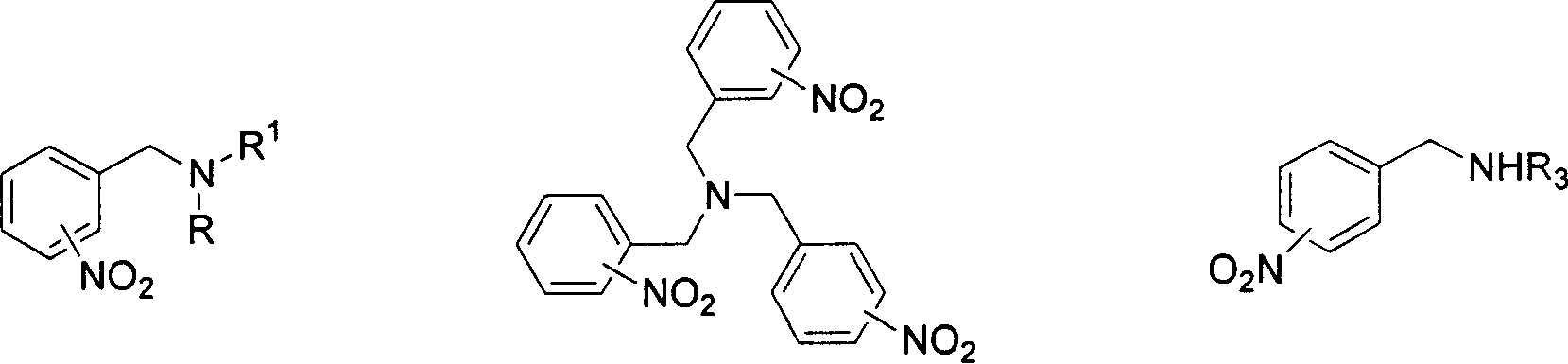
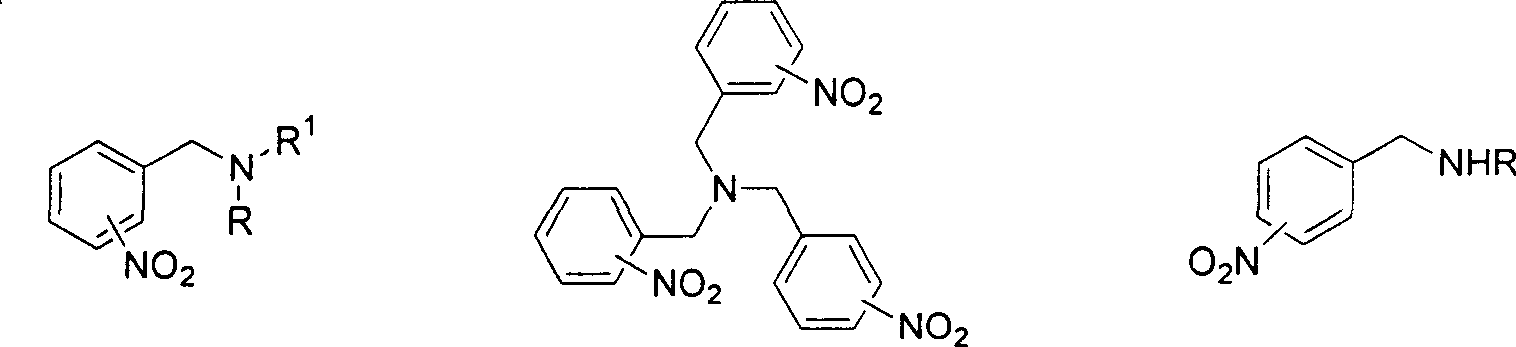
Method for reducing nitroxylbenzyl amine compound to amino-benzylamine hydrochloride
A technology of aminobenzylamine hydrochloride and nitrobenzylamine is applied in the field of reducing nitrobenzylamine compound to aminobenzylamine hydrochloride, and achieves the effects of mild reaction conditions, convenient post-processing and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
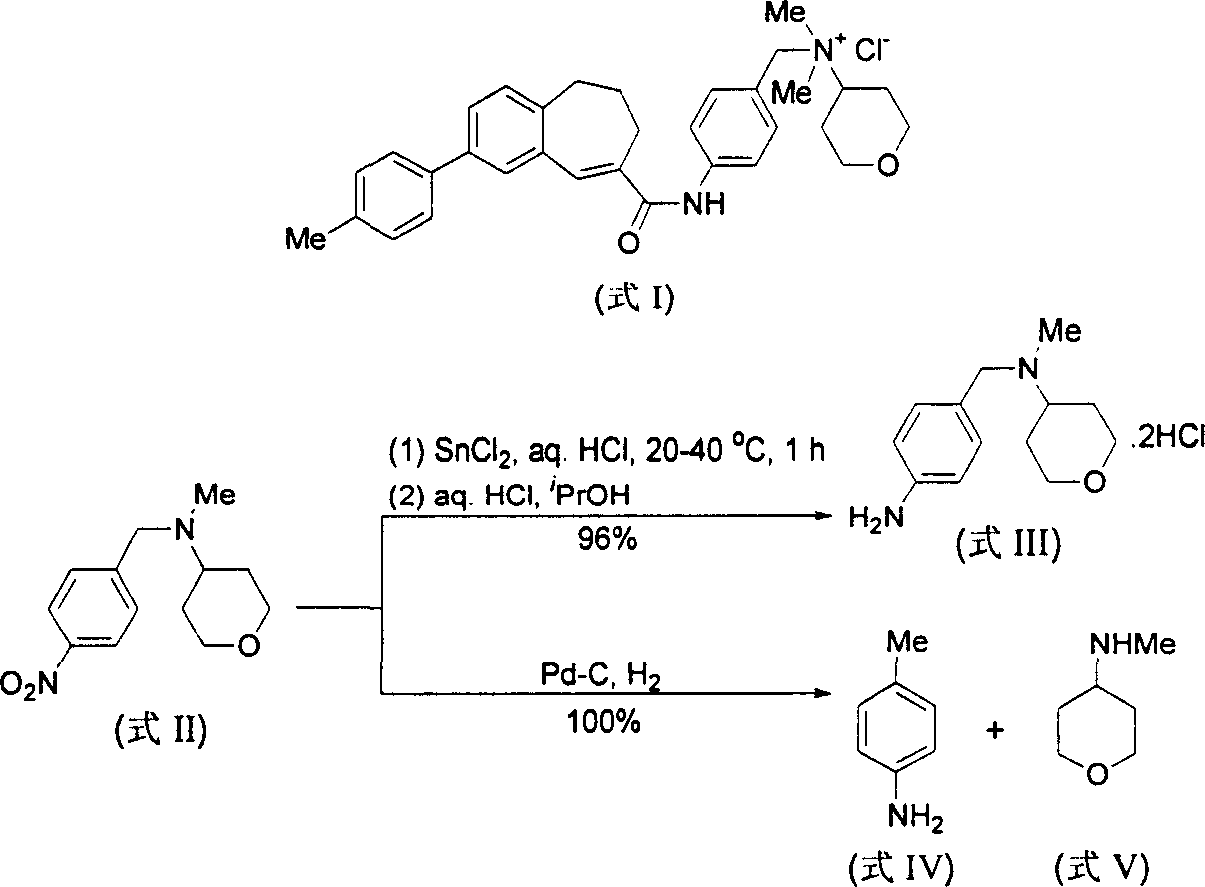
[0053] Embodiment 1, use CHCl 3 Preparation of 4-amino-N,N-dimethylbenzylamine dihydrochloride (formula IX / a) as a source of HCl
[0054] At 25° C., 4-nitro-N, N-dimethylbenzylamine (formula VI / a, 450 mg, 2.5 mmol), 10% Pd / C (45 mg, 10% by weight) and CHCl 3 (2 mL) in methanol (30 mL) was hydrogenated at atmospheric pressure for 2 h, and the Pd / C catalyst was filtered off. The filtrate was distilled off of methanol under reduced pressure to obtain a crude product of yellow crystals. The yellow crystals were then washed with a small amount of ether to remove any non-salt-forming material. Finally by MeOH / Et 2 O was recrystallized to give pale yellow crystalline compound 4-amino-N,N-dimethylbenzylamine dihydrochloride (formula IX / a, 510 mg, 91%).
[0055] m.p.198-200℃(MeOH / Et 2 O);
[0056] 13 C NMR (CD 3 OH): δ133.7, 133.0, 130.5, 123.7, 60.1, 42.0;
[0057] Elemental analysis (C 9 h 16 N 2 Cl 2 ): C, 48.44; H, 7.23; N, 12.55; Found: C, 48.20; H, 7.24; N, 12.32.
Embodiment 2
[0058] Embodiment 2, use concentrated hydrochloric acid as the source of HCl to prepare 4-amino-N, N-dimethylbenzylamine dihydrochloride (formula IX / a)
