature for 3 hours to react, it was cooled to room temperature, 10 mL of water was added, and extracted with 20 mL of diethyl ether. After drying the organic layer with sodium sulfate, the sodium sulfate was filtered off, and the obtained organic layer was concentrated to obtain an oily substance containing 4-acetyldiphenyl ether. This oil was purified by thin-layer chromatography (developing solution: hexane / ethyl acetate) to obtain 0.21 g of 4-acetyldiphenyl ether. Yield: 98%.
[0052] 2) Put 0.17g (1.0mmol) of diphenyl ether, 2mL of 1,2-dichloroethane and 0.27g (2mmol) of aluminum chloride into a nitrogen-substituted 50mL eggplant flask, and stir at 80°C 0.12 g (1.2 mmol) of acetic anhydride was added. Aft...
Embodiment 2
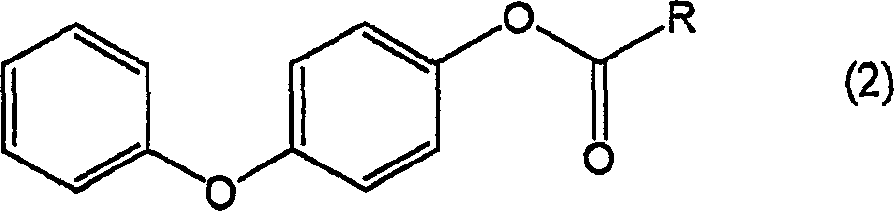
[0058] Add 4mL of acetic acid and 0.1mL of sulfuric acid into 0.21g (1.0mmol) of 4-acetyl diphenyl ether obtained in 3) of Example 1, then add 0.25g (2.2mmol) of 30% aqueous hydrogen peroxide, and stir at 50°C 8 hours. Quantification of the reaction solution by LC revealed that the yield of 4-hydroxydiphenyl ether was 73%, that is, 4-acetoxydiphenyl ether was contained corresponding to a yield of 11%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com