[0059] At 25° C., 4-nitro-N, N-dimethylbenzylamine (formula VI / a, 450 mg, 2.5 mmol), 10% Pd / C (45 mg, 10% by weight) and 37% concentrated hydrochloric acid ( A suspension of 1 mL containing about 8 mmol of HCl) in methanol (30 mL) was hydrogenated at atmospheric pressure for 15 minutes, and hydrogen uptake ceased completely. The Pd / C catalyst was filtered off, and the filtrate was evaporated to remove methanol under reduced pressure to obtain a crude product of yellow crystals. The yellow crystals were then washed with a small amount of ether to remove any non-salt-forming material. Finally by MeOH / Et 2 O was recrystallized to give pale yellow crystalline compound 4-amino-N,N-dimethylbenzylamine dihydrochloride (formula IX / a, 550 mg, 98%). The physical data are the same as in Example 1.
Embodiment 3
[0060] Embodiment 3, preparation 4-amino-N, N-diethylbenzylamine dihydrochloride (formula IX / b)
[0061] Under the same conditions as in Example 2, the reaction was carried out with 4-nitro-N,N-diethylbenzylamine (formula VI / b), and hydrogen absorption was completely stopped after 15 minutes. The crude product was obtained from MeOH / Et 2 Recrystallization from O gave pale yellow crystalline compound 4-amino-N,N-diethylbenzylamine dihydrochloride (Formula IX / b, 100%).
[0062] m.p.180-182℃(MeOH / Et 2 O);
[0063] 13 C NMR (CD 3 OH): δ150.0, 132.2, 117.3, 115.1, 56.2, 46.4, 8.1;
[0064] Elemental analysis (C 11 h 20 N 2 Cl 2 ): C, 52.60; H, 8.03; N, 11.15; Found: C, 52.48; H, 8.03; N, 11.17.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com